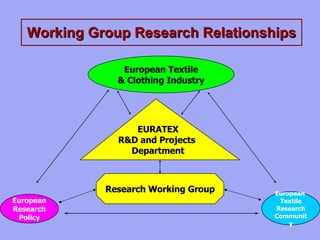
The document discusses the role of SME associations in encouraging research and innovation. It notes that over 95% of companies in the textile and clothing industry are SMEs, and SMEs have specific needs when it comes to research and innovation support. SME associations are well positioned to support the research and innovation needs of their SME members due to their industry knowledge, networking capabilities, and ability to communicate requirements to policymakers. However, associations also face limitations like lack of scientific expertise and potentially conflicting interests among members. The document provides recommendations for how associations can better support SME innovation and how policymakers can help associations in this role.