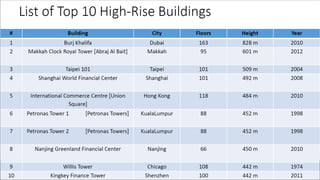
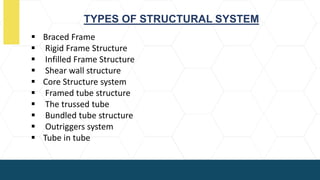
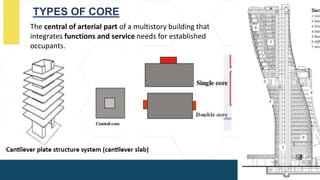
The document outlines various types of high-rise buildings, categorizing them into low-rise, mid-rise, high-rise, skyscrapers, supertall, and megatall based on their height. It discusses the increasing demand for high-rise structures due to factors like land scarcity, economic growth, and technological advancements, along with different structural systems used to support these buildings. Additionally, it explains different structural frameworks such as braced frames and core structures that contribute to the stability and functionality of high-rise designs.