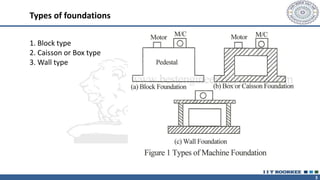
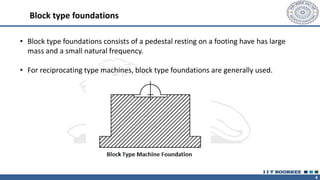
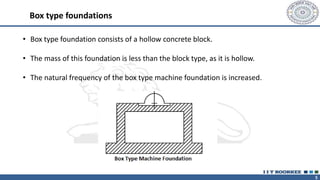
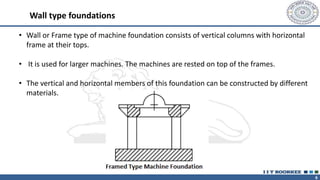
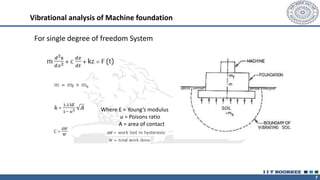
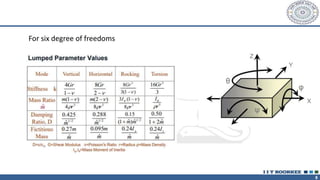
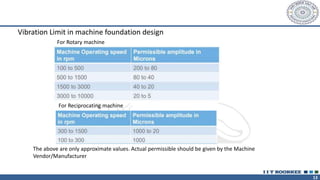
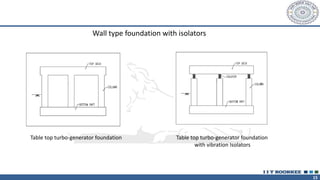
This document discusses different types of machine foundations. It describes three main types: block foundations, which are used for reciprocating machines; box foundations, which are hollow and have a higher natural frequency than block foundations; and wall foundations, which use vertical columns and horizontal frames for larger machines. It also discusses determining soil parameters through laboratory tests, vibration analysis for single and multi-degree of freedom systems, Indian code of practice IS 2974 for designing rotary machine foundations, and common design considerations like foundation mass and isolation.