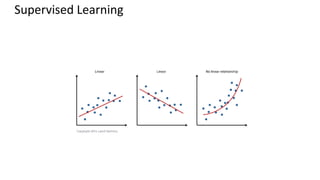
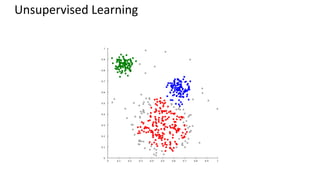
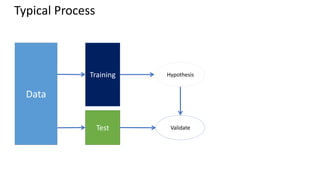
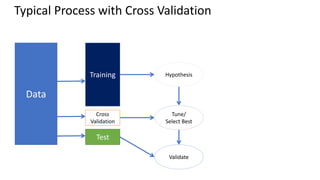
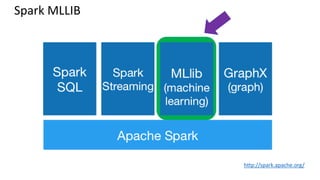
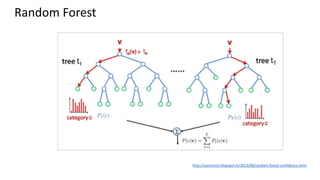
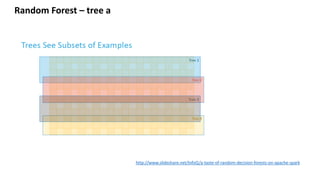
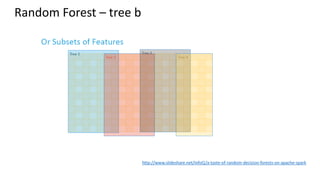
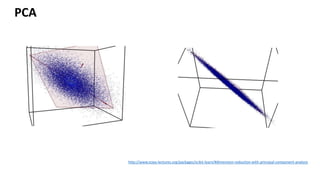
This document provides an introduction to machine learning, including definitions, types of learning (supervised, unsupervised, reinforced), and typical processes. It discusses issues like underfitting and overfitting. It also introduces Spark MLLIB, an Apache Spark library for machine learning that contains parallel algorithms. Key algorithms in MLLIB mentioned include k-means clustering, random forests, and principal component analysis (PCA).


![At a basic level, machine learning is about predicting the future based on
the past. [Hal Daumé III]
Systems that automatically learn programs from data. [Domingos]
Teaching a computer about the world. [Mark Dredze]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/machinelearning101-170329061751/85/Machine-learning-101-3-320.jpg)