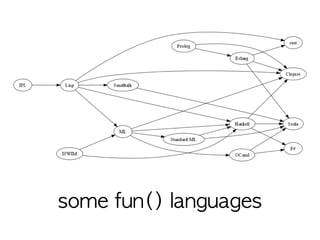
The document outlines the evolution of various high-level programming languages, such as Fortran and Lisp, focusing on aspects like recursion, garbage collection, and type systems. It discusses several languages, including OCaml, Scala, and Haskell, detailing features like lazy evaluation, object-oriented components, and compatibility with JVM. Additionally, it mentions their applications in fields like research, natural language processing, and highlights developments supported by grants from companies like IBM and Sun.









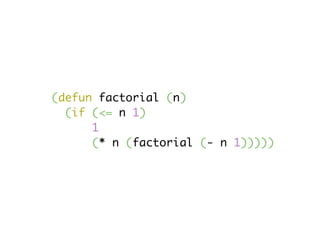

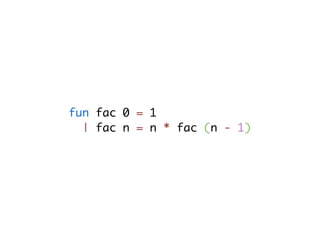


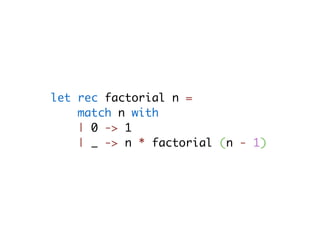



![-- type
factorial :: Integer -> Integer
-- using recursion
factorial 0 = 1
factorial n = n * factorial (n - 1)
-- using lists
factorial n = product [1..n]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/linuxconffptalk-110125223414-phpapp01/85/Linuxconf-2011-parallel-languages-talk-20-320.jpg)



![(def factorial
(fn [n]
(loop [cnt n acc 1]
(if (zero? cnt)
acc
(recur (dec cnt) (* acc cnt))))))](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/linuxconffptalk-110125223414-phpapp01/85/Linuxconf-2011-parallel-languages-talk-24-320.jpg)








![| count factorial |
count := 0.
factorial := 1.
[ count > 0 ] whileTrue:
[ factorial := factorial *
(count := count - 1) ]
Transcript show: factorial](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/linuxconffptalk-110125223414-phpapp01/85/Linuxconf-2011-parallel-languages-talk-33-320.jpg)





