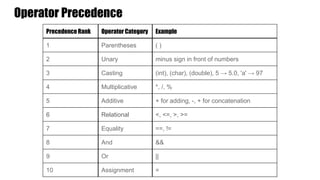
Chapter 2 of 'Building Java Programs' covers primitive data types, their operations, and variable declaration, including examples of integer division and casting. It introduces for loops, explaining their syntax, structure, and nested loops. The chapter also includes details on operator precedence and shorthand expressions for variable assignment.
























![Class Constants
public class ClassConstant {
public static final int SIZE = 20;
//final means it cannot be changed after declaring
public static void main(String[] args) {
for (int i = 1; i <= SIZE; i++) {
for (int j = 1; j <= SIZE; j++) {
System.out.print("*");
}
System.out.println();
}
}
}
Class constant naming convention:
ALL_CAPS_WITH_UNDERSCORES](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/chapter2buildingjavaprograms-170209193524/85/For-Loops-and-Variables-in-Java-26-320.jpg)