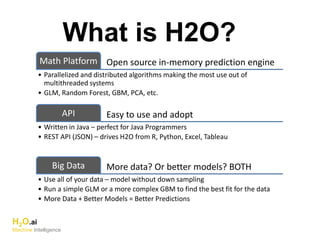
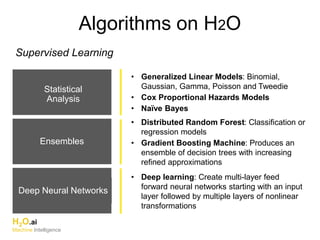
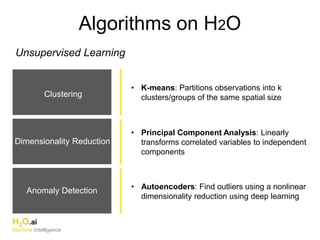
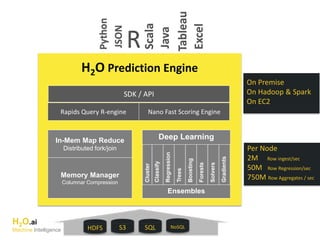
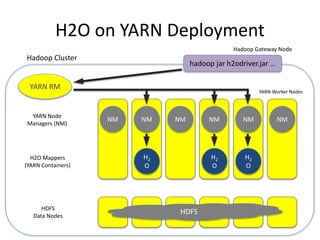
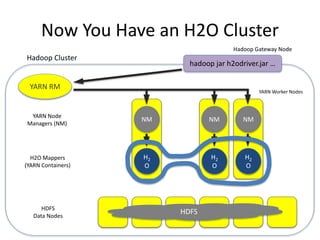
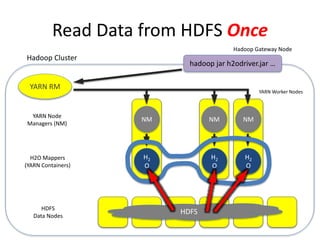
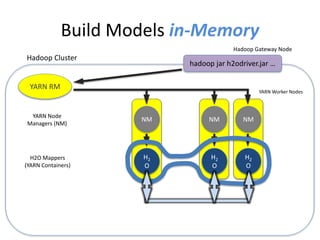
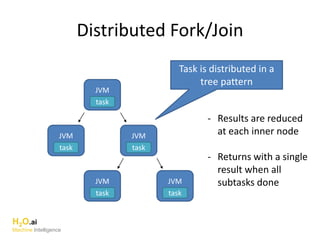
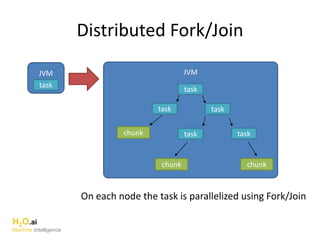
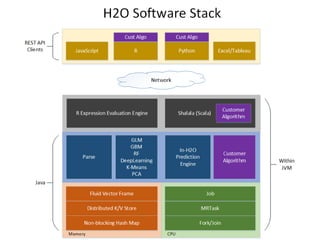
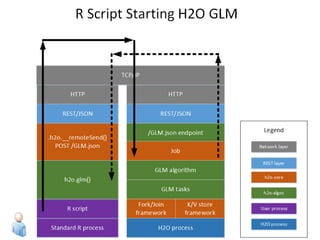
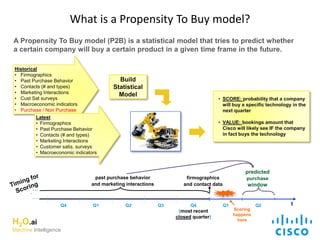
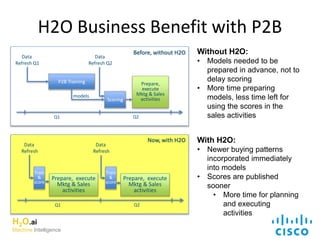
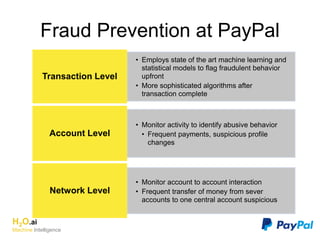
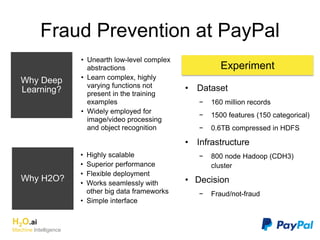
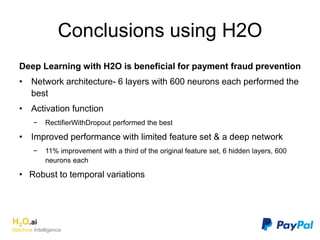
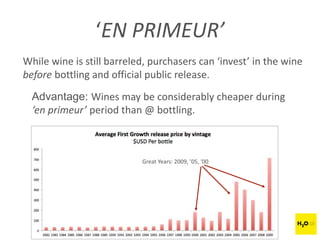
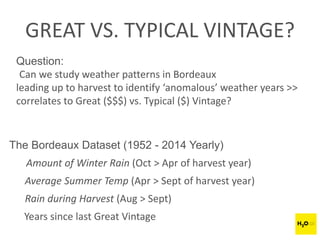
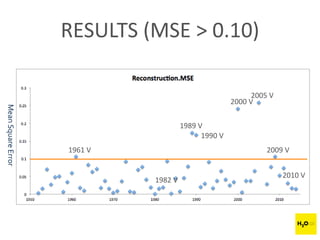
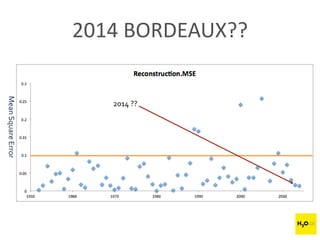
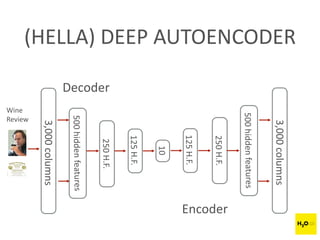
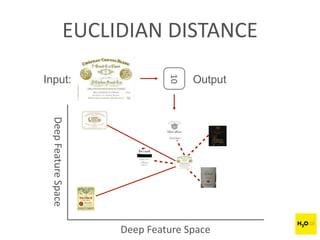
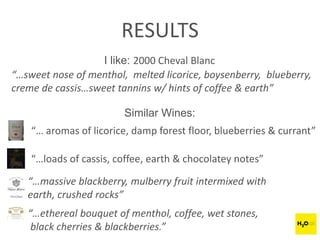
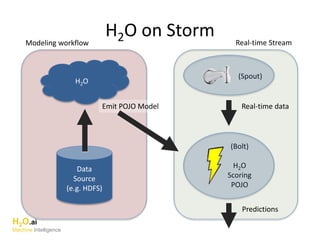
The document discusses H2O.ai, an open-source in-memory prediction engine offering machine learning solutions for big data environments. It covers the architecture, processing capabilities, and algorithms used in H2O, along with applications in propensity to buy modeling and fraud prevention. The presentation also highlights a case study on Bordeaux wines, demonstrating unsupervised learning techniques for vintage quality prediction.