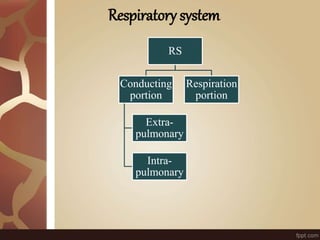
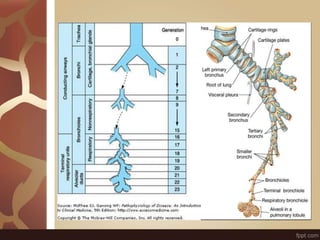
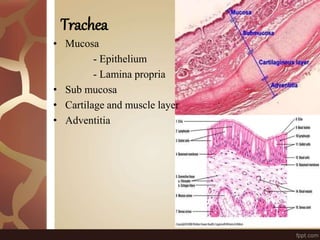
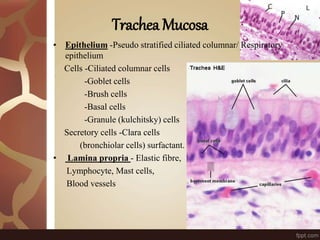
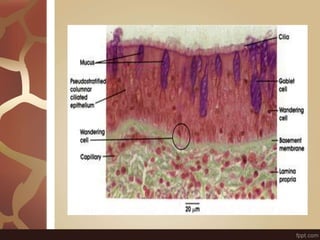
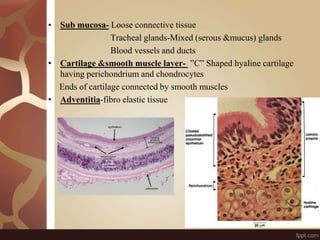
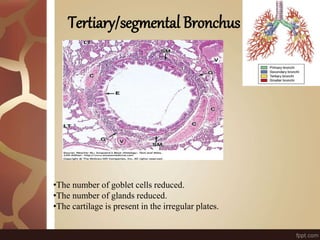
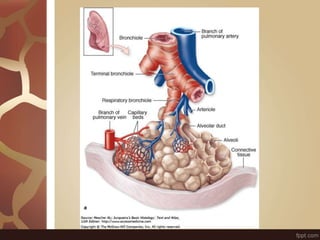
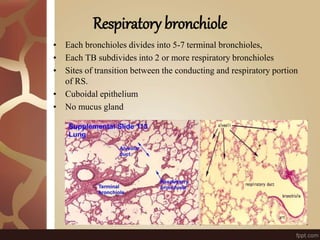
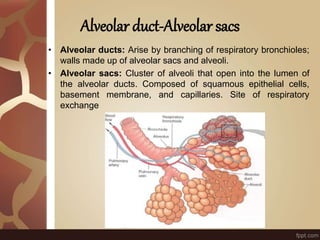
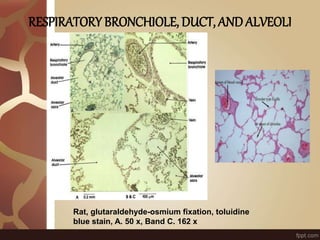
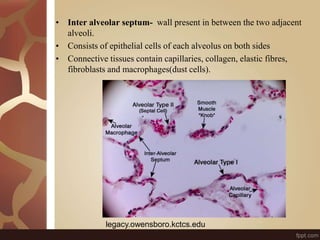
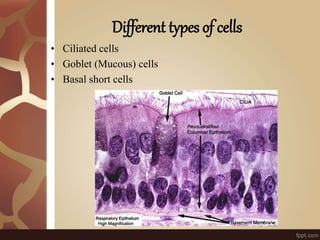
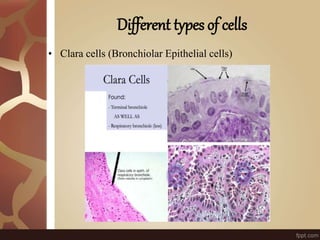
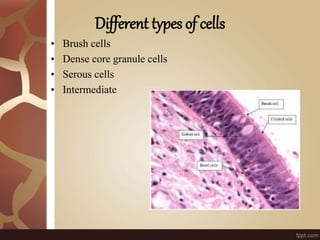
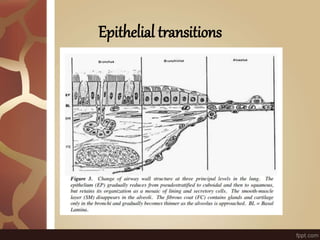
The document summarizes the histology of the lungs. It describes the conducting and respiratory portions of the respiratory system. In the conducting portion, it details the different cell types found in the trachea, bronchi, and bronchioles. It then discusses the respiratory portion including respiratory bronchioles, alveolar ducts, alveolar sacs, and alveoli. It notes that alveoli are lined by type I and type II alveolar cells and surrounded by capillaries, facilitating gas exchange.