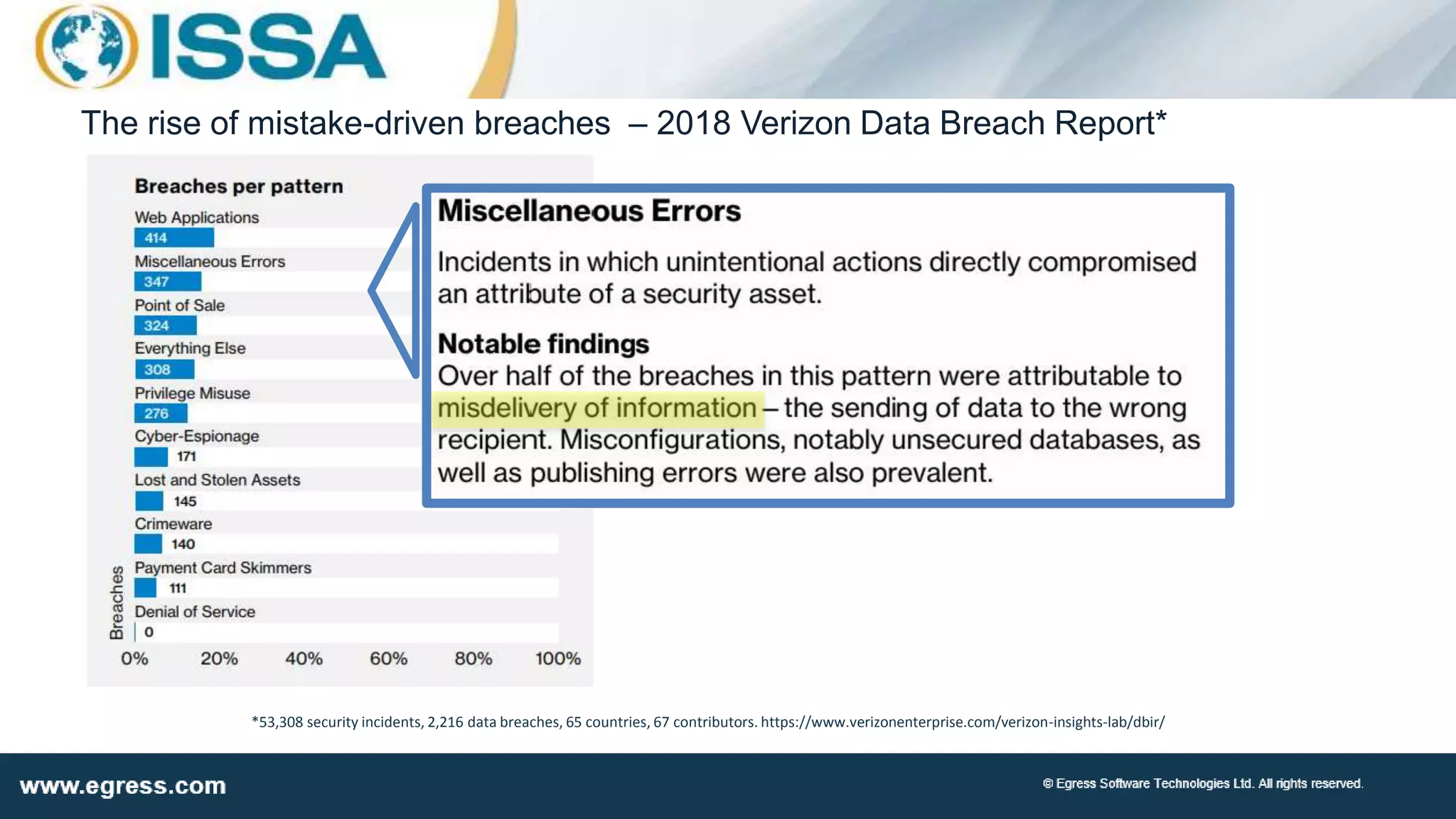
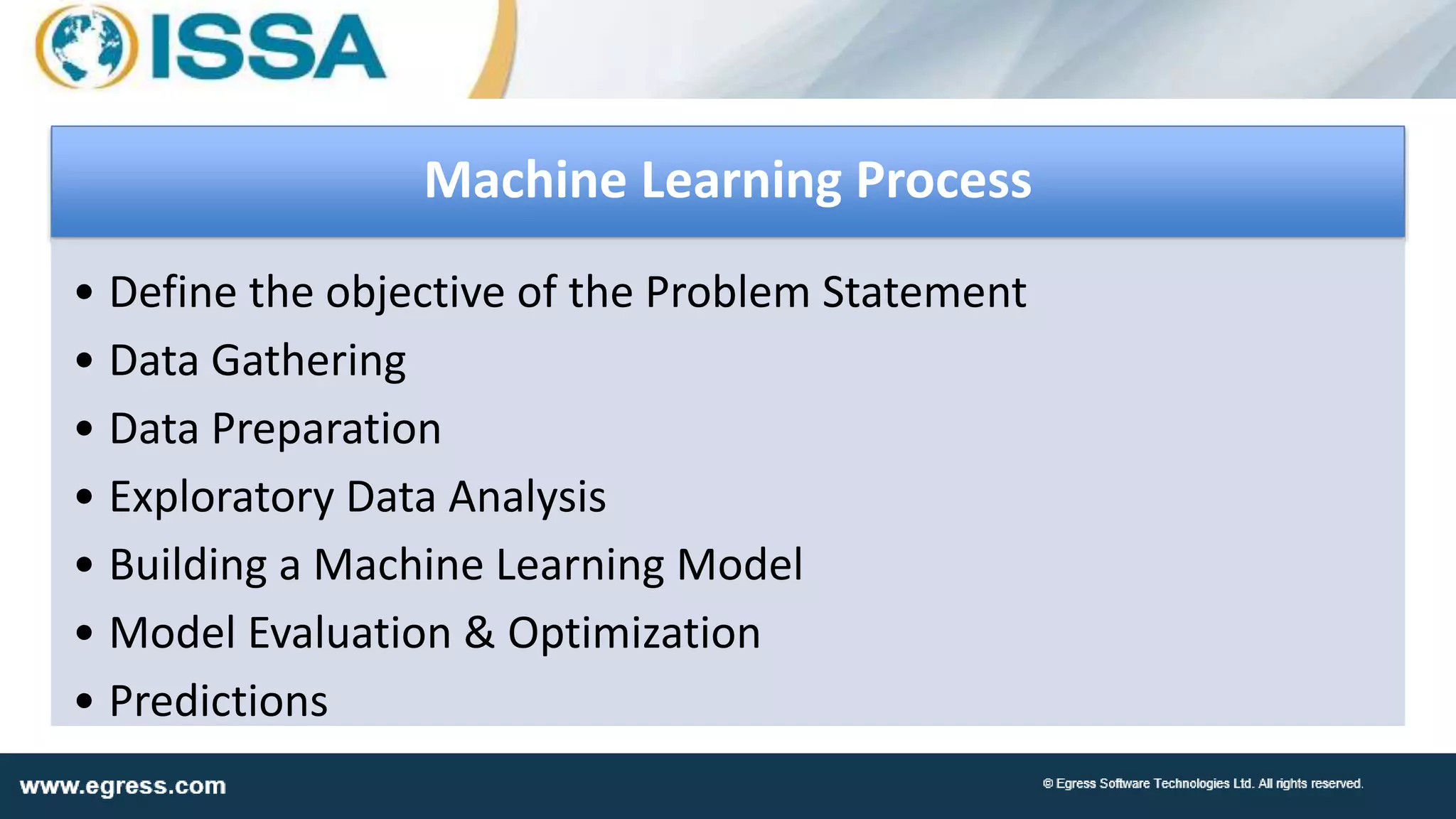
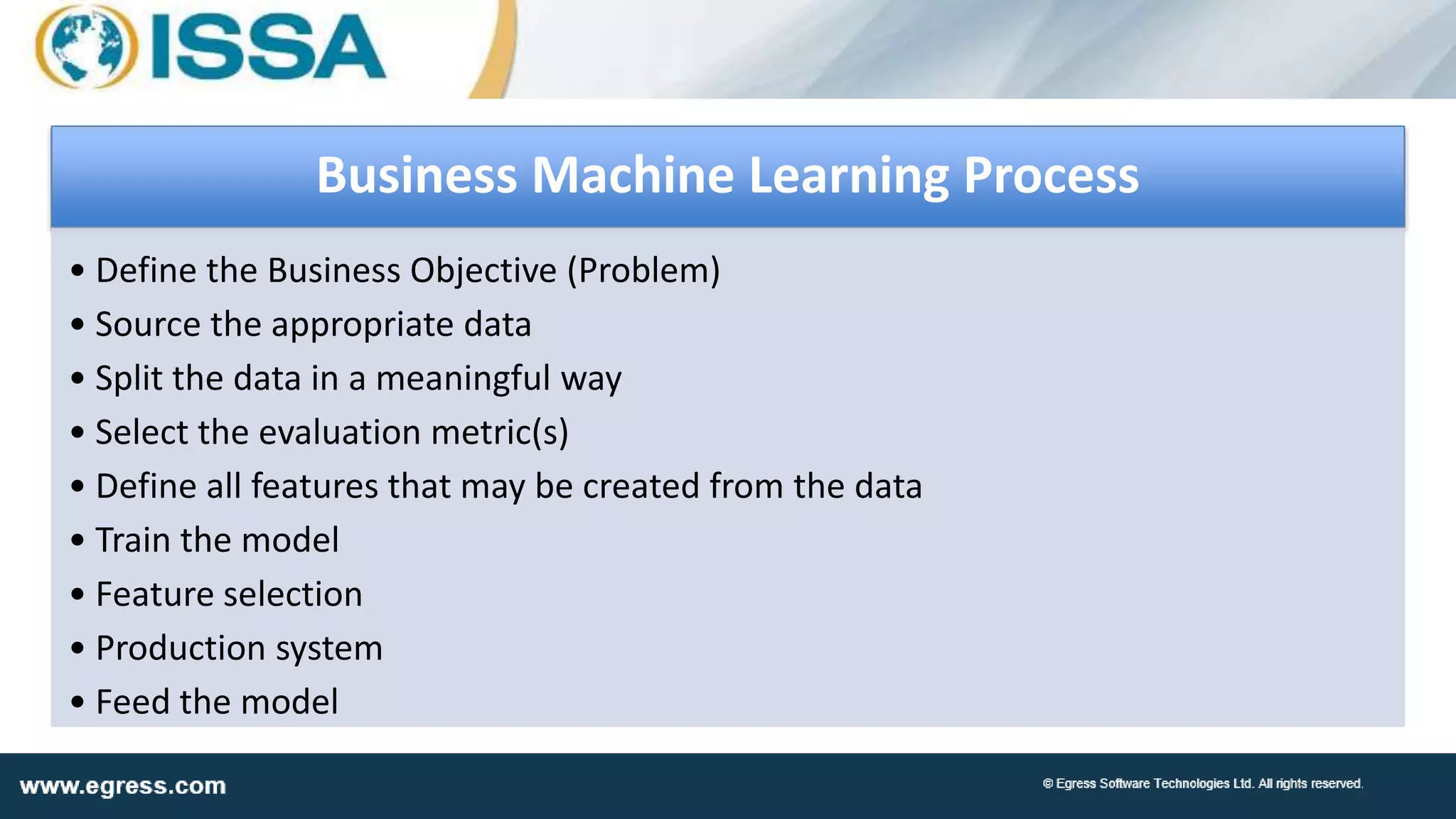
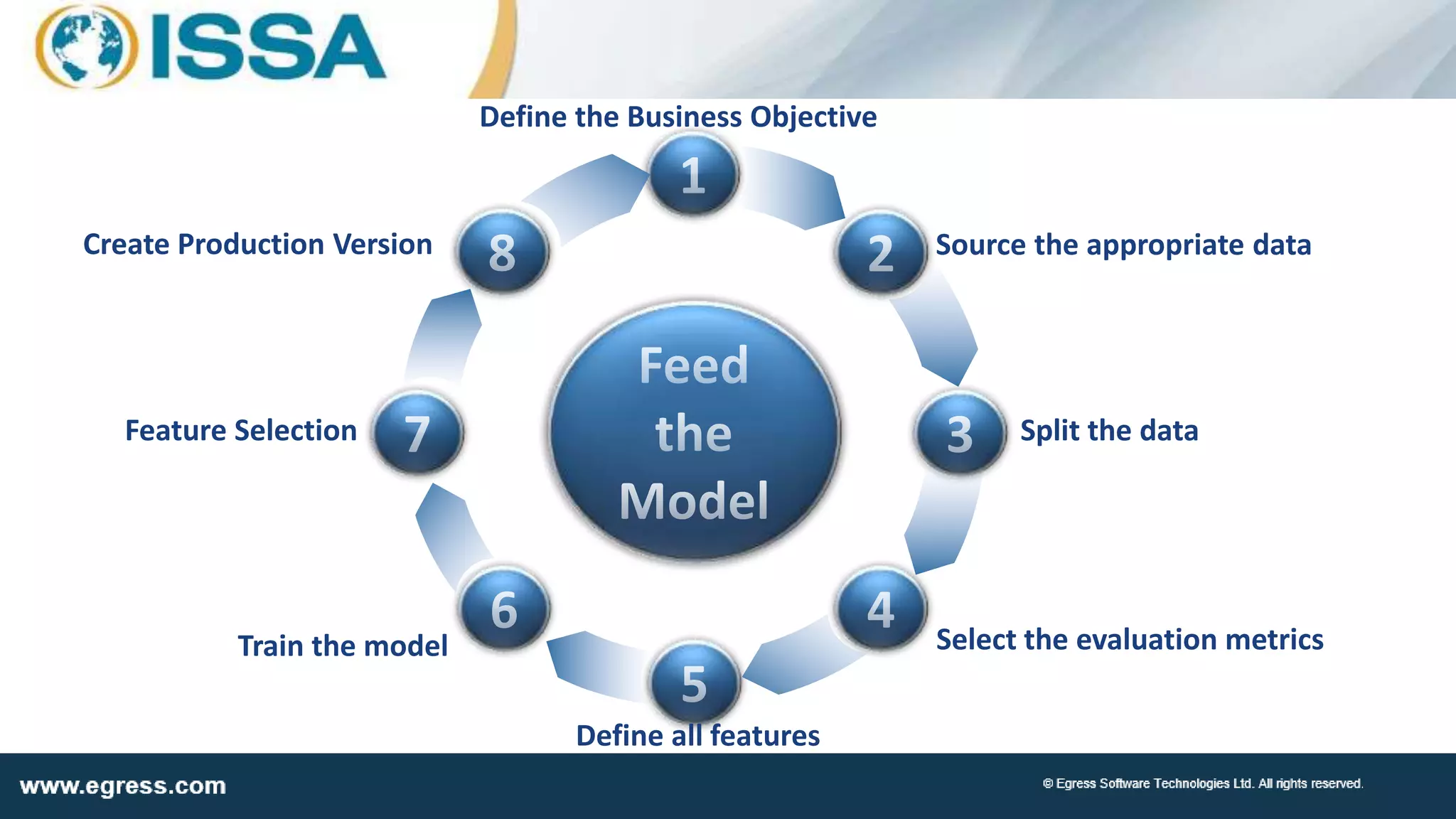
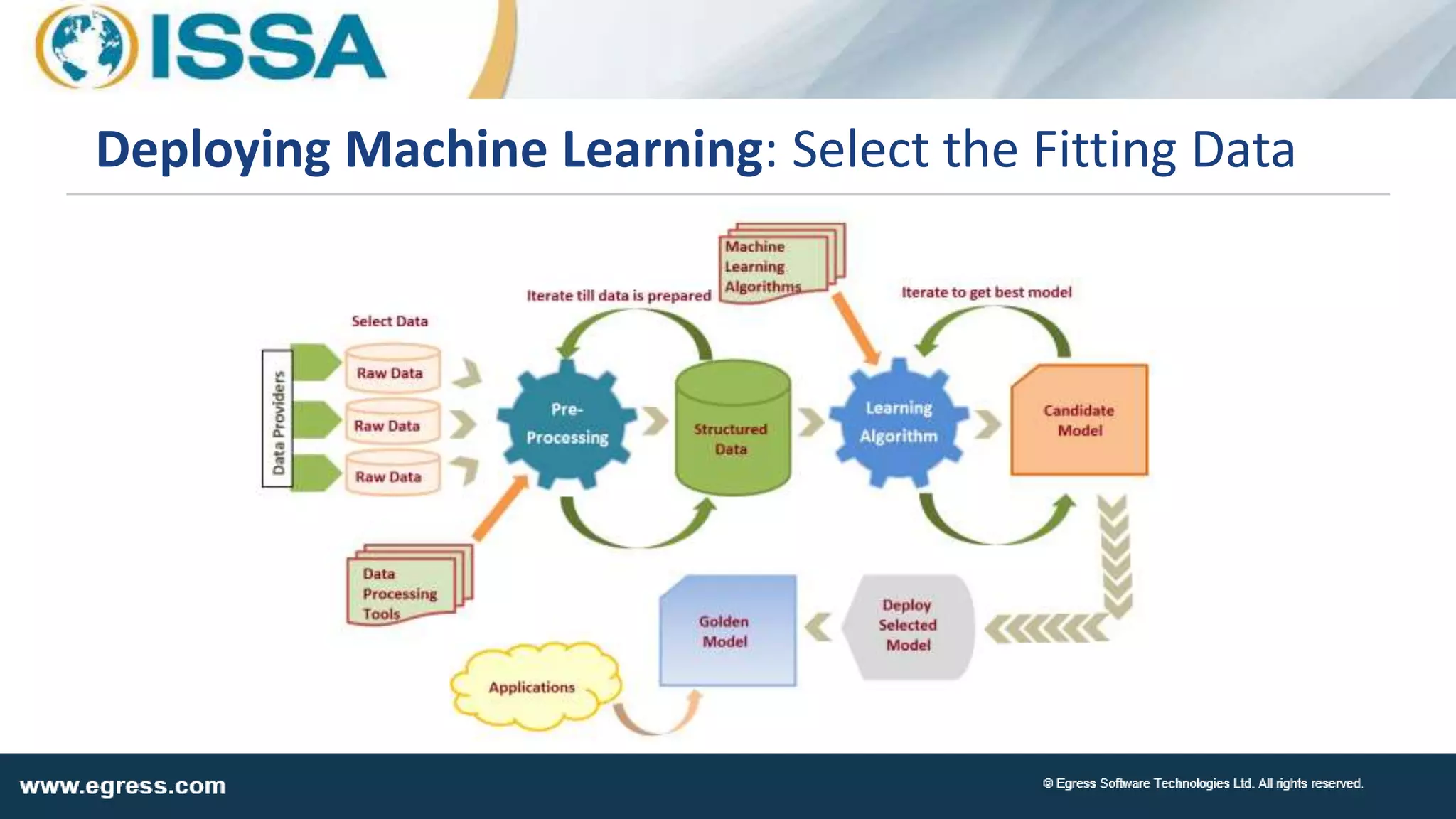
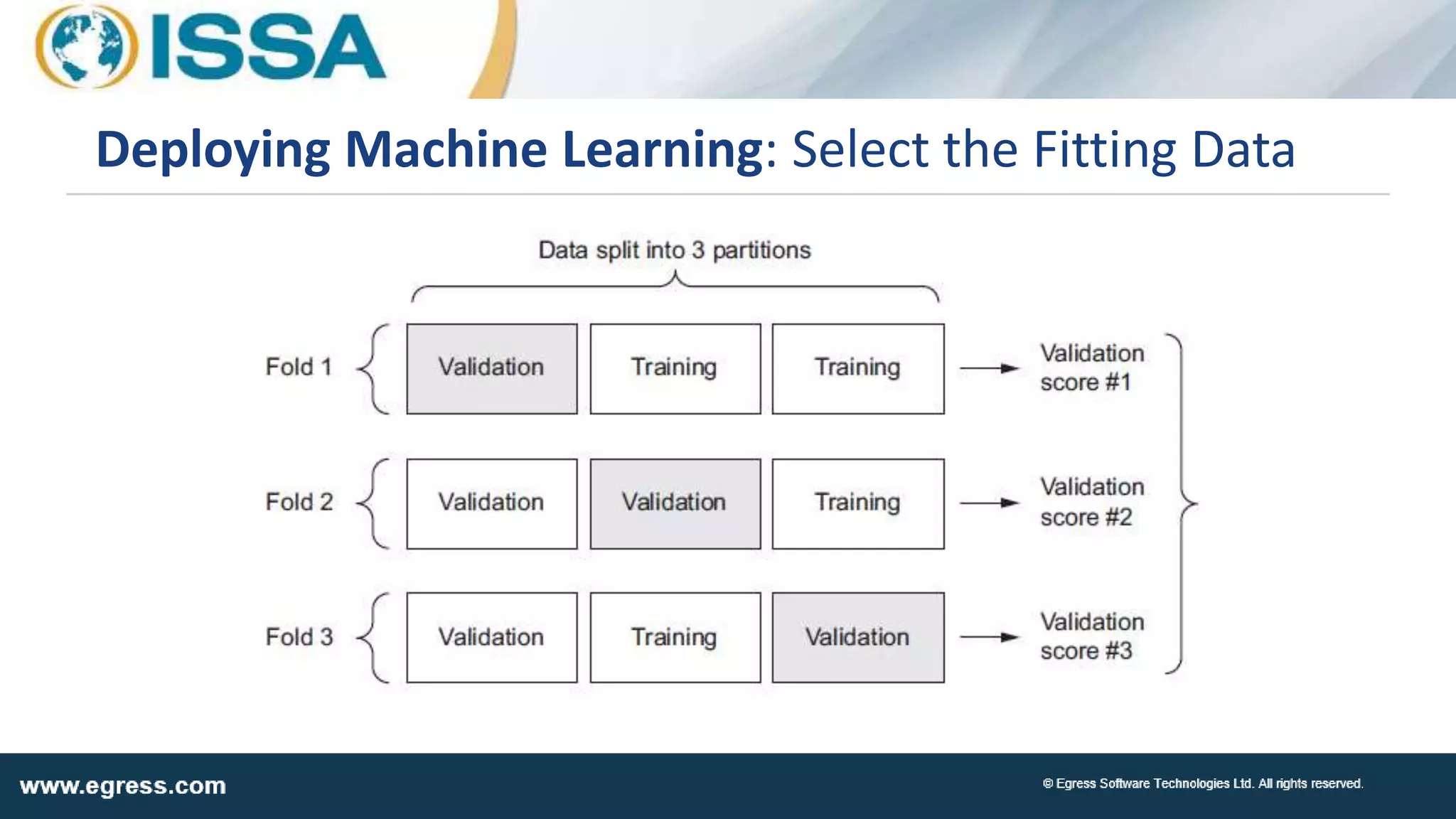
The document discusses the application of machine learning in data security, particularly how organizations can combat data breaches and ensure compliance with regulations like CCPA by using machine learning techniques. It highlights various processes, pitfalls in deploying machine learning, and the importance of defining real-world problems to be solved. Egress Software Technologies, led by Jon Mead, integrates machine learning to enhance user protection against accidental data sharing and improve risk assessment strategies.