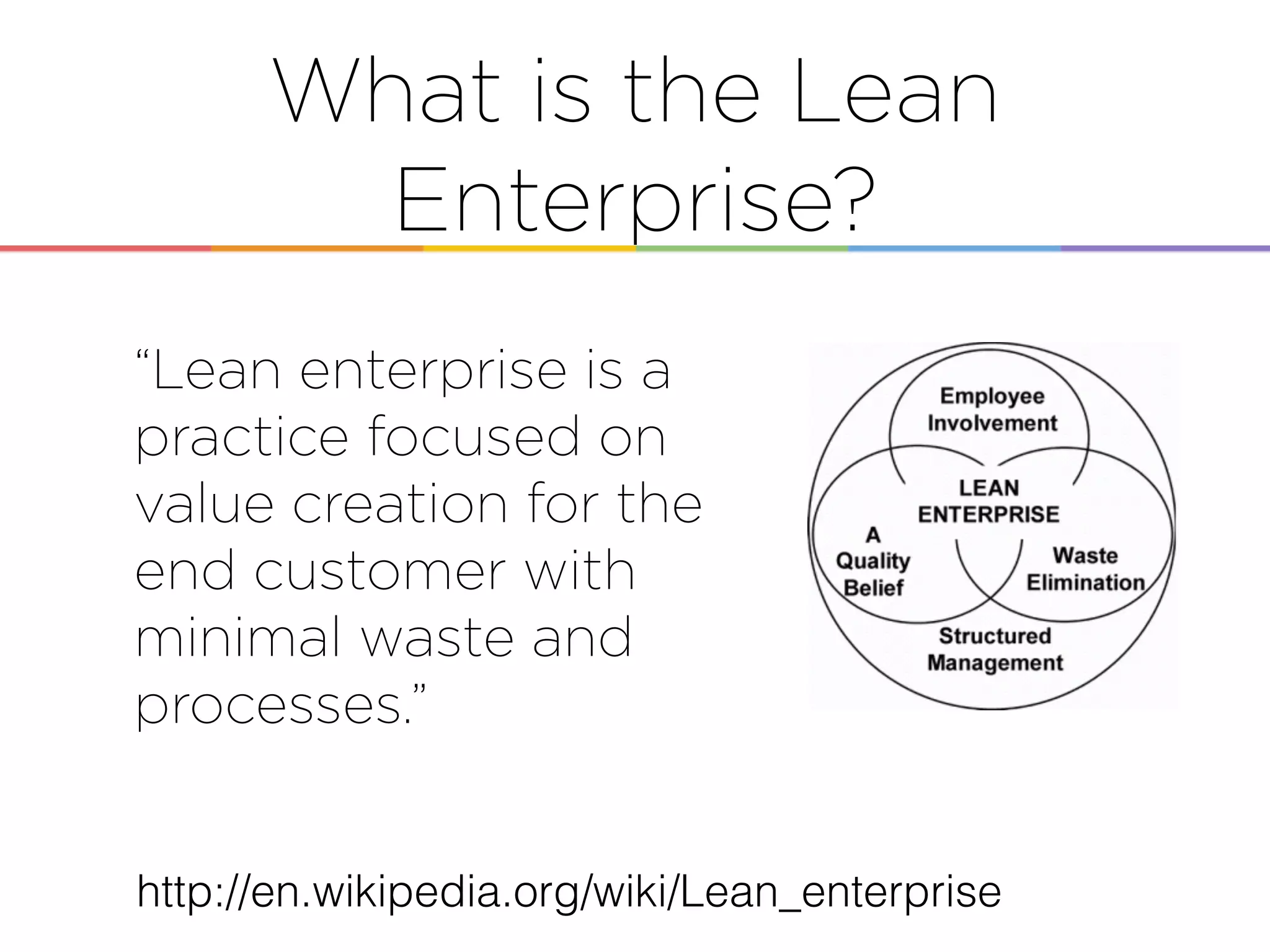
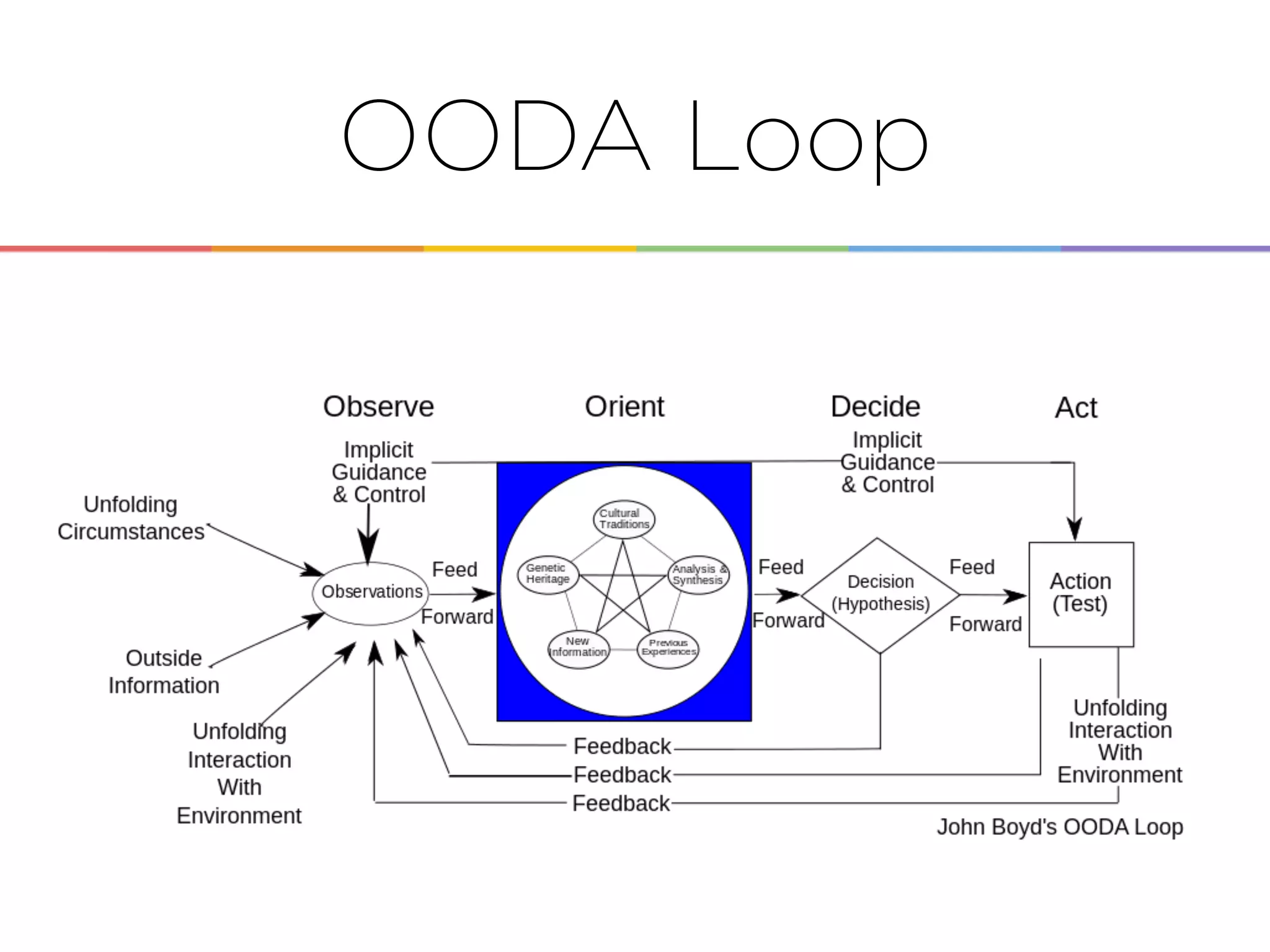
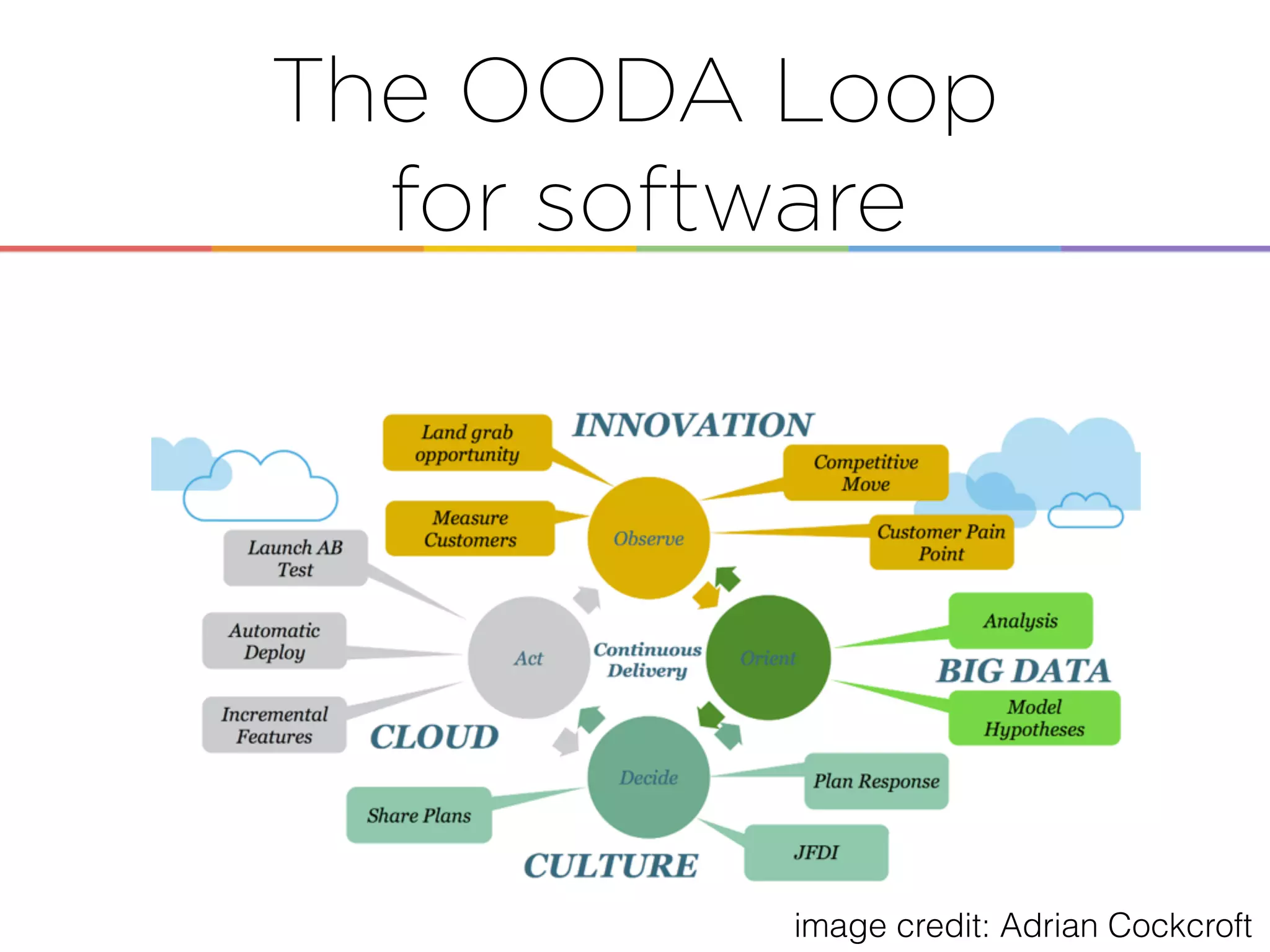
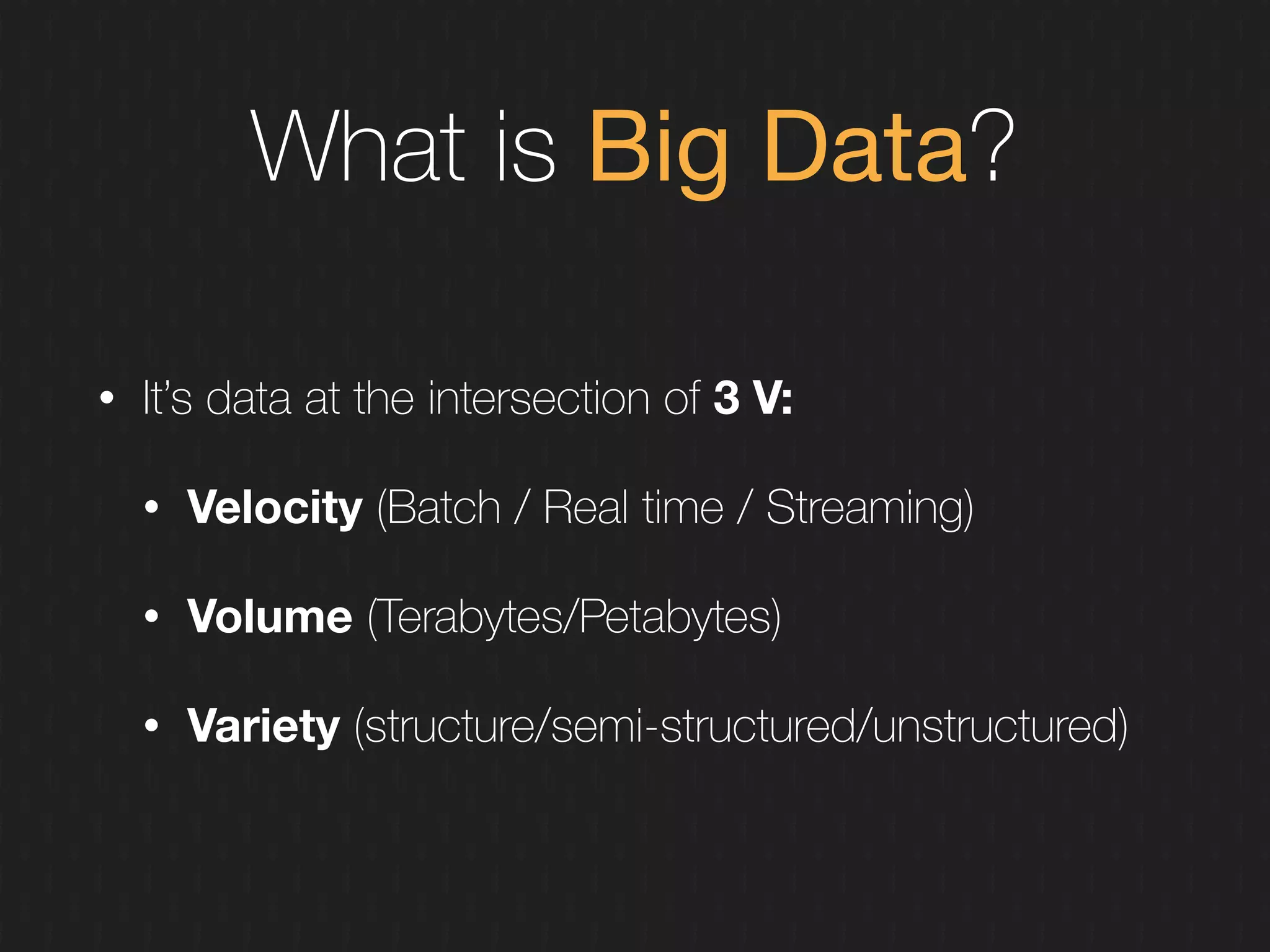
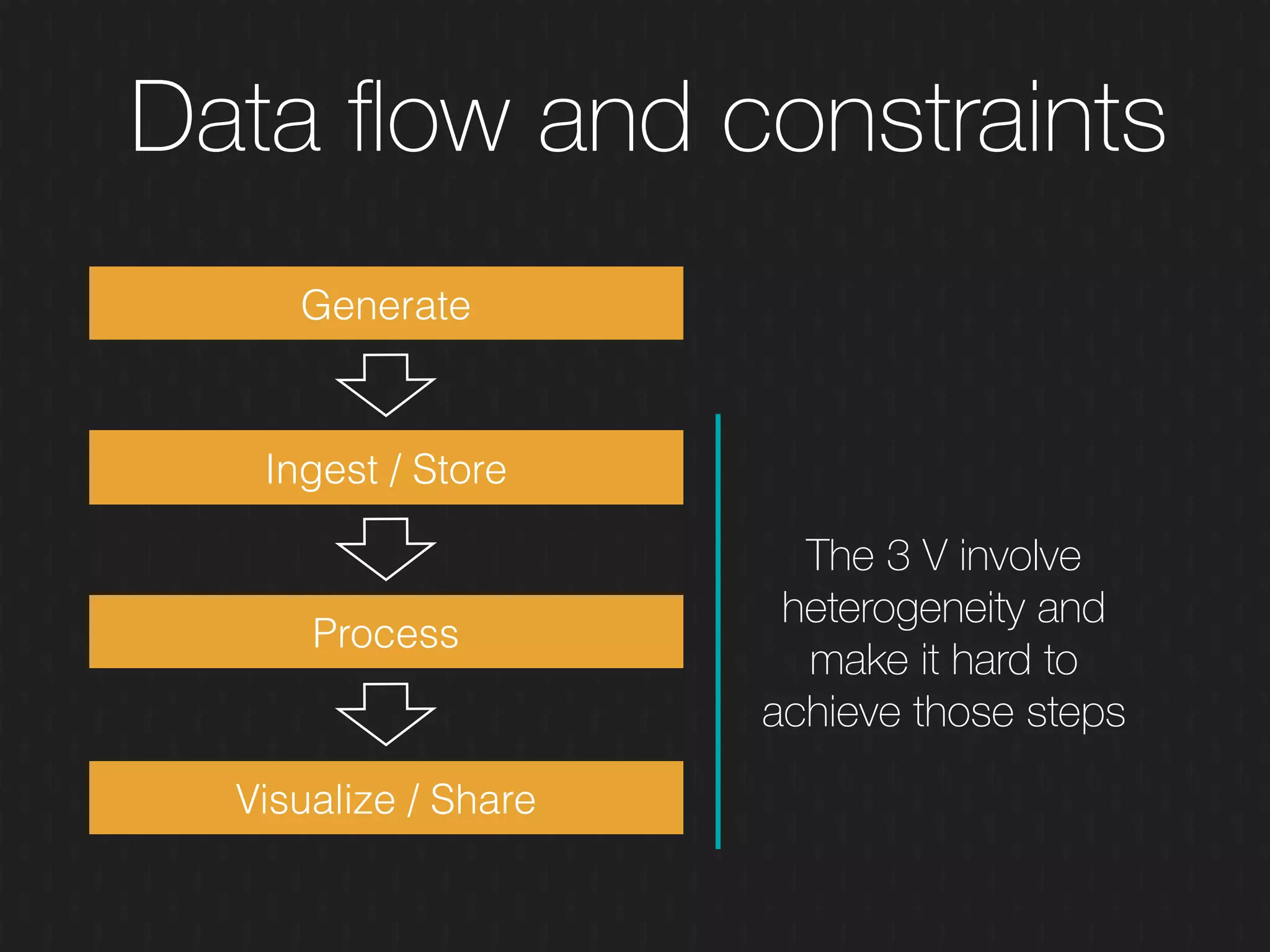
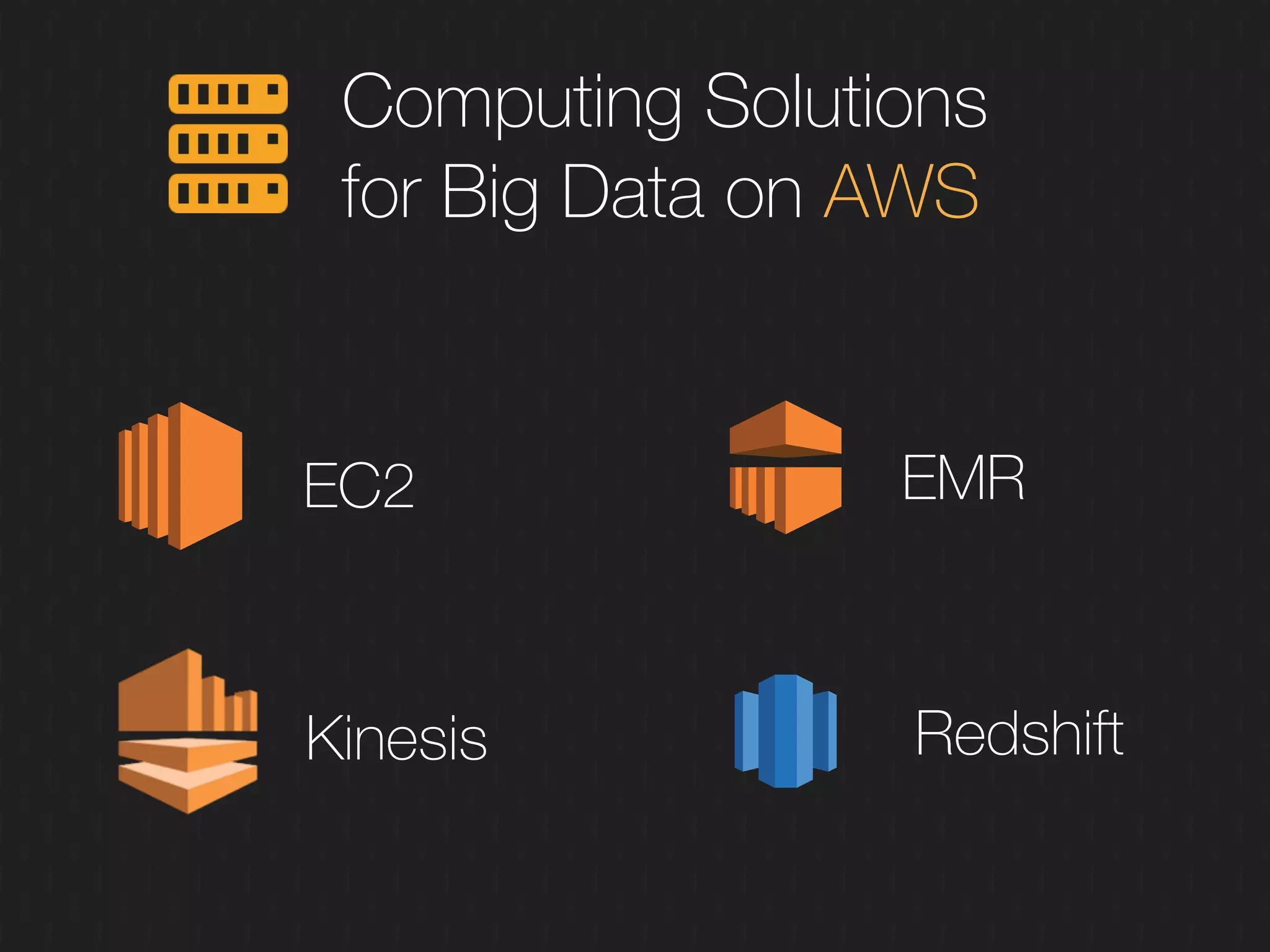
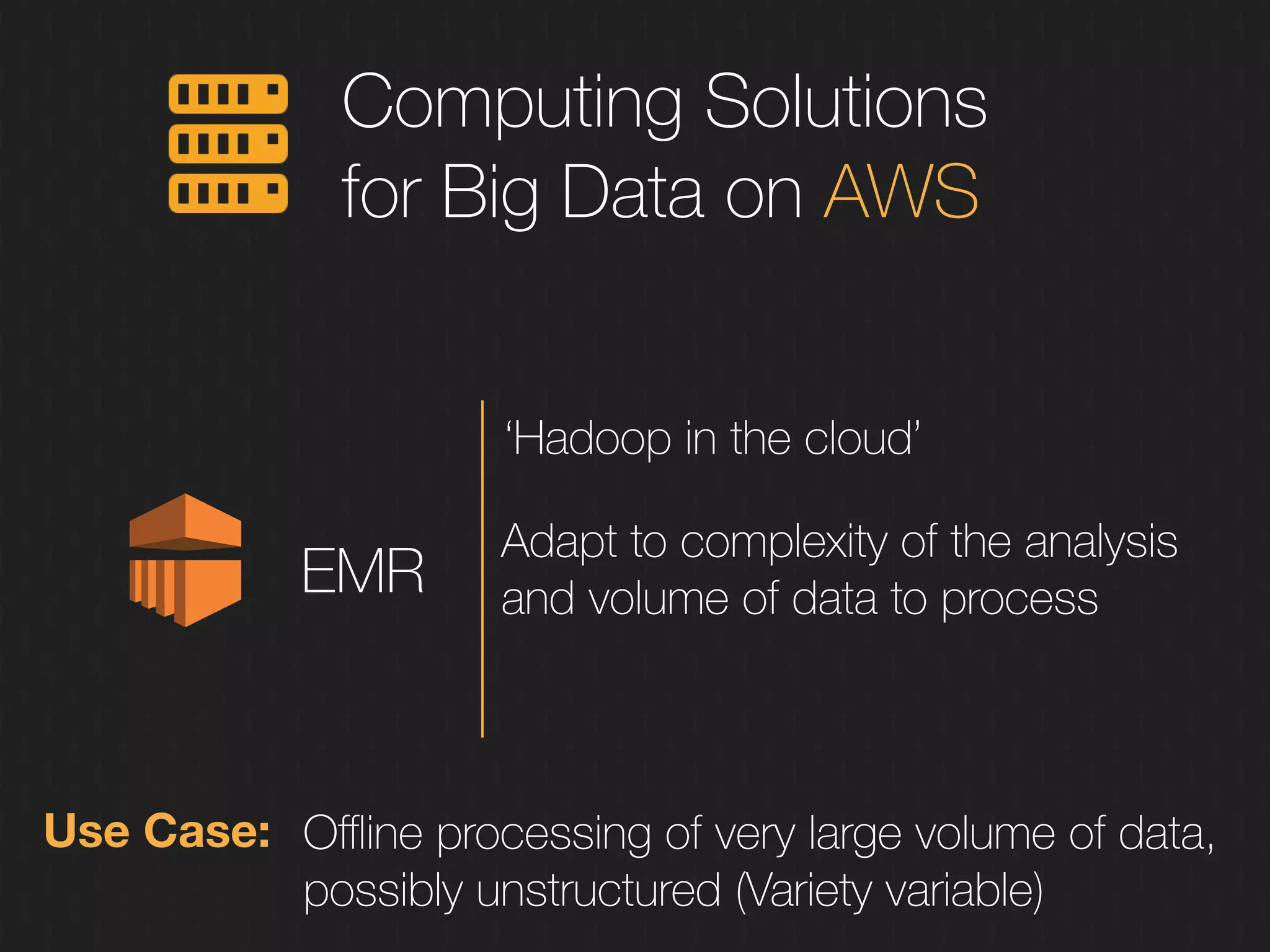
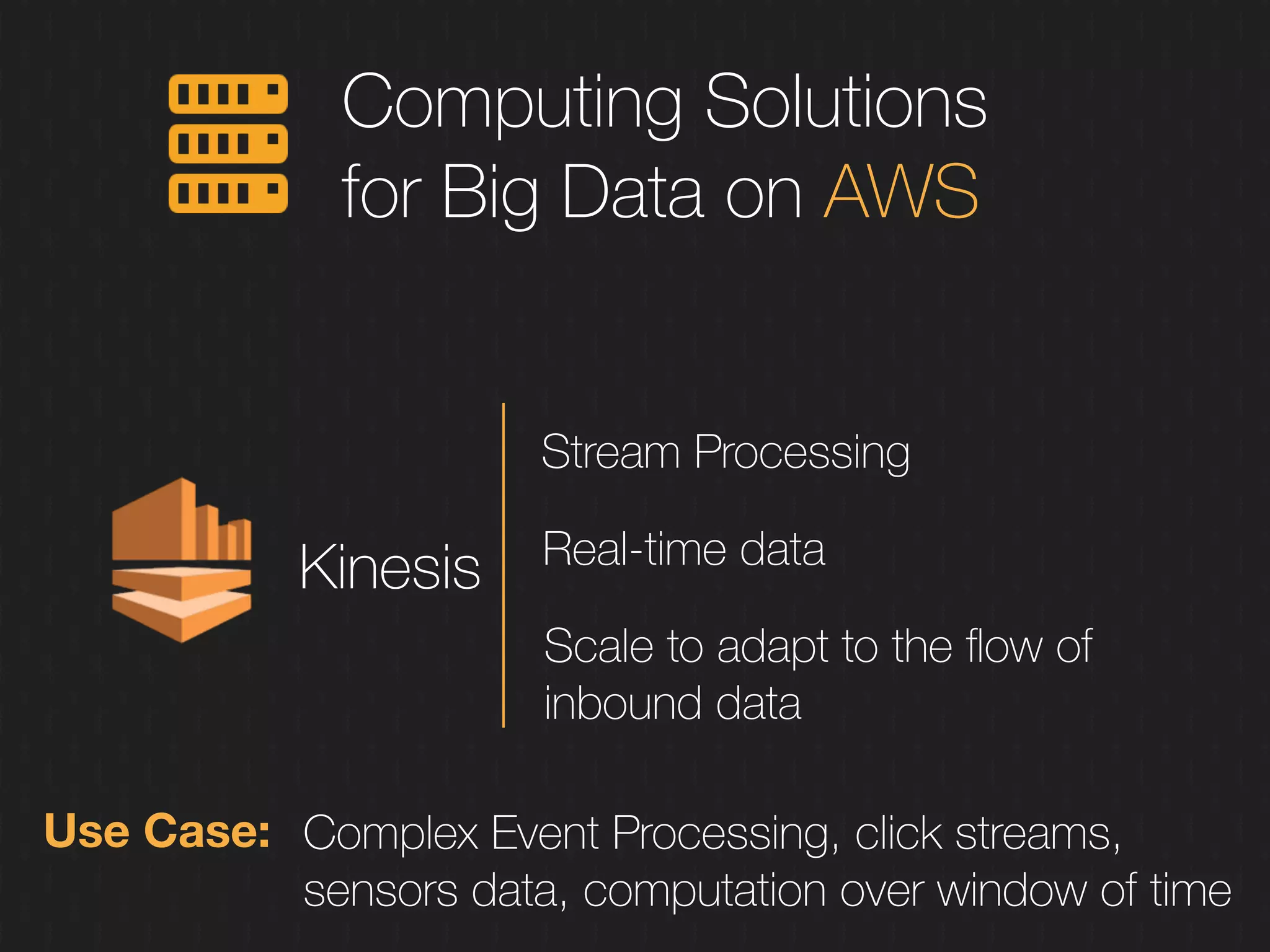
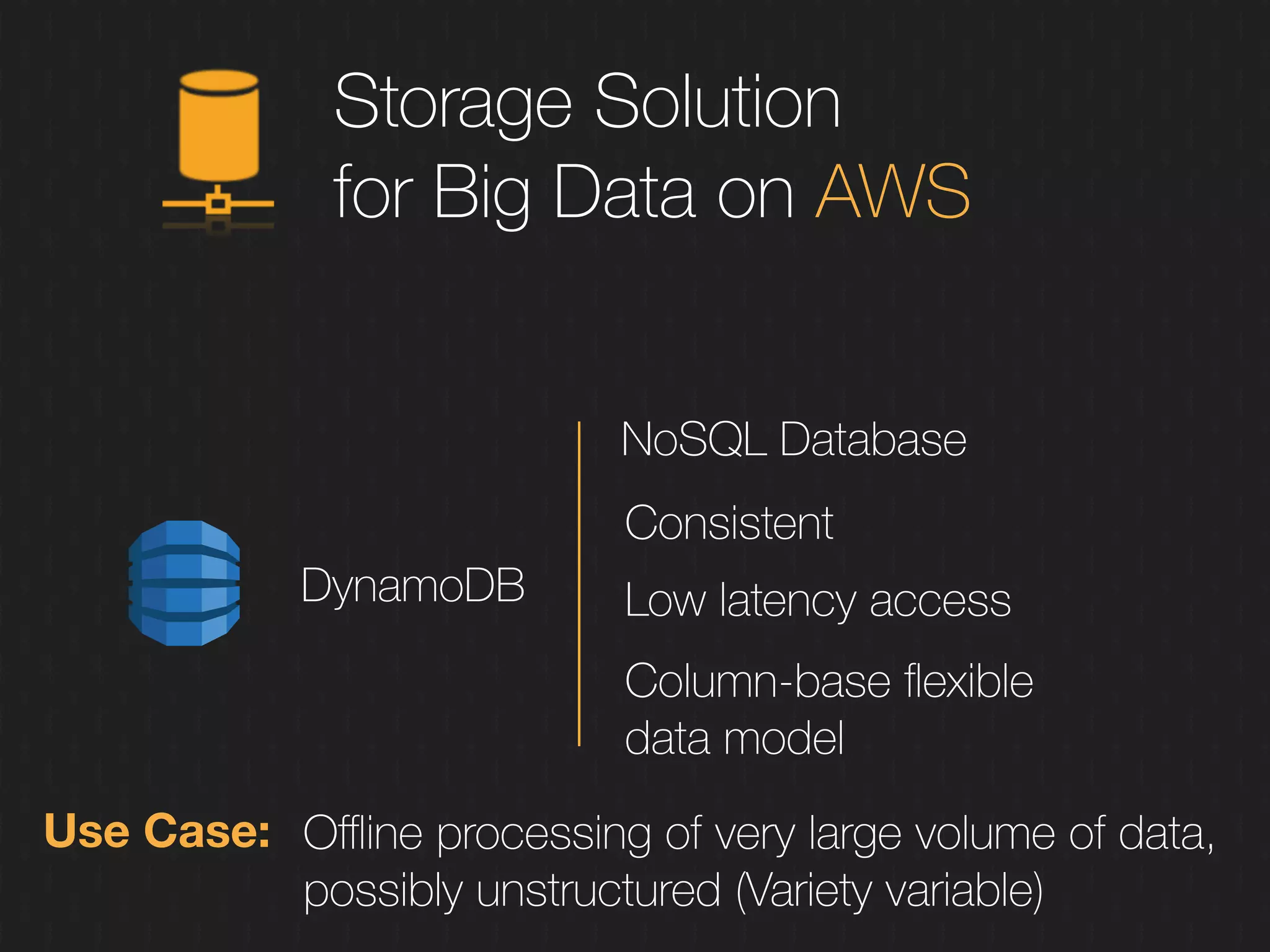
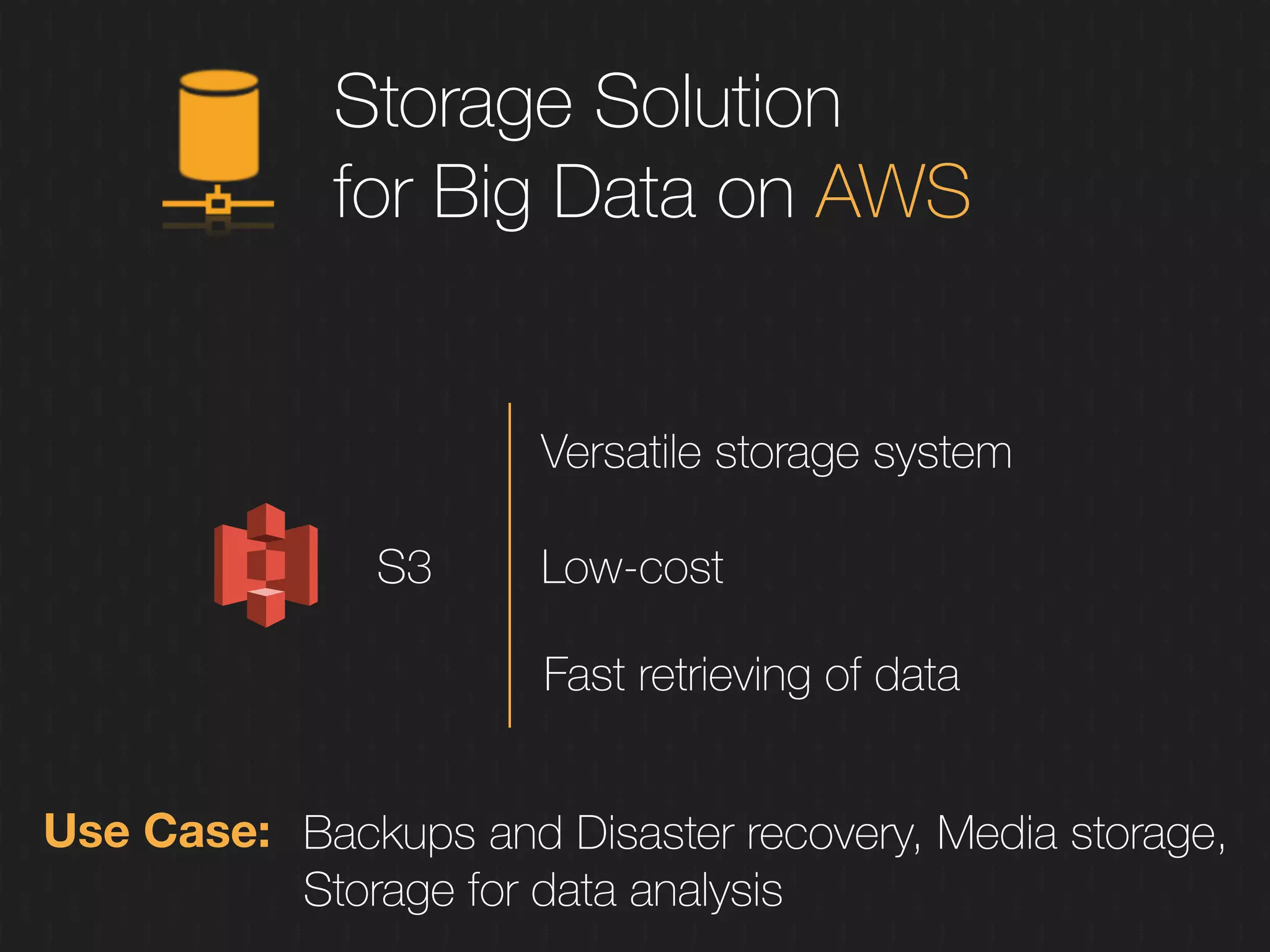
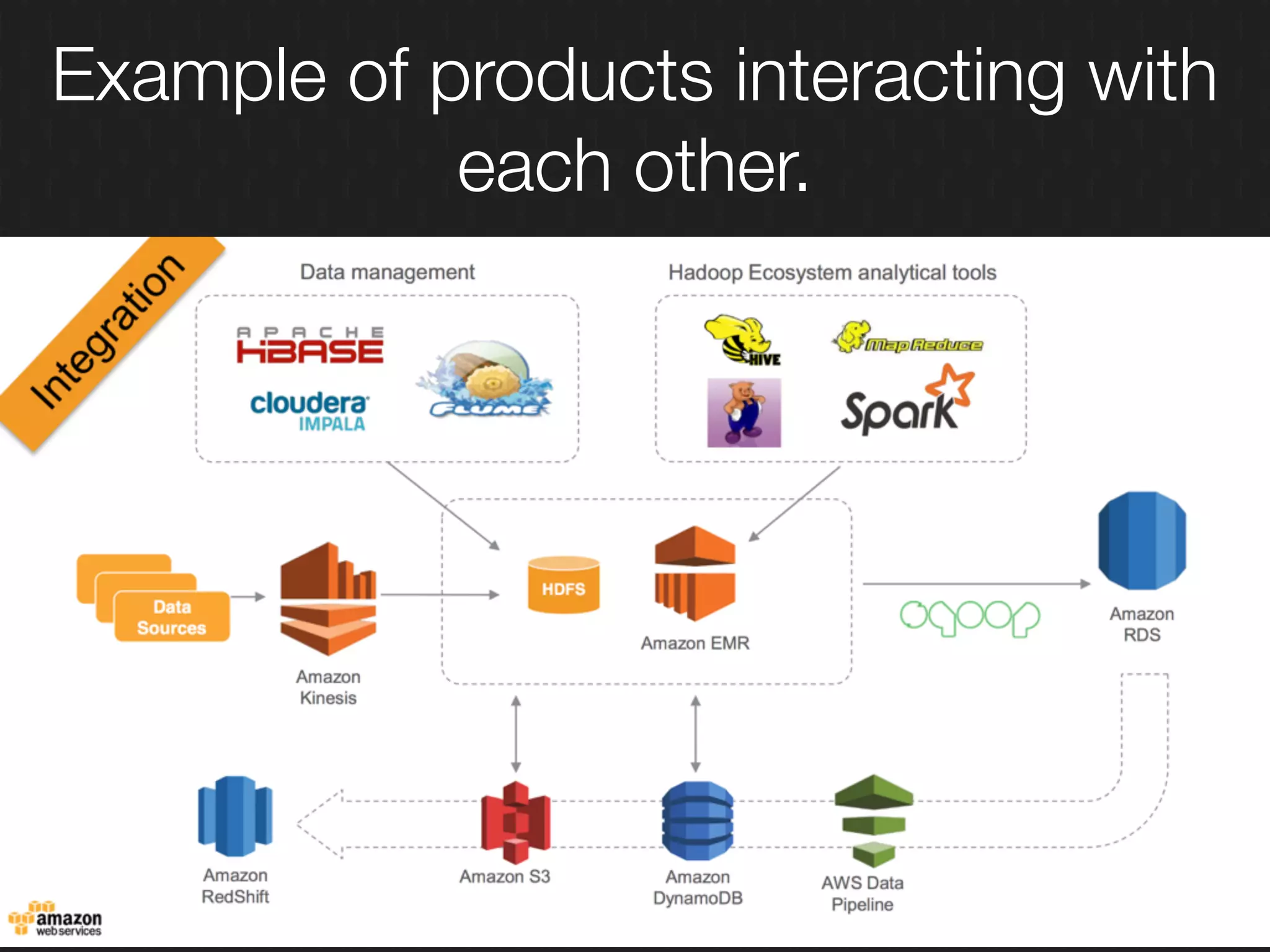
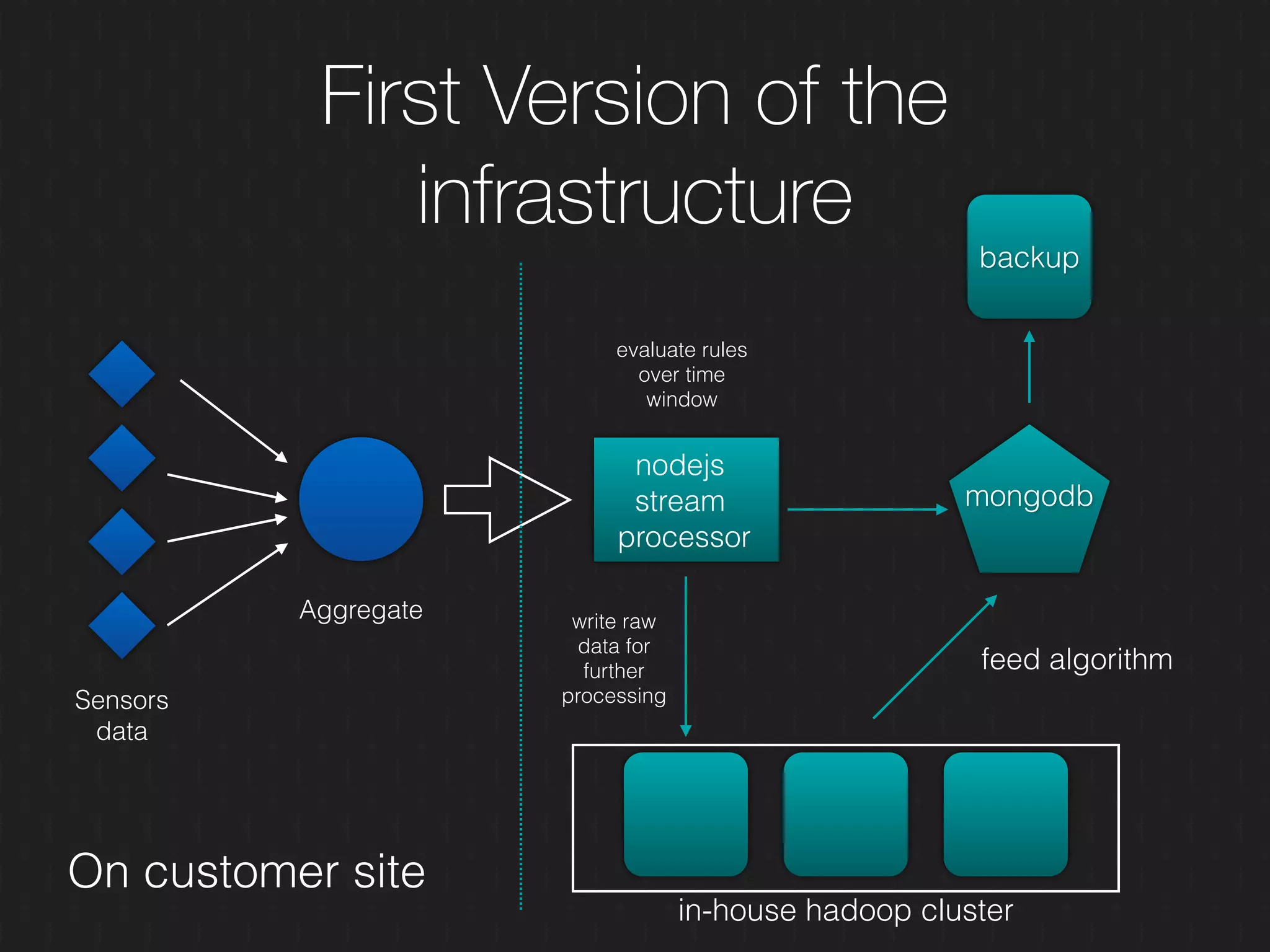
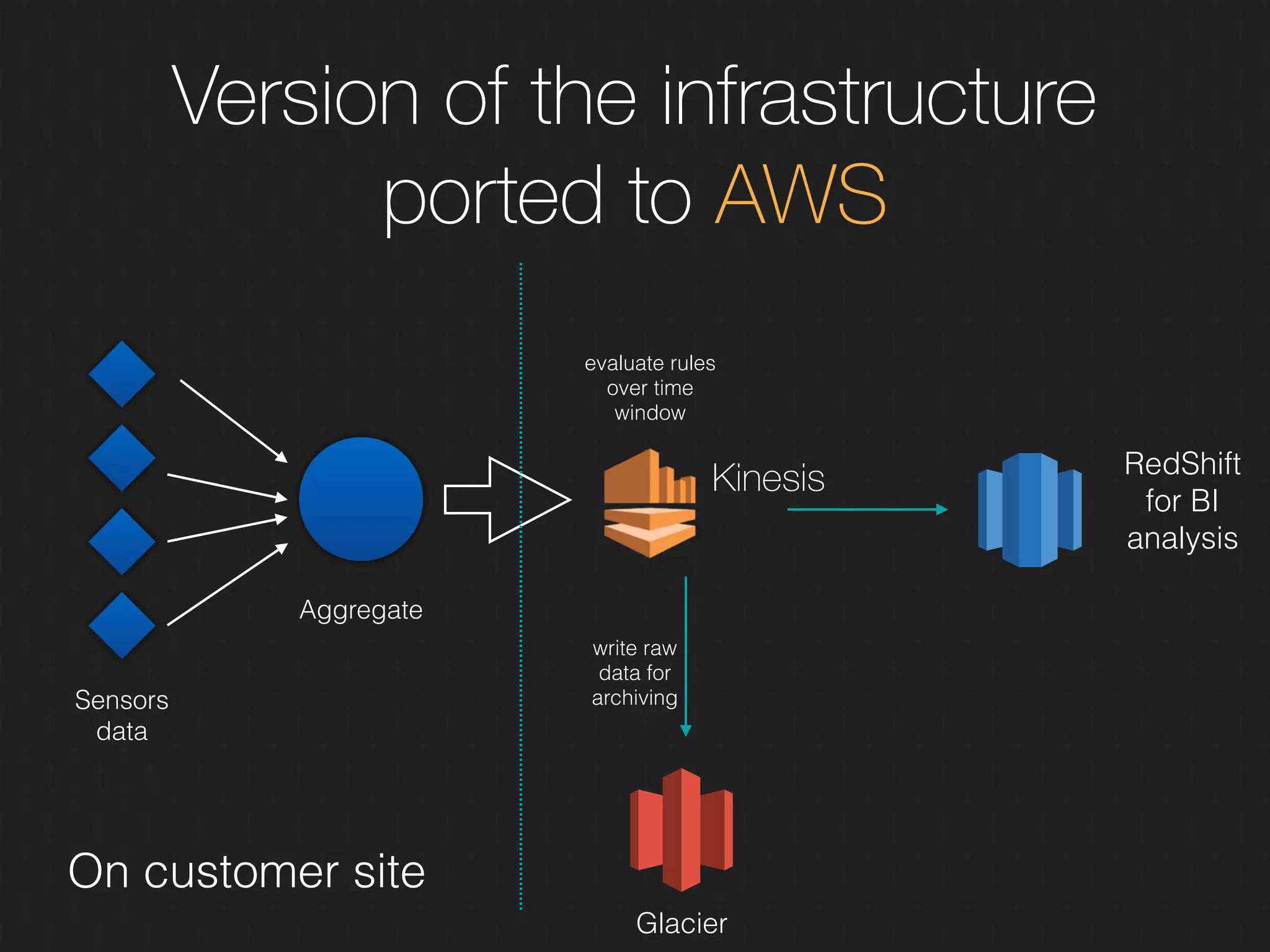
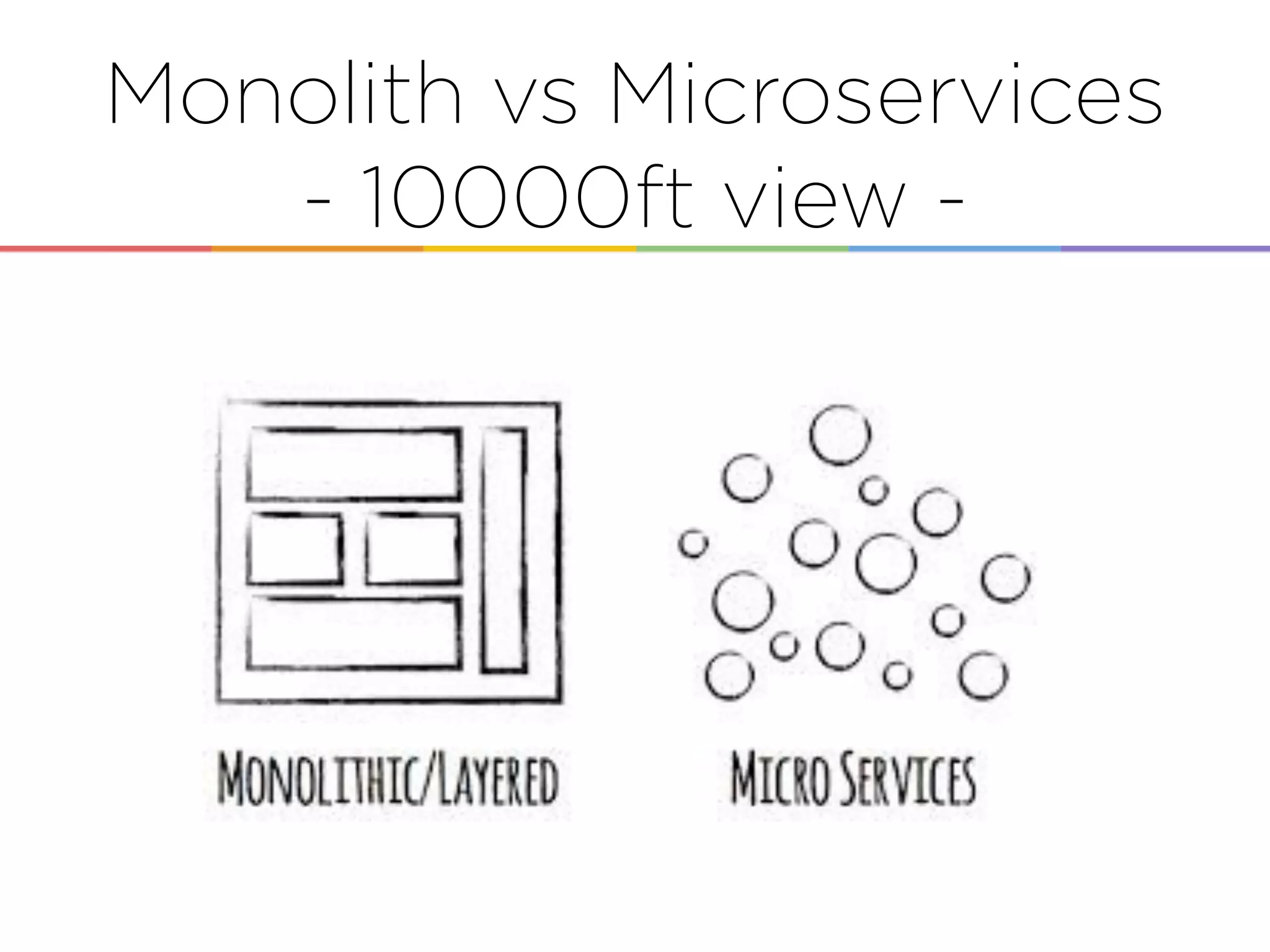
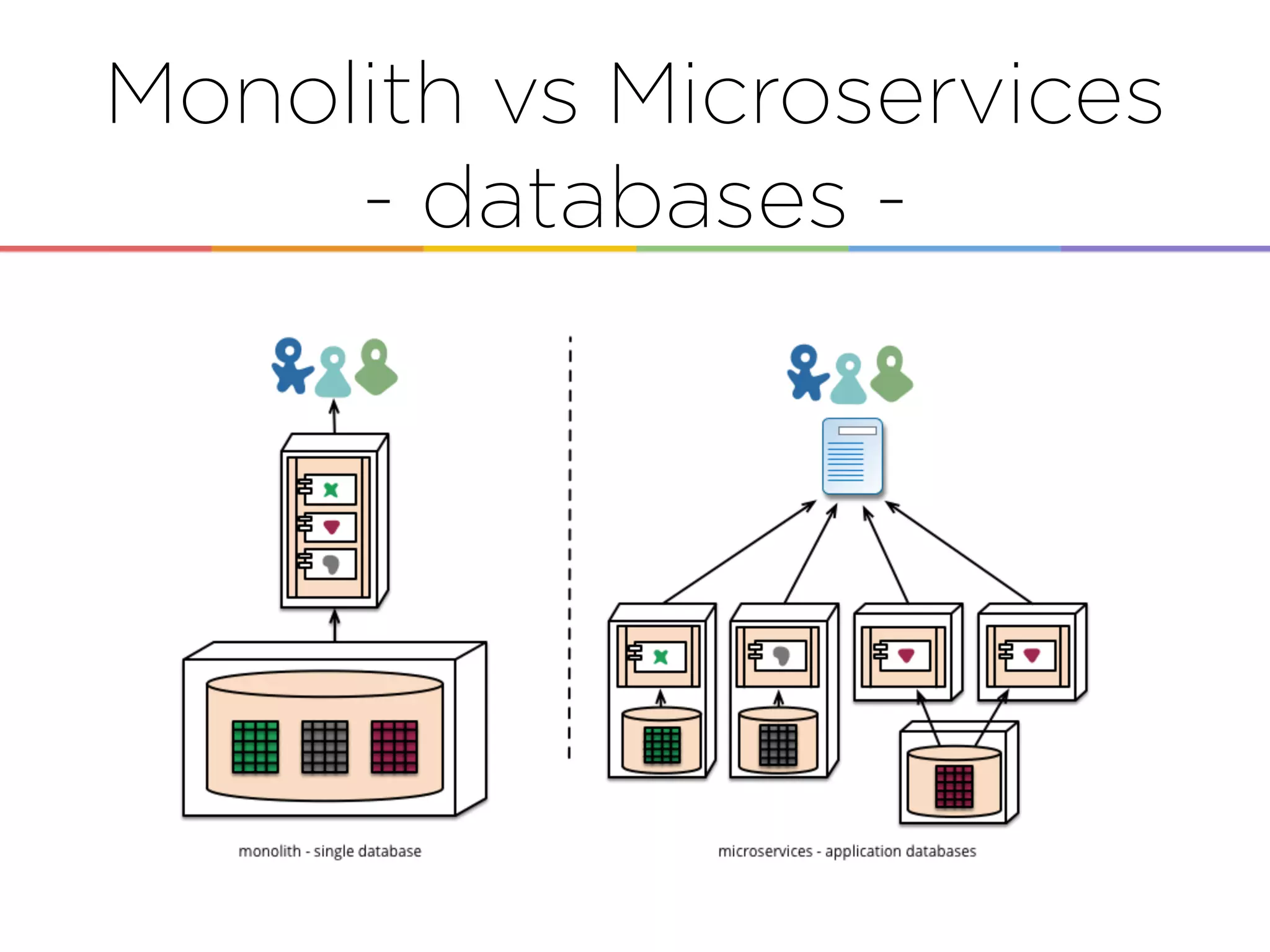
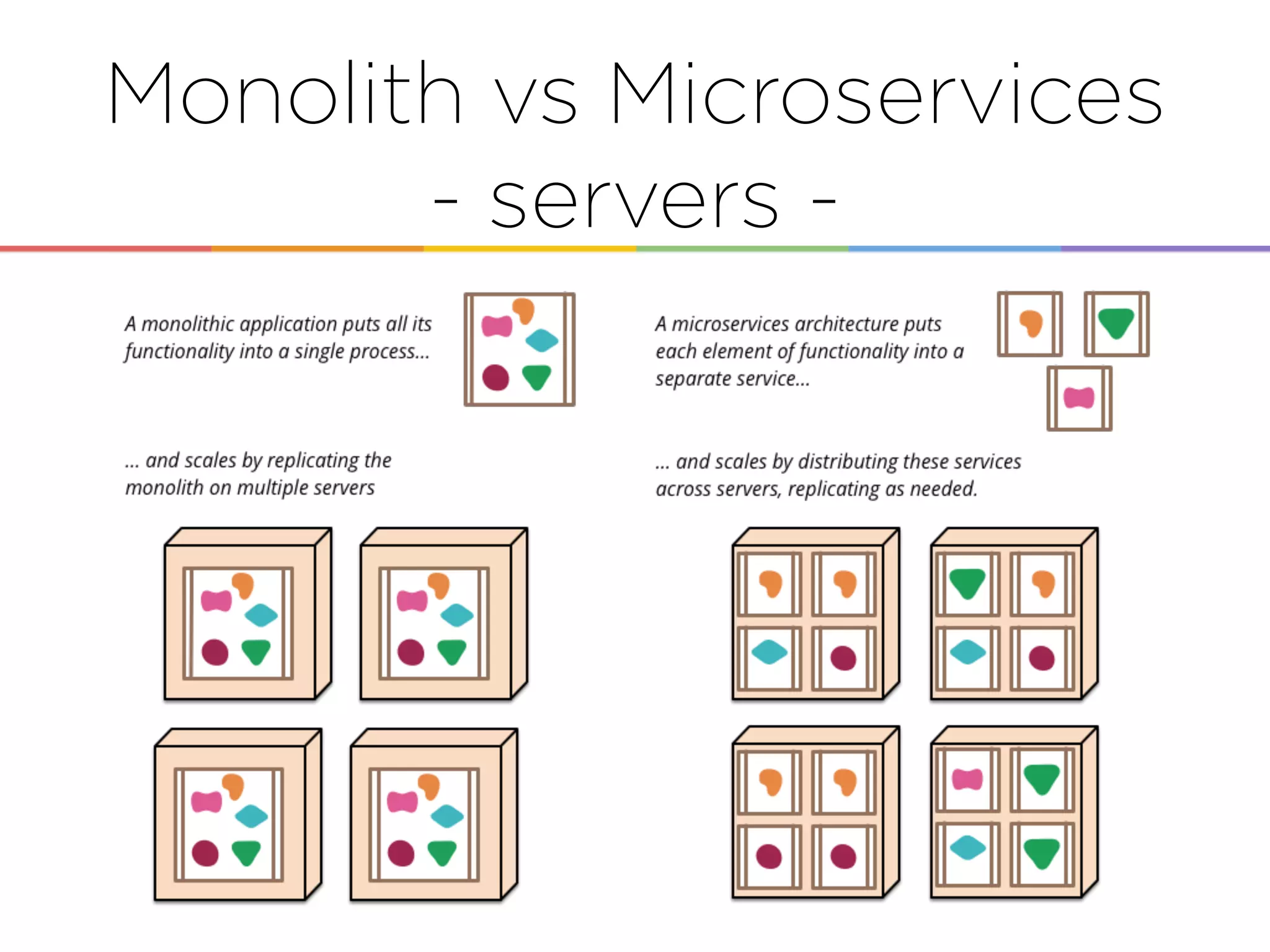
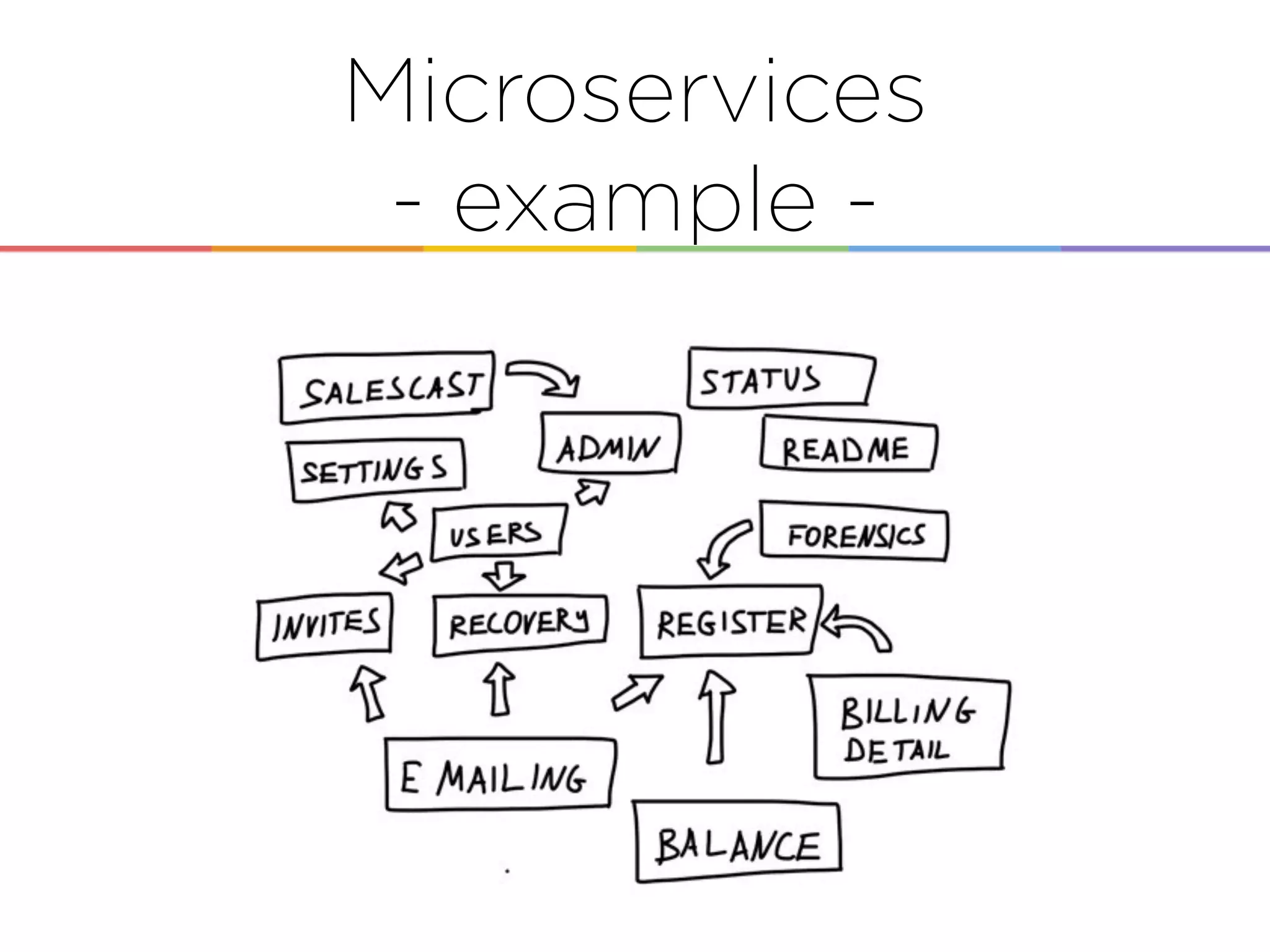
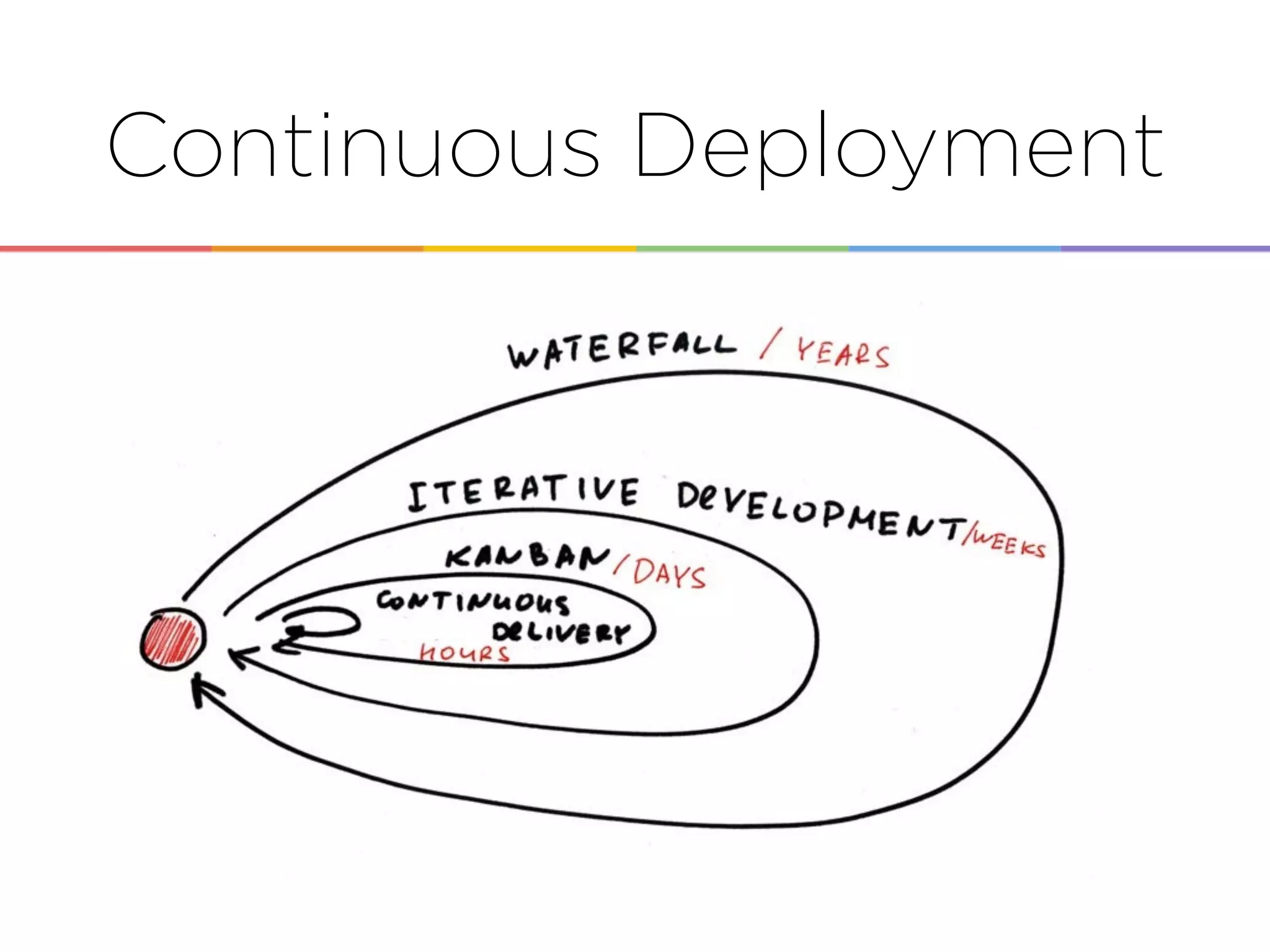
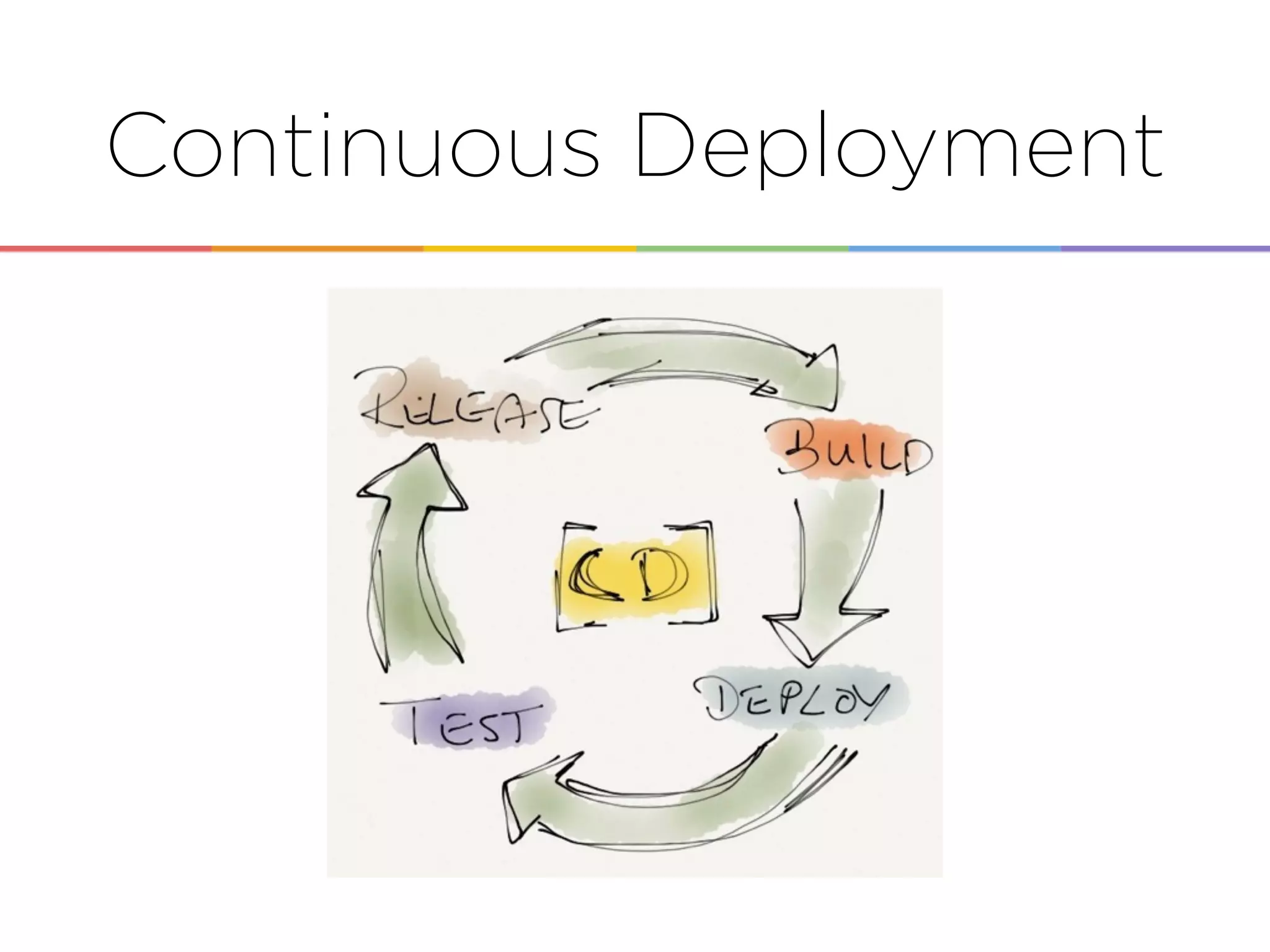
This document discusses enabling the lean enterprise through technologies like microservices, continuous integration/deployment, and cloud computing. It begins by defining the lean enterprise and the OODA loop concept. It then explains how technologies like AWS, big data, and microservices can help organizations continuously observe, orient, decide, and act. Specific AWS services like EC2, EMR, Kinesis, Redshift, S3, and DynamoDB are reviewed. The benefits of breaking up monolithic systems into microservices and implementing devops practices like CI/CD are also summarized.