The document explains searching in lists using Python, focusing on linear search, a method to find the position of a specific element by comparing it sequentially with each item in the list. It provides examples both with unsorted and sorted lists, detailing how to implement linear search through loops while storing the position of the found element. The document also describes the steps required to perform this search and how to handle positive and negative results indicating whether the searched number was found or not.









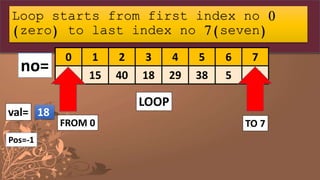
![So now Let Us understand this linear
search with another example
If there is a sequence of numbers in a list
no=[10,15,40,18,29,38,5,37]
Example Unsorted numbers:
0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7
10 15 40 18 29 38 5 37
no=](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/listpart4-200716140818/85/LIST-IN-PYTHON-PART-4-SEARCHING-IN-LIST-10-320.jpg)

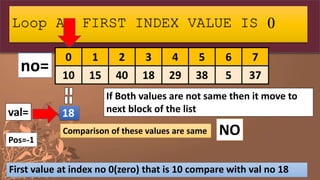
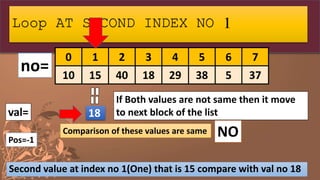
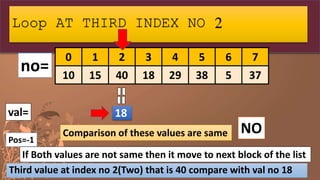



![no=[10,15,40,18,29,38,5,37]
Step 1: Declare the list and initialize it with some
values
0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7
10 15 40 18 29 38 5 37
no=](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/listpart4-200716140818/85/LIST-IN-PYTHON-PART-4-SEARCHING-IN-LIST-19-320.jpg)
![no=[10,15,40,18,29,38,5,37]
0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7
10 15 40 18 29 38 5 37
no=
pos=-1 Step 2: Declare one variable to store the position with -1
and value of pos. will overwrite when number found in
the list.
Pos=-1](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/listpart4-200716140818/85/LIST-IN-PYTHON-PART-4-SEARCHING-IN-LIST-20-320.jpg)
![no=[10,15,40,18,29,38,5,37]
0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7
10 15 40 18 29 38 5 37
no=
pos=-1
val=int(input(“Enter the value”))
Step 3: Accept the value to be searched from the user and
store in a variable.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/listpart4-200716140818/85/LIST-IN-PYTHON-PART-4-SEARCHING-IN-LIST-21-320.jpg)
![no=[10,15,40,18,29,38,5,37]
0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7
10 15 40 18 29 38 5 37
no=
pos=-1
val=int(input(“Enter the value”))
k=len(no)
for x in range(0,k):
Step 4: Start the loop from starting index to the last index
no](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/listpart4-200716140818/85/LIST-IN-PYTHON-PART-4-SEARCHING-IN-LIST-22-320.jpg)
![no=[10,15,40,18,29,38,5,37]
0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7
10 15 40 18 29 38 5 37
no=
pos=-1
val=int(input(“Enter the value”))
k=len(no)
for x in range(0,k):
Step 5: Compare the search no with
the list of no.’s one by one using index
no.
if no[x]==val:
pos=x
break](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/listpart4-200716140818/85/LIST-IN-PYTHON-PART-4-SEARCHING-IN-LIST-23-320.jpg)
![no=[10,15,40,18,29,38,5,37]
0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7
10 15 40 18 29 38 5 37
no=
pos=-1
val=int(input(“Enter the value”))
k=len(no)
for x in range(0,k):
if no[x]==val:
pos=x
break
Step 6: if no. found pos store
the index number and loop
will stop there only and if pos
is negative it means number
not found and if positive then
number found
if pos<0:
print(“No. not found”)
else:
print(“No found at pos=“,pos+1)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/listpart4-200716140818/85/LIST-IN-PYTHON-PART-4-SEARCHING-IN-LIST-24-320.jpg)
![For loop with range:
no=[10,15,40,18,29,38,5,37]
pos=-1
val=int(input(“Enter the value”))
k=len(no)
for x in range(0,k):
if no[x]==val:
pos=x
break
if pos<0:
print(“No. not found”)
else:
print(“No found at pos=“,pos+1
While loop:
no=[10,15,40,18,29,38,5,37]
pos=-1
val=int(input(“Enter the value”))
k=len(no)
x=0
while x<k:
if no[x]==val:
pos=x
break
if pos<0:
print(“No. not found”)
else:
print(“No found at pos=“,pos+1
Step 1 We declare the list of numbers in a variable no](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/listpart4-200716140818/85/LIST-IN-PYTHON-PART-4-SEARCHING-IN-LIST-25-320.jpg)
![For loop with range:
no=[10,15,40,18,29,38,5,37]
pos=-1
val=int(input(“Enter the value”))
k=len(no)
for x in range(0,k):
if no[x]==val:
pos=x
break
if pos<0:
print(“No. not found”)
else:
print(“No found at pos=“,pos+1
While loop:
no=[10,15,40,18,29,38,5,37]
pos=-1
val=int(input(“Enter the value”))
k=len(no)
x=0
while x<k:
if no[x]==val:
pos=x
break
if pos<0:
print(“No. not found”)
else:
print(“No found at pos=“,pos+1
Step 2 we set the pos to negative value, if number not found it remains -1
means number not exists in a list](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/listpart4-200716140818/85/LIST-IN-PYTHON-PART-4-SEARCHING-IN-LIST-26-320.jpg)
![For loop with range:
no=[10,15,40,18,29,38,5,37]
pos=-1
val=int(input(“Enter the value”))
k=len(no)
for x in range(0,k):
if no[x]==val:
pos=x
break
if pos<0:
print(“No. not found”)
else:
print(“No found at pos=“,pos+1
While loop:
no=[10,15,40,18,29,38,5,37]
pos=-1
val=int(input(“Enter the value”))
k=len(no)
x=0
while x<k:
if no[x]==val:
pos=x
break
if pos<0:
print(“No. not found”)
else:
print(“No found at pos=“,pos+1
Next step is to accept the value in a variable val from user to be searched in a
list](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/listpart4-200716140818/85/LIST-IN-PYTHON-PART-4-SEARCHING-IN-LIST-27-320.jpg)
![For loop with range:
no=[10,15,40,18,29,38,5,37]
pos=-1
val=int(input(“Enter the value”))
k=len(no)
for x in range(0,k):
if no[x]==val:
pos=x
break
if pos<0:
print(“No. not found”)
else:
print(“No found at pos=“,pos+1
While loop:
no=[10,15,40,18,29,38,5,37]
pos=-1
val=int(input(“Enter the value”))
k=len(no)
x=0
while x<k:
if no[x]==val:
pos=x
break
if pos<0:
print(“No. not found”)
else:
print(“No found at pos=“,pos+1
Next find the length of list no and store it inside the variable k.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/listpart4-200716140818/85/LIST-IN-PYTHON-PART-4-SEARCHING-IN-LIST-28-320.jpg)
![For loop with range:
no=[10,15,40,18,29,38,5,37]
pos=-1
val=int(input(“Enter the value”))
k=len(no)
for x in range(0,k):
if no[x]==val:
pos=x
break
if pos<0:
print(“No. not found”)
else:
print(“No found at pos=“,pos+1
While loop:
no=[10,15,40,18,29,38,5,37]
pos=-1
val=int(input(“Enter the value”))
k=len(no)
x=0
while x<k:
if no[x]==val:
pos=x
break
if pos<0:
print(“No. not found”)
else:
print(“No found at pos=“,pos+1
Next start the loop that starts from 0 to k means last number.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/listpart4-200716140818/85/LIST-IN-PYTHON-PART-4-SEARCHING-IN-LIST-29-320.jpg)
![For loop with range:
no=[10,15,40,18,29,38,5,37]
pos=-1
val=int(input(“Enter the value”))
k=len(no)
for x in range(0,k):
if no[x]==val:
pos=x
break
if pos<0:
print(“No. not found”)
else:
print(“No found at pos=“,pos+1
While loop:
no=[10,15,40,18,29,38,5,37]
pos=-1
val=int(input(“Enter the value”))
k=len(no)
x=0
while x<k:
if no[x]==val:
pos=x
break
if pos<0:
print(“No. not found”)
else:
print(“No found at pos=“,pos+1
Next check the number exists or not using if condition,if yes then loop stop and
pos will store the index number as position.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/listpart4-200716140818/85/LIST-IN-PYTHON-PART-4-SEARCHING-IN-LIST-30-320.jpg)
![For loop with range:
no=[10,15,40,18,29,38,5,37]
pos=-1
val=int(input(“Enter the value”))
k=len(no)
for x in range(0,k):
if no[x]==val:
pos=x
break
if pos<0:
print(“No. not found”)
else:
print(“No found at pos=“,pos+1)
While loop:
no=[10,15,40,18,29,38,5,37]
pos=-1
val=int(input(“Enter the value”))
k=len(no)
x=0
while x<k:
if no[x]==val:
pos=x
break
if pos<0:
print(“No. not found”)
else:
print(“No found at pos=“,pos+1)
At last if the pos is still negative it means search number does not exist in a list
and if pos is positive, it means number exists in a list](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/listpart4-200716140818/85/LIST-IN-PYTHON-PART-4-SEARCHING-IN-LIST-31-320.jpg)