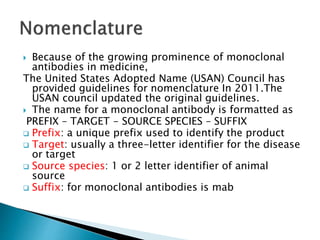
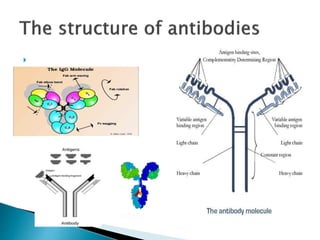
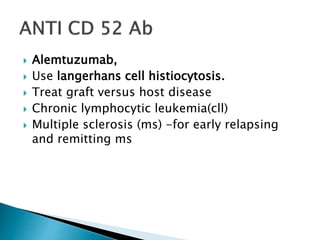
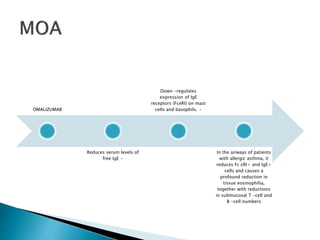
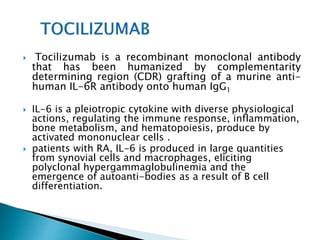
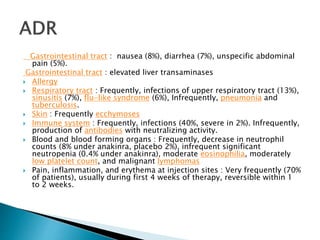
An antibody is a protein produced by the immune system to identify and neutralize foreign objects like bacteria and viruses. Antibodies recognize specific antigens unique to their target. Biological therapies for treating diseases employ substances like monoclonal antibodies, interferons, and interleukins. Monoclonal antibodies in particular are increasingly prominent in medicine. They are named using a standardized nomenclature indicating the target, source species, and whether it is a monoclonal, chimeric, or humanized antibody. Common examples of monoclonal antibodies used for treatment include rituximab, infliximab, and adalimumab.















![ Atacicept is a fusion protein containing the extracellular,
ligand-binding portion of the TACI (transmembrane
activator and calcium-modulator and cyclophilin-ligand
[CAML]-interactor) receptor, and a modified Fc portion of
human IgG that blocks BLyS (similar to belimumab).
It also contains a B-cell activating factor (a proliferation-
inducing ligand [APRIL]). Levels of both APRIL and BlyS are
increased in SLE patients, suggesting that blocking both
would be more beneficial than blocking either one alone.
The agent would also block both plasma and B cells.
Mavrilimumab, currently in Phase 2b, is a human
monoclonal antibody targeting the alpha subunit of the
granulocyte macrophage colony-stimulating factor
receptor, which inhibits the mononuclear phagocyte
pathway](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/biologicaltherapeuticagentsppt-180107062712/85/Biological-therapeutic-agents-ppt-19-320.jpg)

![ Humanized monoclonal antibody. Potential
uses may be found in oncology and in
treatment of inflammatory autoimmune
disorders, such as systemic lupus
erythematosus (SLE).
Use only in LN & NEUROPSYCHIATRIC
involment.
Other use- adult acute lymphoblastic
leukemia (ALL) / follicular lymphoma.[3]
Early results from a phase II trial for Diffuse
large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/biologicaltherapeuticagentsppt-180107062712/85/Biological-therapeutic-agents-ppt-21-320.jpg)

















![ IN GENERAL
INJECTION SITE PAIN
FEVER
FLUE LIKE SYMPTOMS
DIFFICULT, BURNING,
OR PAINFUL
URINATION
FREQUENT URGE TO
URINATE
LOWER BACK OR SIDE
PAIN
SORE THROAT
UNUSUAL TIREDNESS
OR WEAKNESS
NOTE -Patients who
use certolizumab have
an increased risk of
developing serious and
sometimes fatal
infections (eg,
bacterial, viral, or
fungal infections;
tuberculosis [TB]).](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/biologicaltherapeuticagentsppt-180107062712/85/Biological-therapeutic-agents-ppt-41-320.jpg)























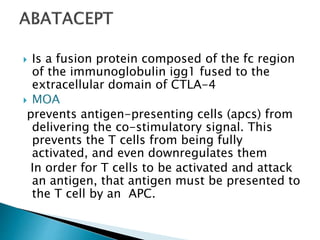





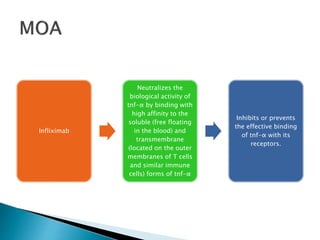



![ Serious infections
Reactivation of hepatitis B
Reactivation of tuberculosis[17]
Lethal hepatosplenic t-cell lymphoma
(generally only when combined with 6-
mercaptopurine)
Drug-induced lupus
Demyelinating central nervous system
disorders
Psoriasis and psoriasiform skin lesions
New-onset vitiligo](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/biologicaltherapeuticagentsppt-180107062712/85/Biological-therapeutic-agents-ppt-76-320.jpg)