Embed presentation
Downloaded 22 times


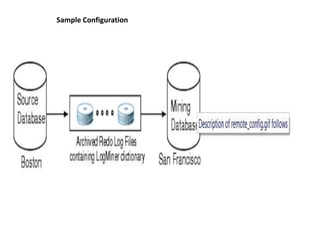




Log Miner in Oracle allows users to analyze redo log files to perform auditing, determine causes of errors, and aid in performance tuning and capacity planning. It requires a source and mining database running the same Oracle version with a LogMiner dictionary and redo log files. Users direct Log Miner operations using PL/SQL packages to build the dictionary, add log files, start the session, query results, and end the session.





