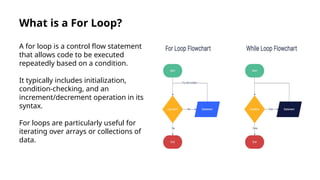
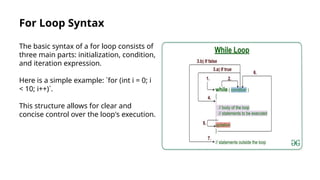
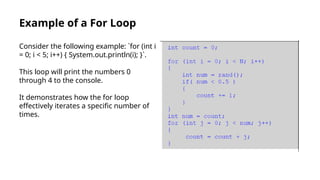
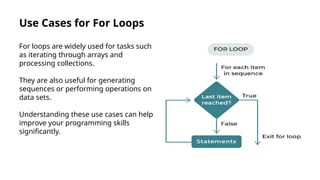
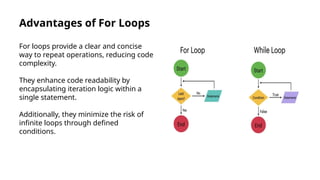
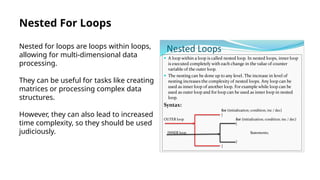
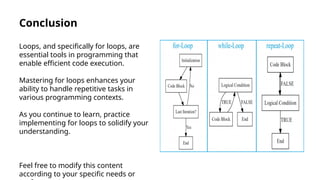
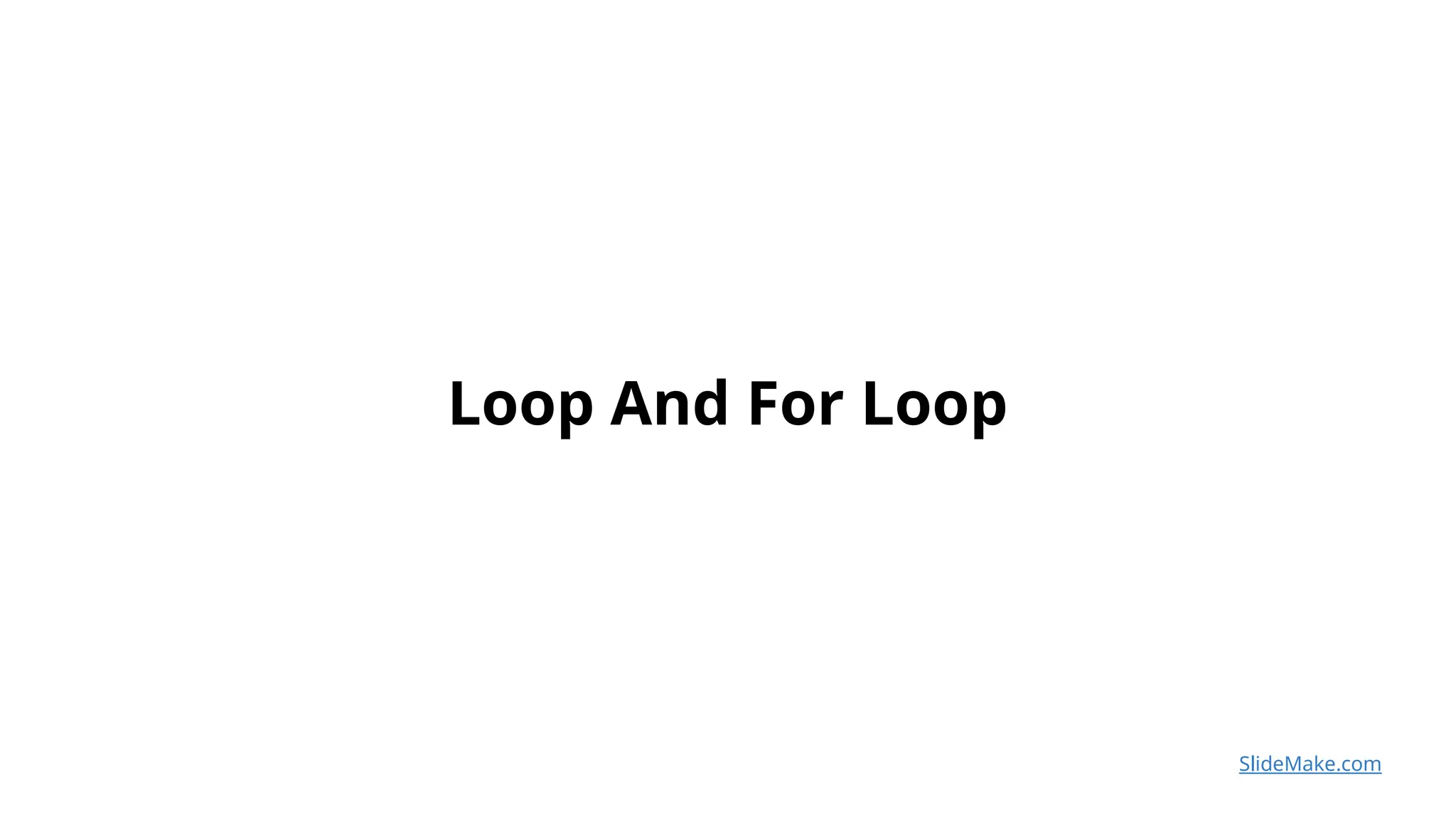The document provides an introduction to loops in programming, emphasizing their importance in automating repetitive tasks and improving code efficiency. It specifically focuses on for loops, detailing their syntax, use cases, advantages, and common mistakes associated with them. Additionally, it explains nested for loops and encourages practice to enhance programming skills.