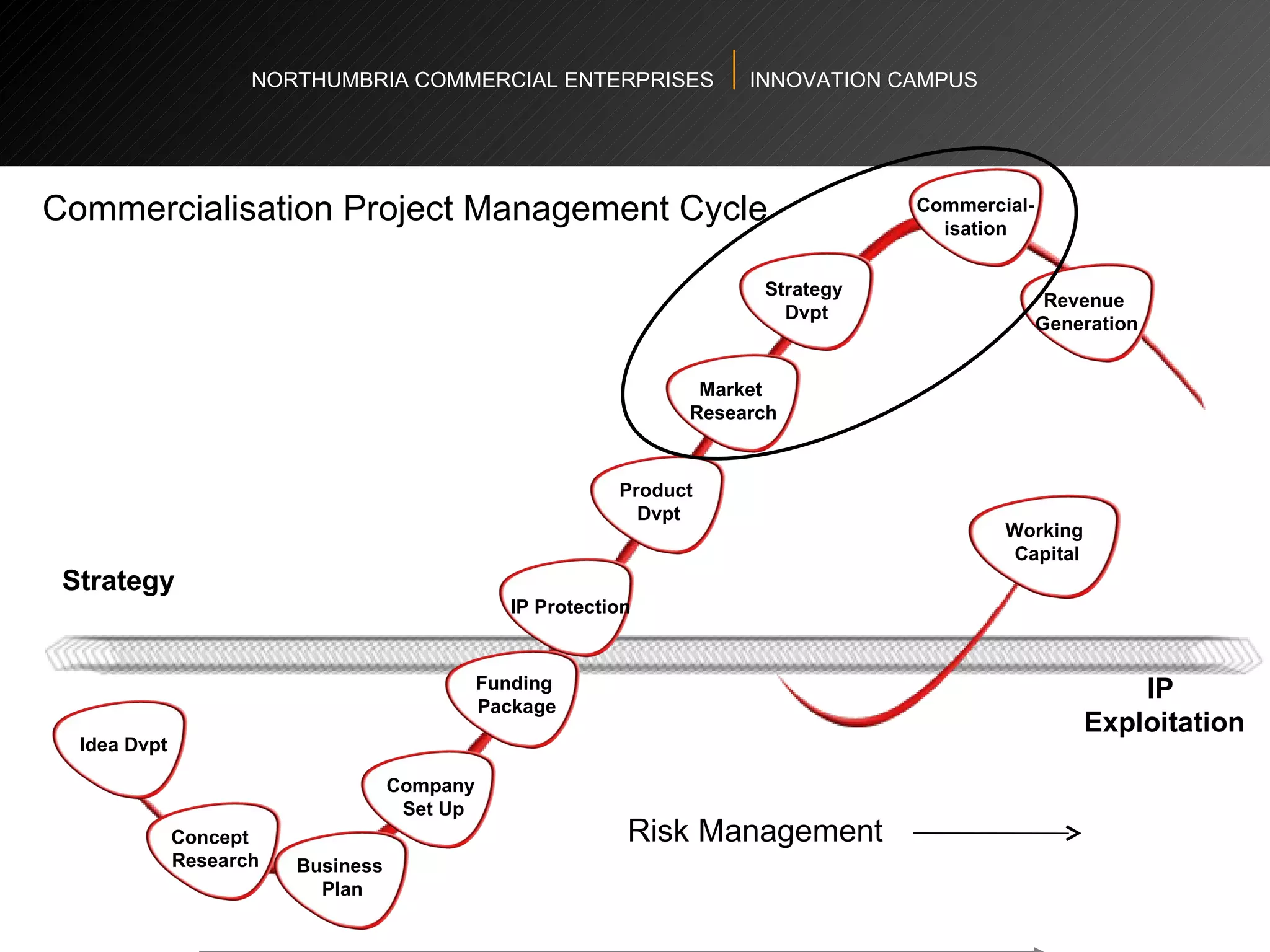
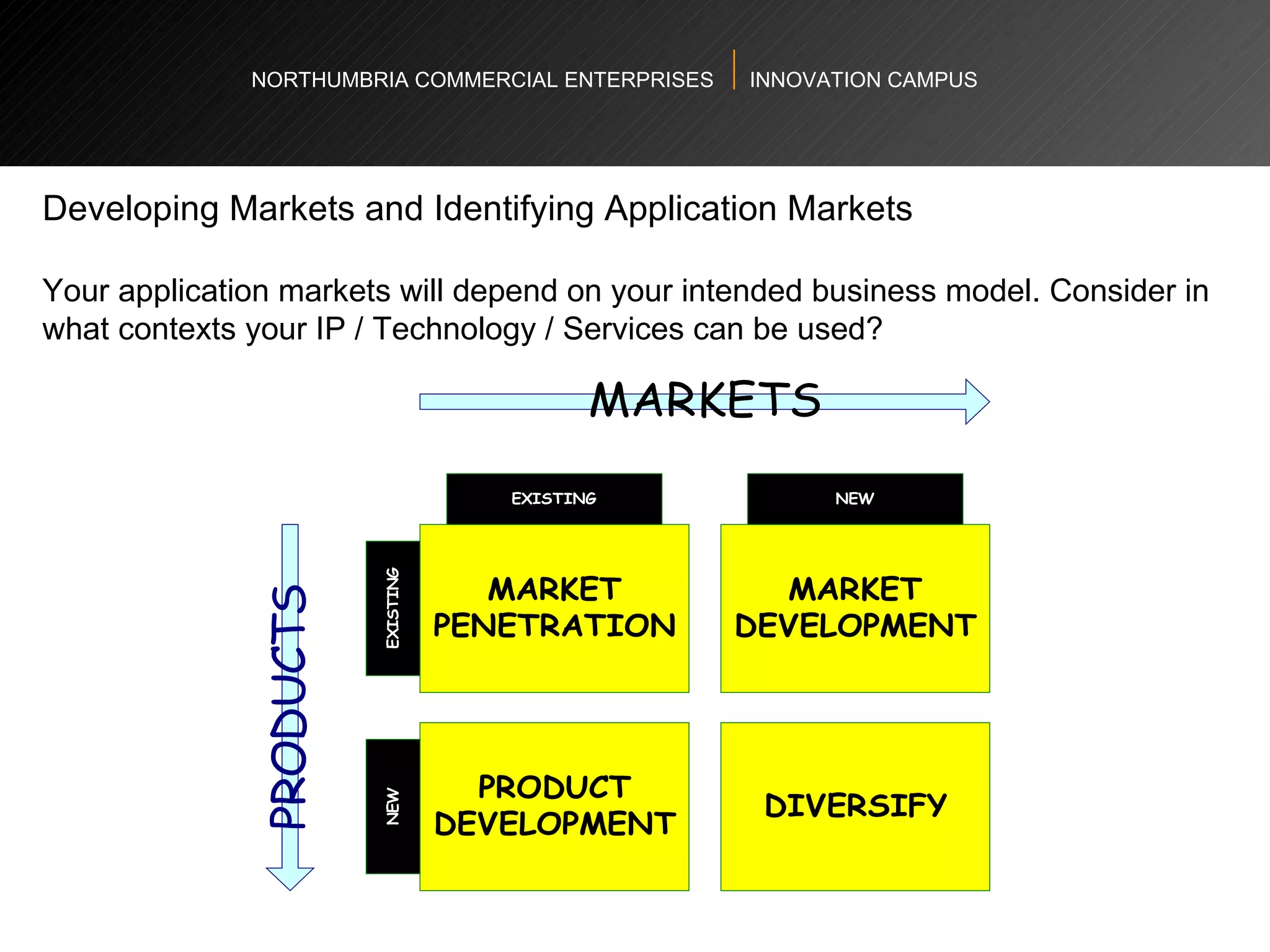
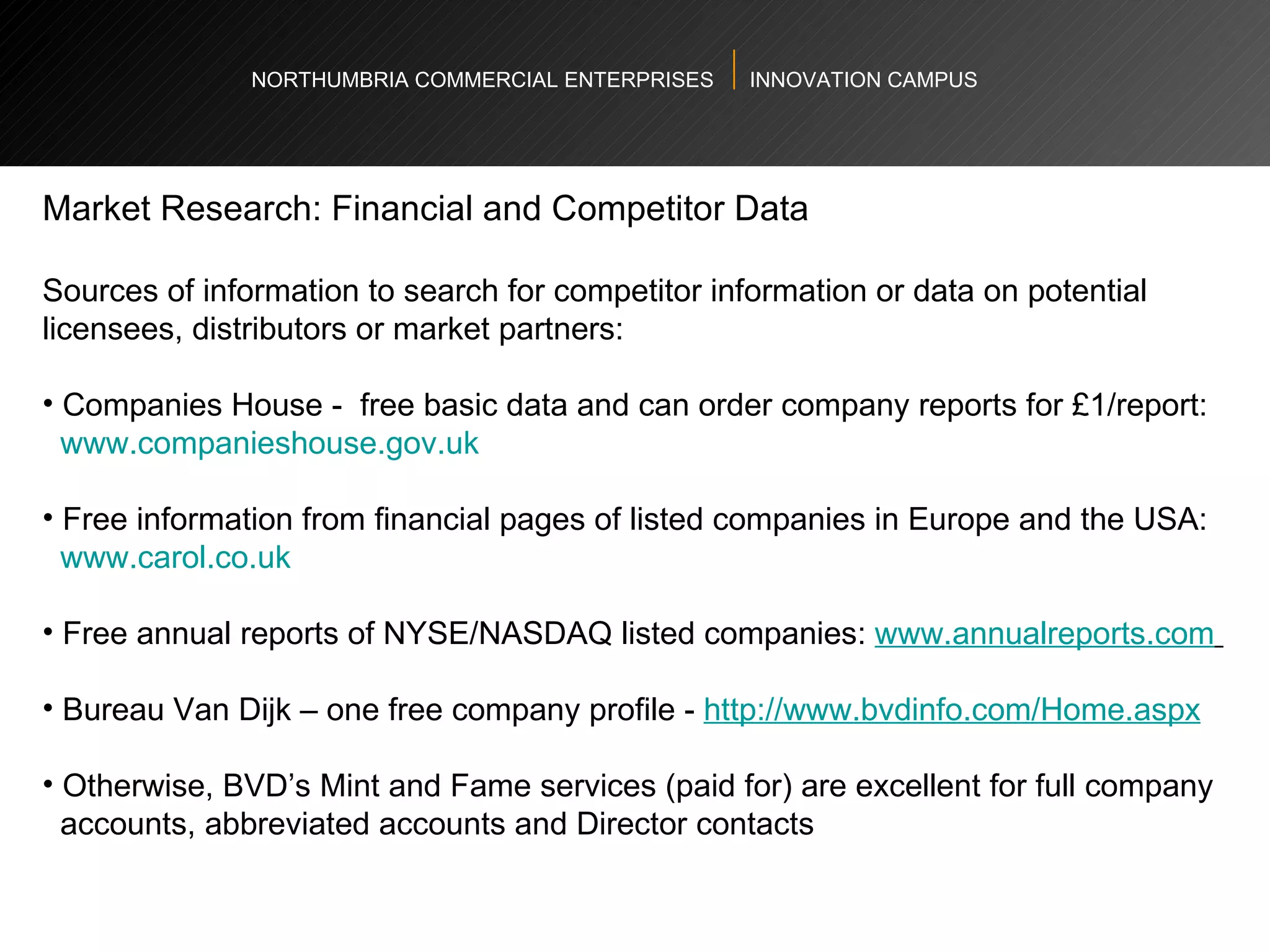
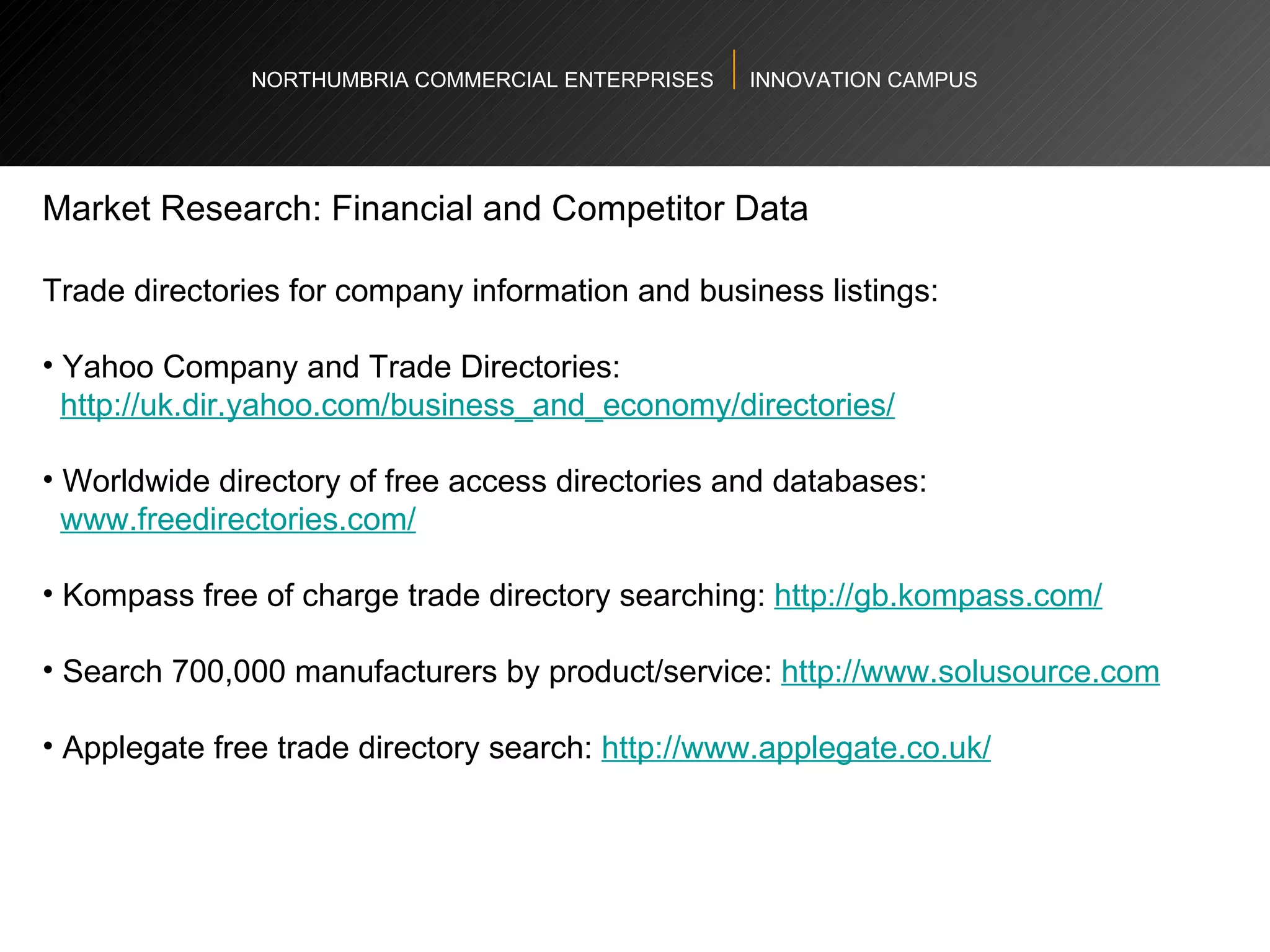
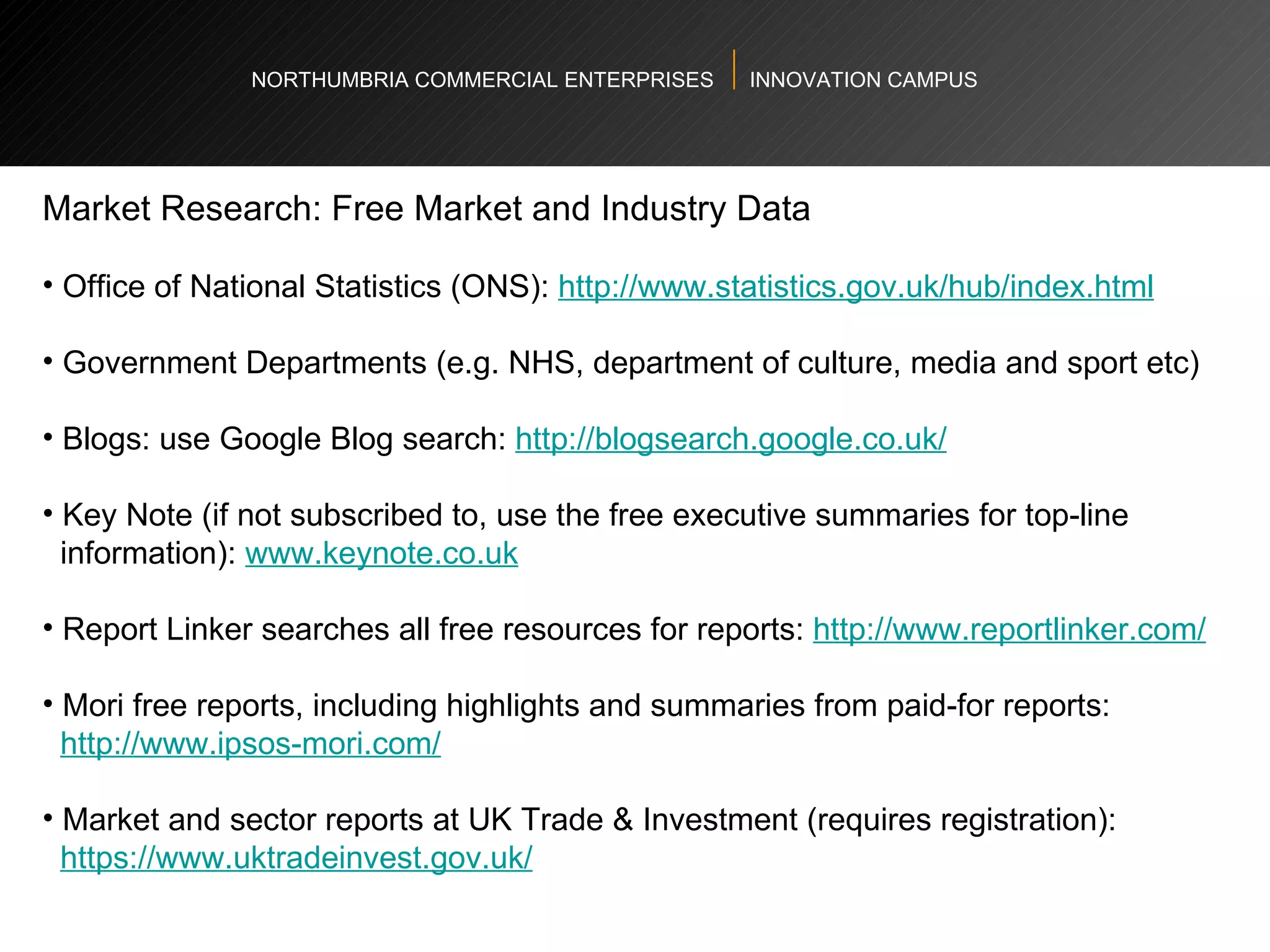
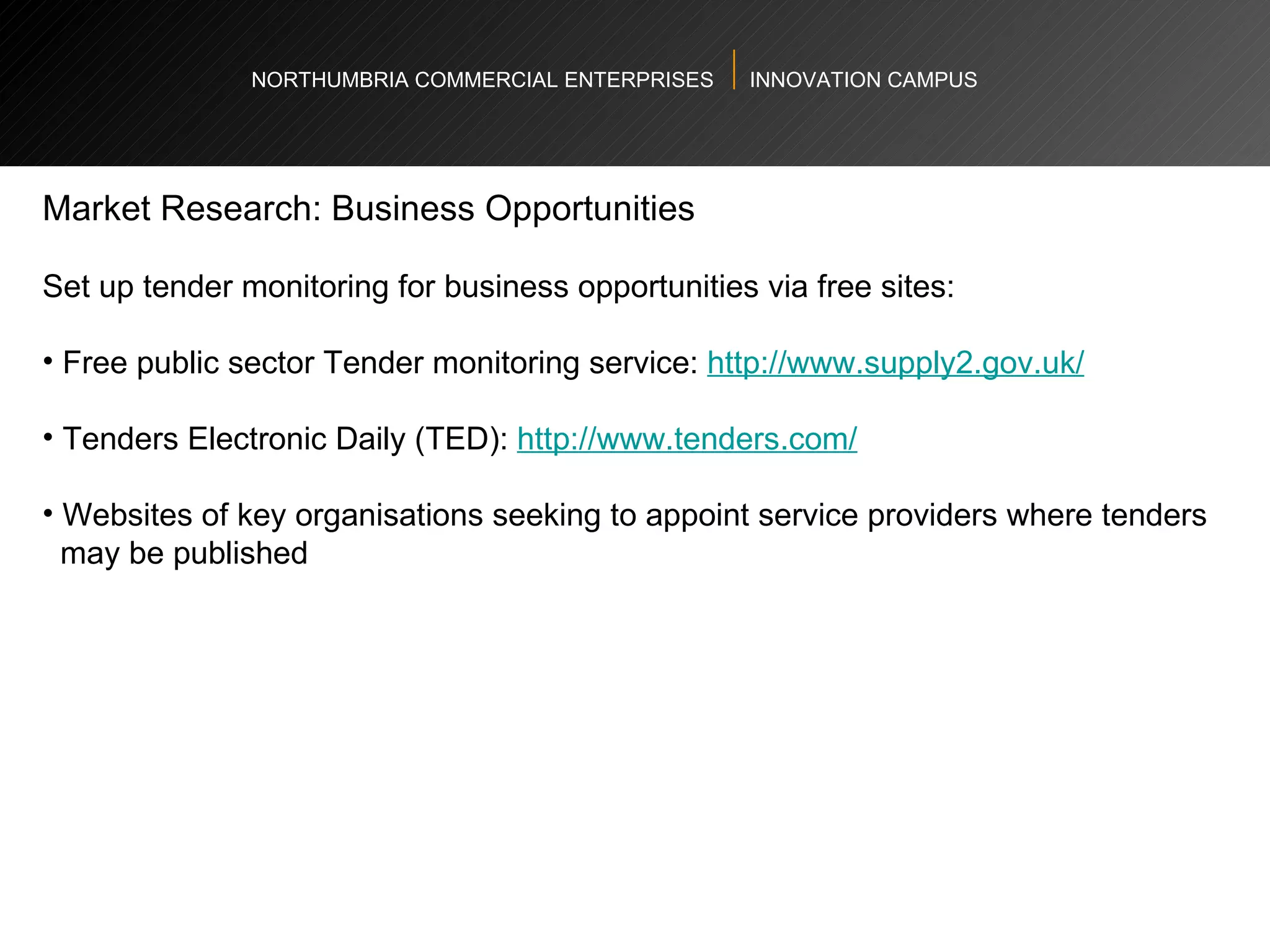
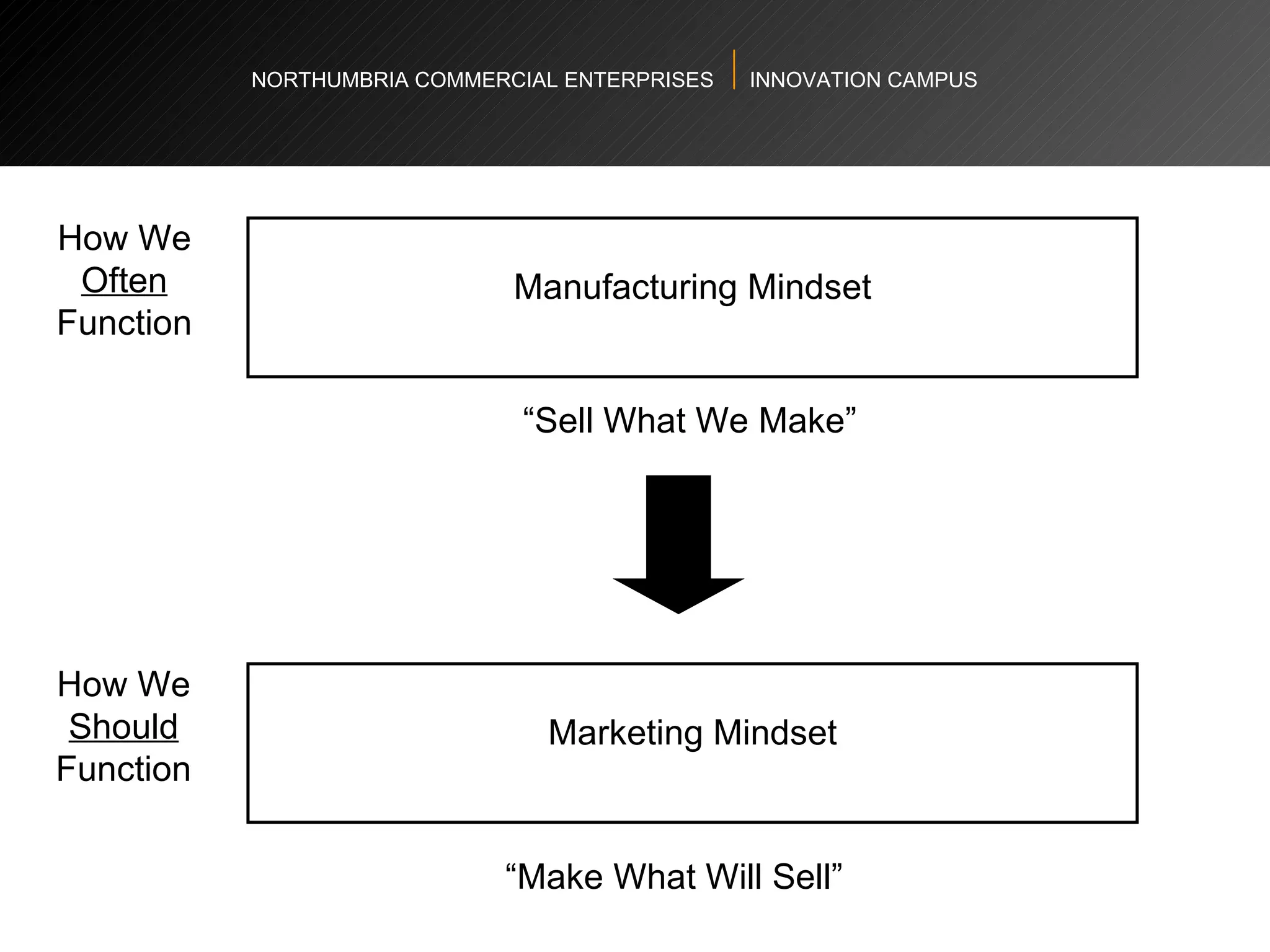
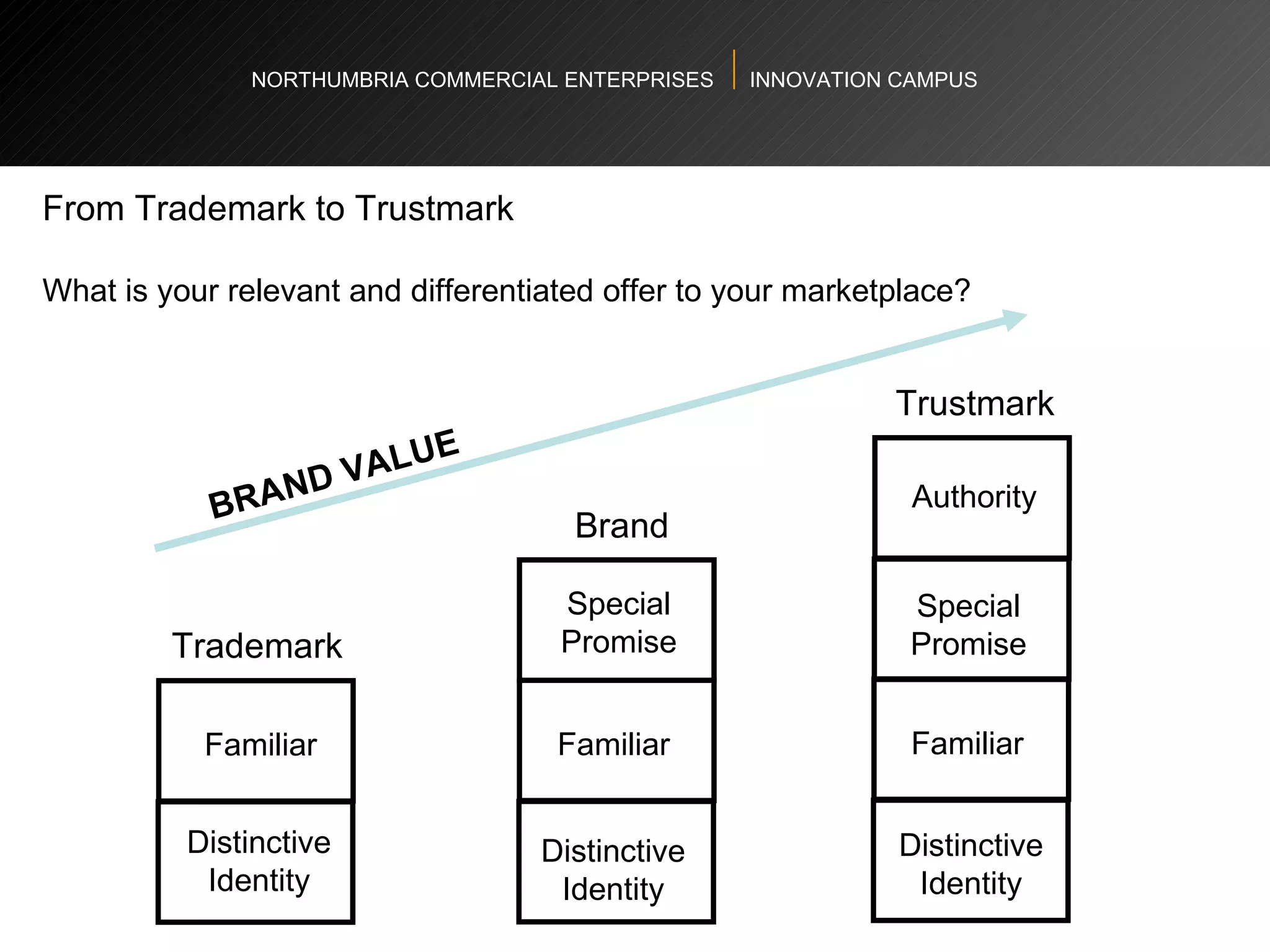
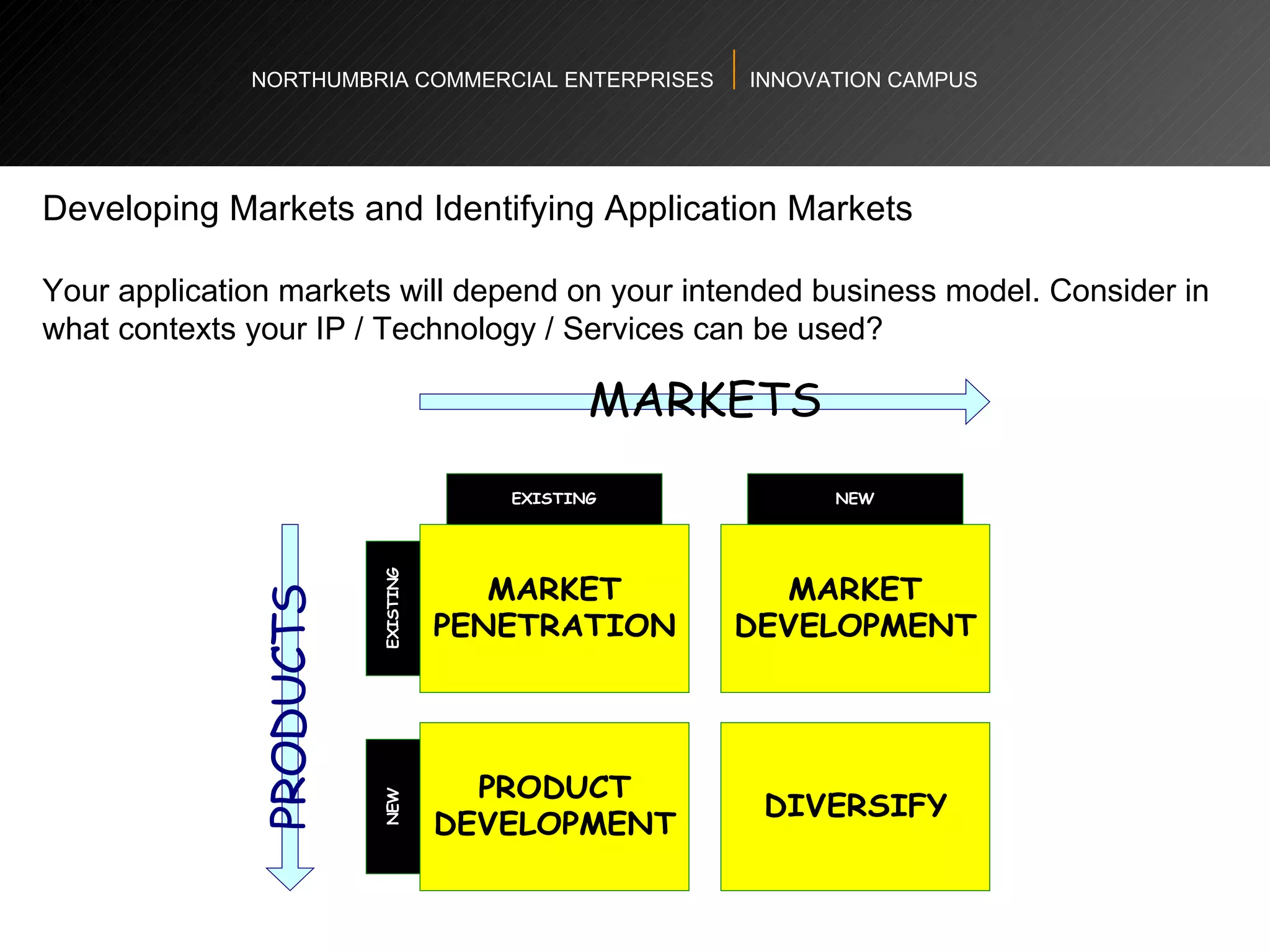
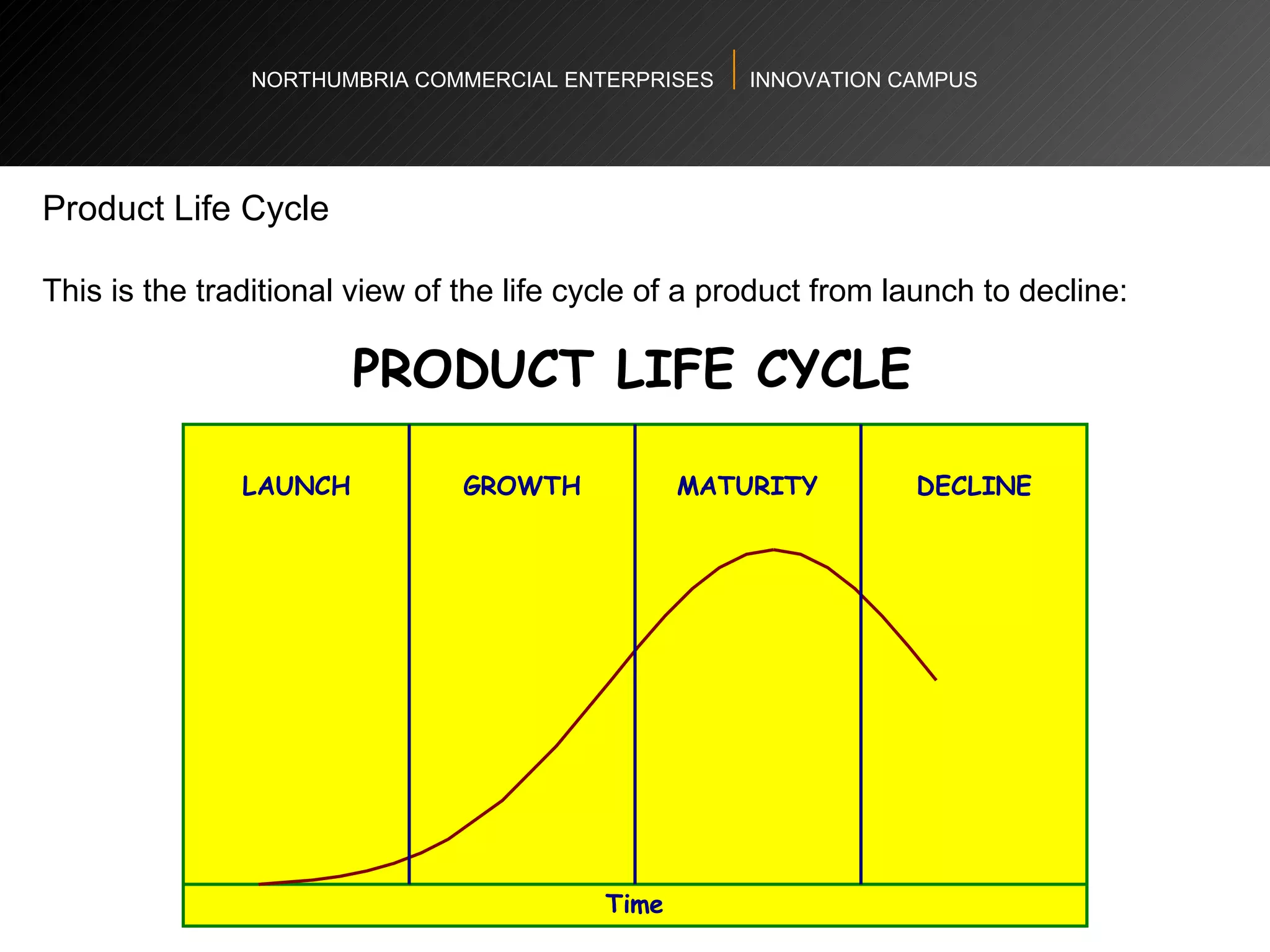
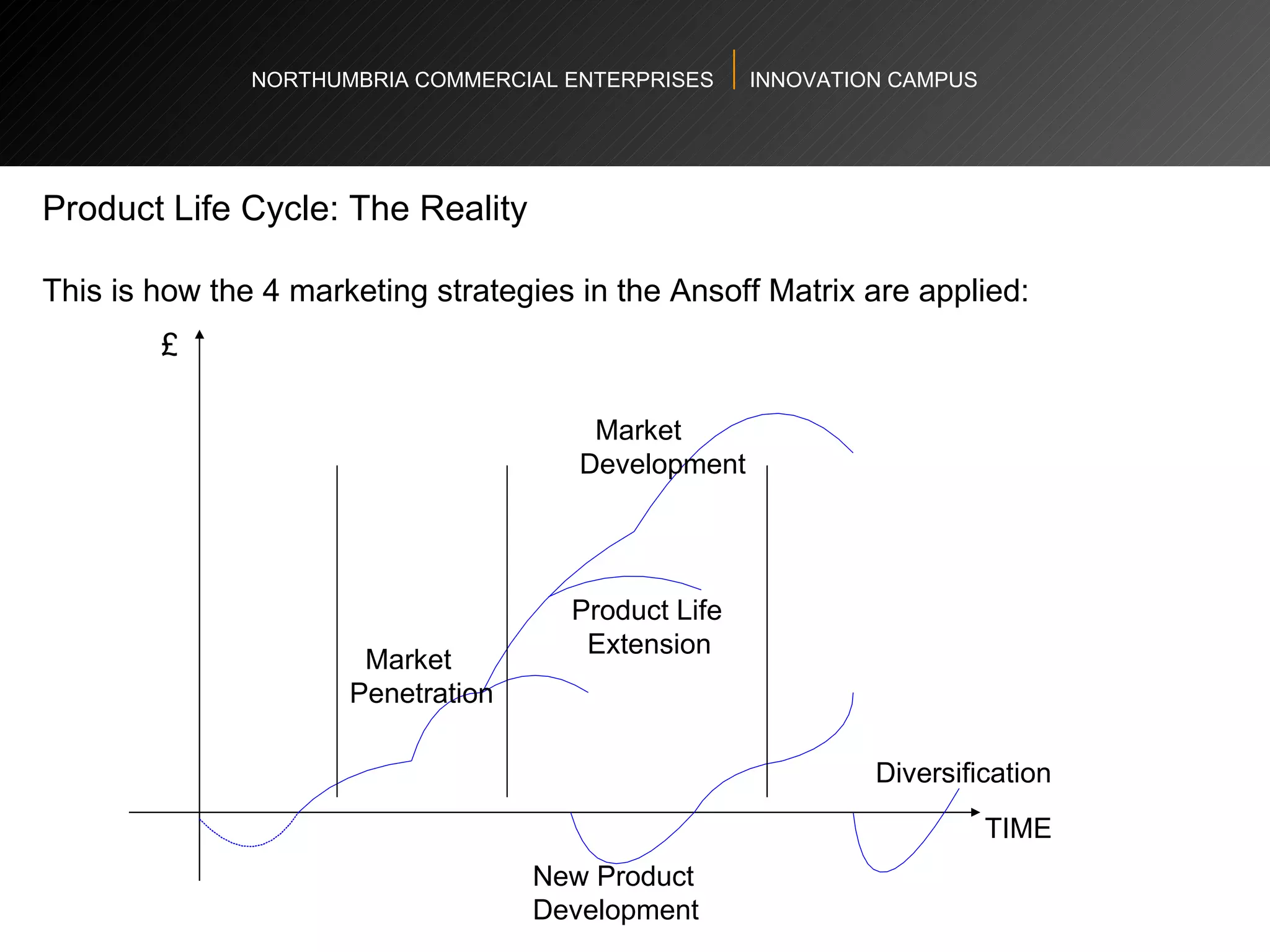
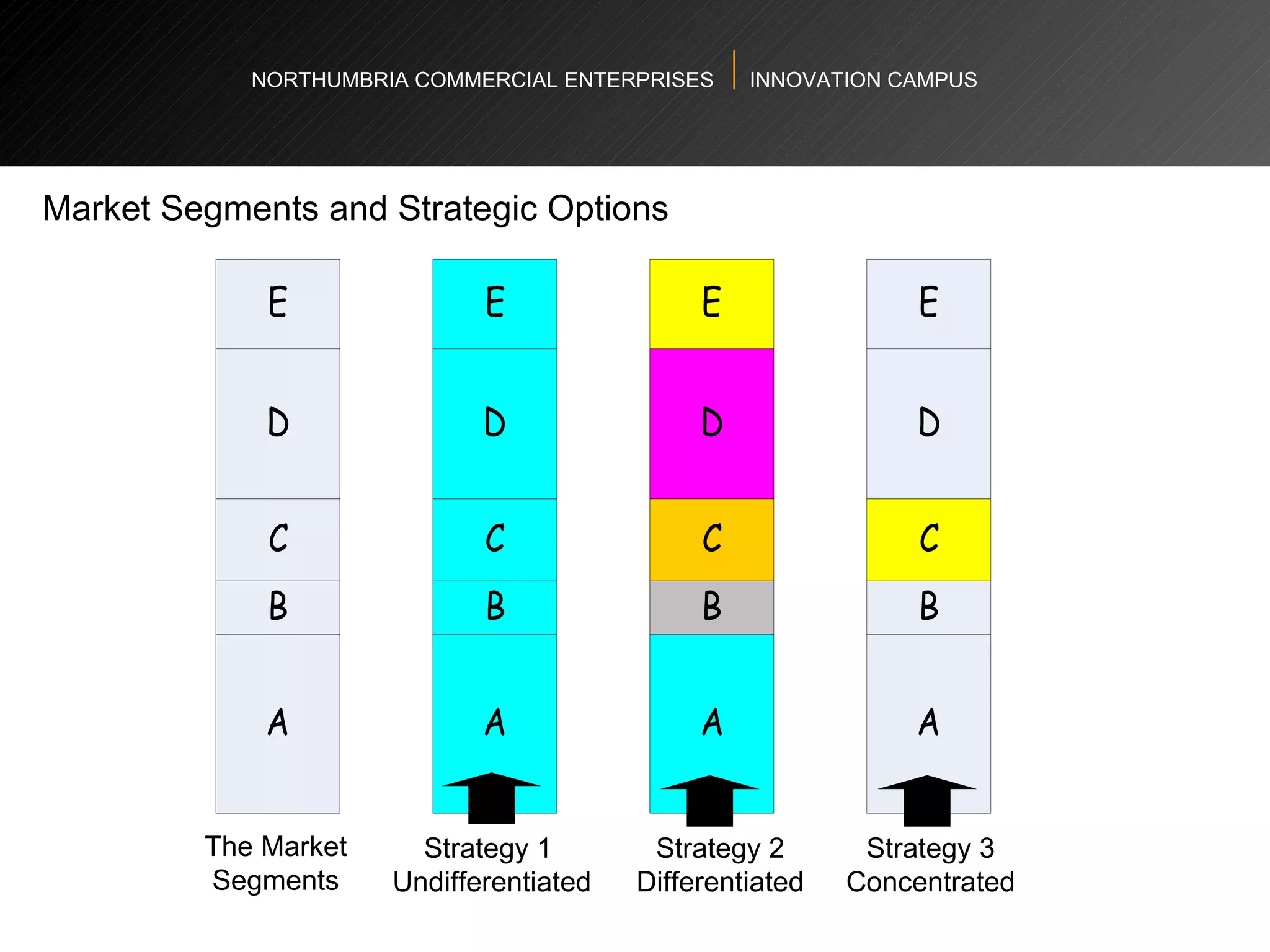
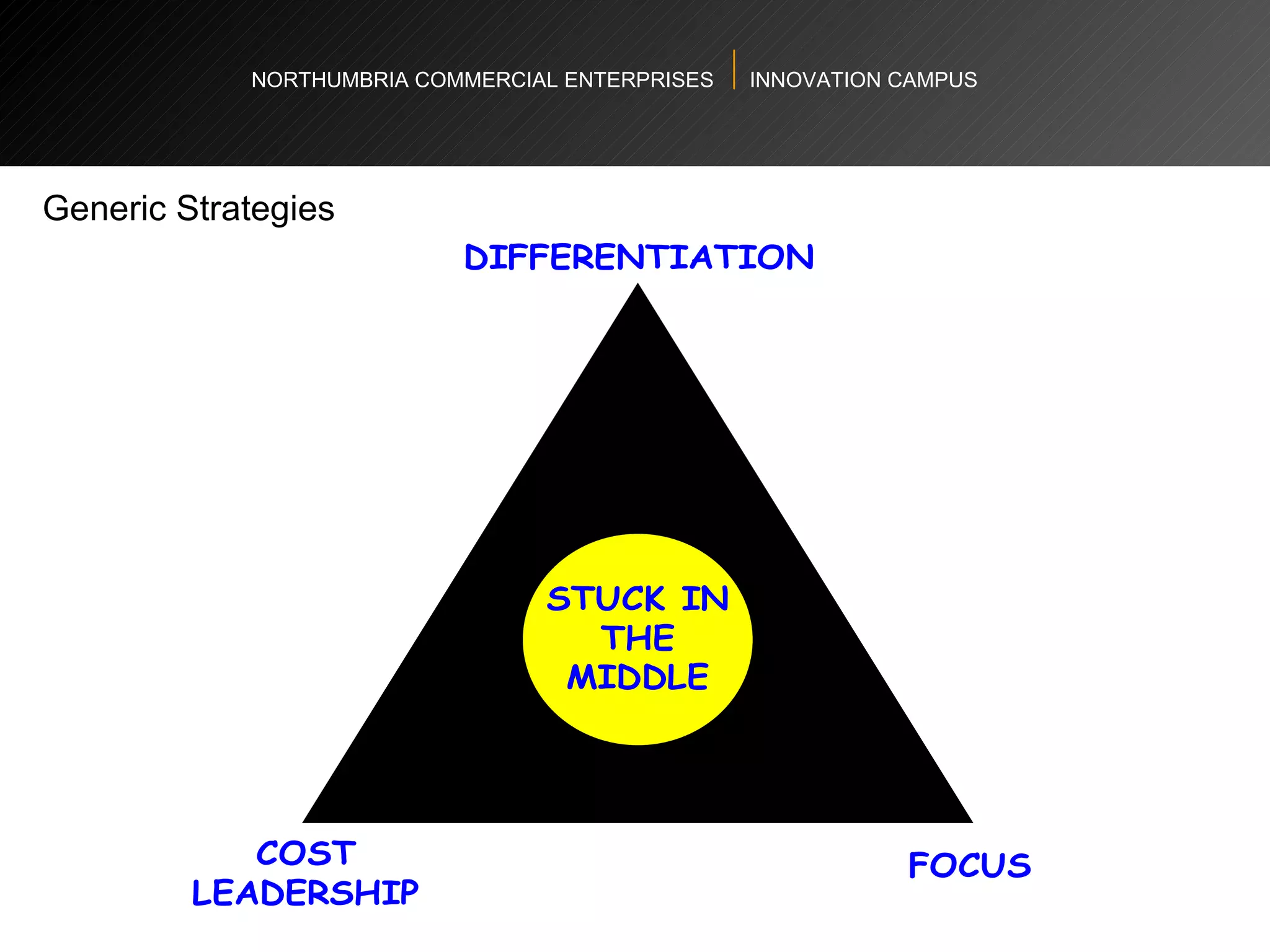
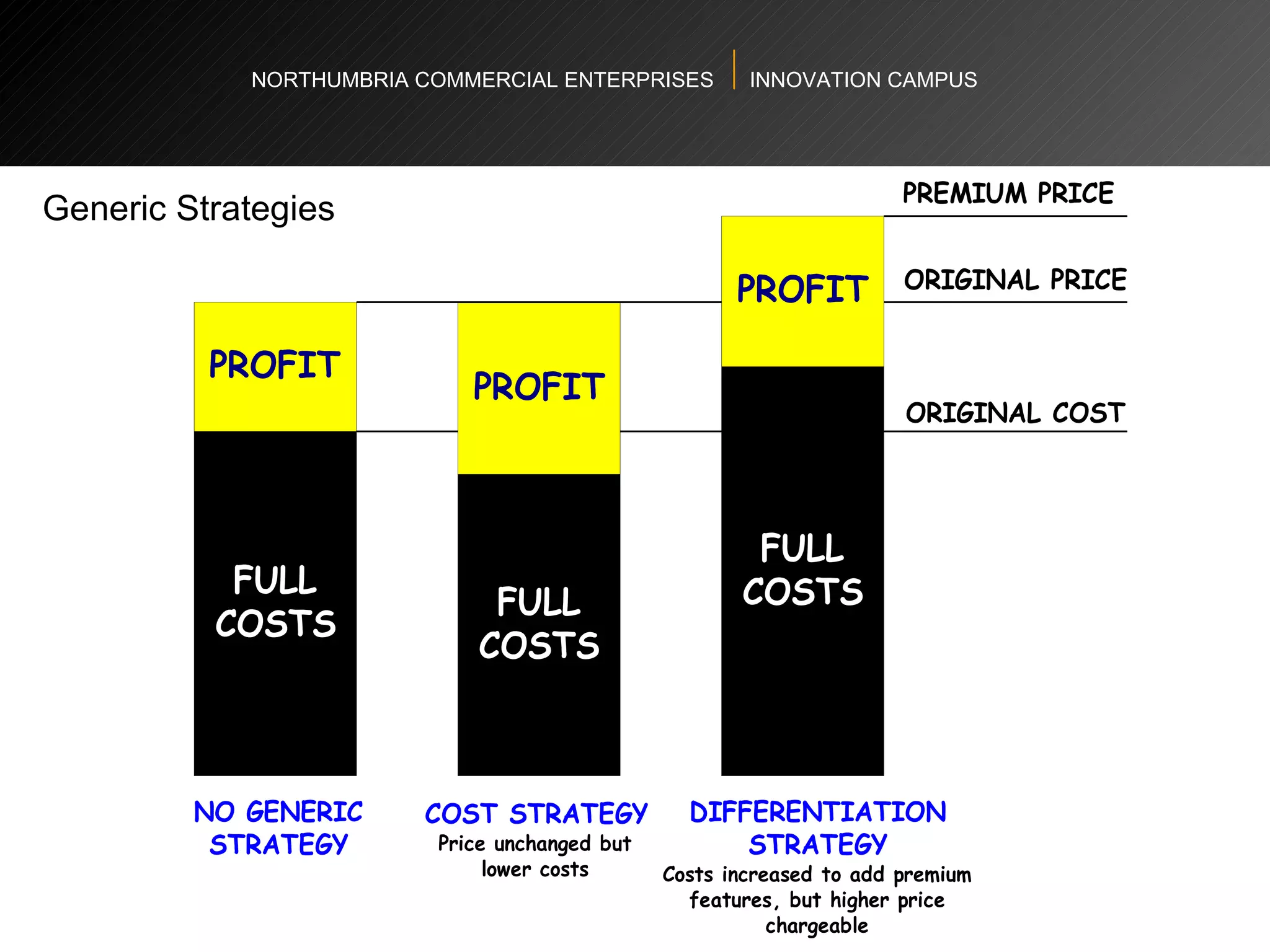
The document provides an agenda and overview for a workshop on understanding, finding, and developing markets. It discusses defining markets based on customer needs, identifying application markets, characteristics of different market types, sources and strategies for market research, licensing as an exploitation strategy, valuing and negotiating intellectual property, and developing go-to-market strategies including licensing. Key points covered include market segmentation, pricing strategies, conducting desk research, evaluating licensing opportunities, and negotiating royalty structures.

























![NORTHUMBRIA COMMERCIAL ENTERPRISES INNOVATION CAMPUS Thanks for Listening ... Q&A Ross Golightly [email_address] Tel: 07984 379 558 / 0191 4604126 www.twitter.com/RossGolightly www.spheraconsulting.co.uk](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/northumbriacommercialessentialsworkshop5slides-100415085822-phpapp01/75/Workshop-5-slides-48-2048.jpg)