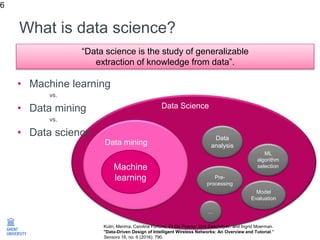
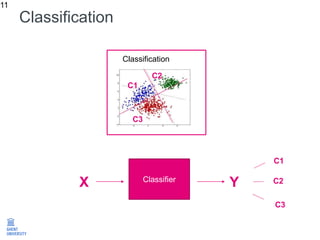
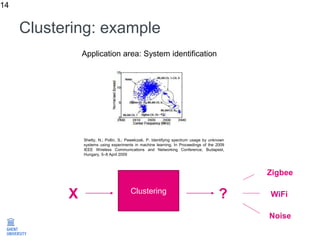
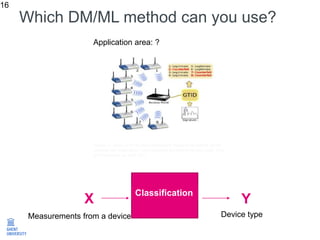
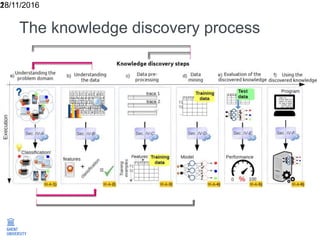
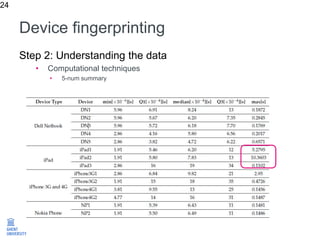
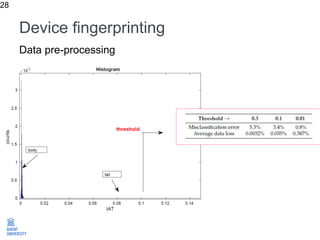
The document discusses the application of machine learning in improving wireless network performance, focusing on data-driven design and various machine learning approaches such as regression, classification, clustering, and anomaly detection. It emphasizes the importance of data collection, pre-processing, and evaluation in achieving effective device fingerprinting and network security solutions. The conclusion highlights the potential of data traces for optimizing network performance and the need for collaboration among experts in various fields.