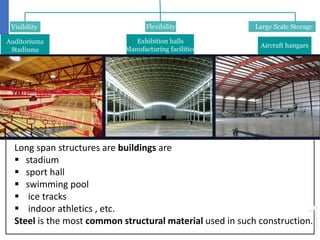
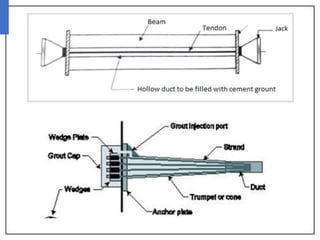
This document discusses long span structures, which are buildings with unobstructed column-free spaces greater than 15-20 meters used for stadiums, arenas, and pools. Steel is commonly used due to its ability to span large distances. Prestressed concrete is also used, which involves pre-tensioning or post-tensioning tendons to put concrete into compression and improve its strength. Pre-tensioning tensions tendons before pouring concrete, while post-tensioning does so afterwards. Segmental and composite construction are also discussed as methods to achieve long spans.