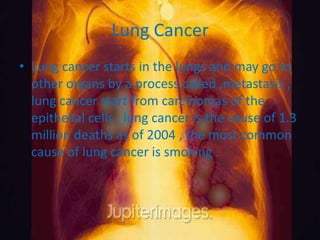
This document discusses lung cancer, including its causes, types, symptoms, and treatment options. Lung cancer starts in the lungs and is often caused by smoking. The two main types are small cell lung cancer and non-small cell lung cancer. Non-small cell lung cancer includes squamous cell carcinoma, adenocarcinoma, and large-cell carcinoma. Common symptoms include shortness of breath, coughing up blood, and chest pain. Treatment options include surgery, chemotherapy, and radiation therapy. For early-stage non-small cell lung cancer, surgery may be curative without additional treatment.