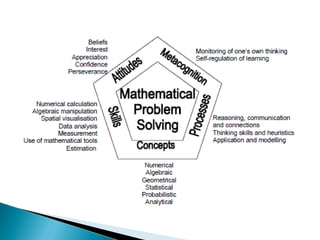
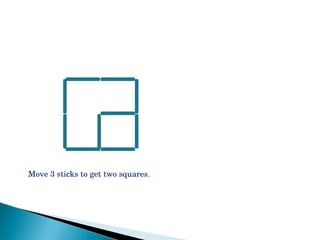
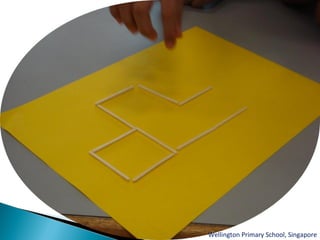
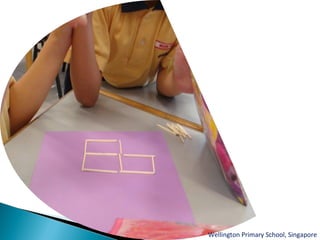
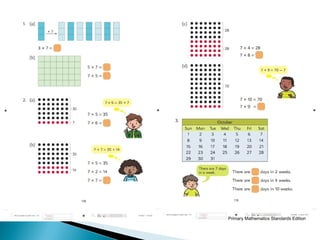
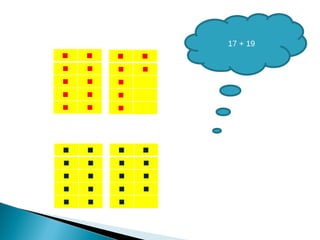
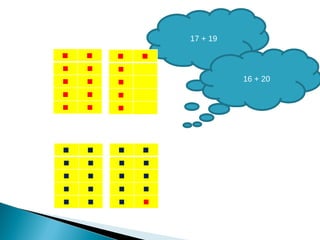
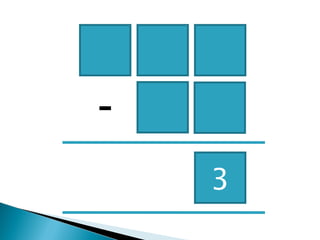
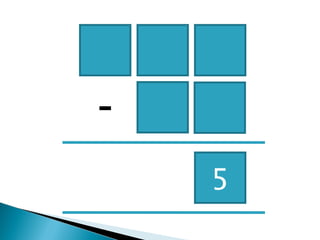
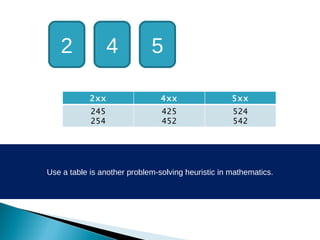
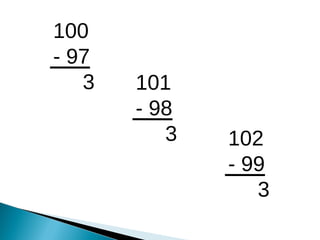The document discusses various problem solving heuristics for lower primary mathematics. It provides 14 examples of word problems demonstrating different heuristics students can use to solve problems, such as using tables, looking for patterns, guess and check, and breaking problems into steps. The heuristics allow students to systematically solve problems even if they are initially unfamiliar.