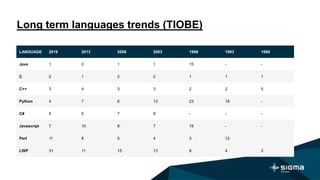
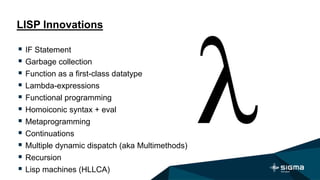
Nikolay Mozgovoy is a developer, mentor, and teacher who has worked with Sigma Software since 2013. He is also a prizewinner and organizer for Global Game Jam Ukraine. This document discusses the history and innovations of the Lisp programming language, which was created in 1960. It highlights Lisp's features like recursion, functions as first-class citizens, homoiconic syntax, and metaprogramming abilities. The primary Lisp dialects today are Scheme, Common Lisp, and Clojure.







![Original LISP Syntax
S-Expressions (for “symbolic expression”): ( · ) + an infinite set of atomic symbols:
AB
(A · B)
((AB · C) · D)
(A·((B ·(C · NIL)) ·(D · NIL)))
M-Expressions:
car[x]
car[cons[(A · B);x]]
cons (“construct”)
car (“contents of address register”)
cdr (“contents of decrement register”)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lisp-180524125023/85/LISP-9-320.jpg)
![LISP VS Fortran/Algol ancestor
var animals = new[] { "dog", "cat", "rat" };
void PrintAnimals()
{
foreach (var animal in animals)
{
Console.WriteLine(animal);
}
}
PrintAnimals();
#lang racket
(define animals (list "dog" "cat" "rat"))
(define (print-animals x) (map print animals))
(print-animals)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lisp-180524125023/85/LISP-10-320.jpg)
![Metaprogramming
(defn pow2 [x] (* x x))
(defn inc [x] (+ x 1))
(def strategy (read-string "[pow2 inc inc]")) ; user input
(def input (read-string "12")) ; user input
((apply comp (eval strategy)) input) ; 196](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lisp-180524125023/85/LISP-13-320.jpg)
![Metaprogramming (2)
(defn drive-to-home [] "driving to home")
(defn drive-to-work [] "driving to work")
(defn drive-to-garage [] "driving to garage")
(defn recharge [] "recharging")
(defn get-driving-program []
`(drive-to-home drive-to-work recharge drive-to-garage))
(map #(println (%))
(map eval (get-driving-program)))](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lisp-180524125023/85/LISP-14-320.jpg)

![Macros: creating missing constructs
;while macros application
(define x 10)
(while (> x 0) do
(displayln x)
(set! x (- x 1)))
; prints 10, 9, 8 , 7, 6, 5, 4, 3, 2, 1
;while macros definition
(define-syntax while
(syntax-rules (do)
[(while cond do body ...)
(let loop ()
(when cond body ...
(loop)))]))](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lisp-180524125023/85/LISP-16-320.jpg)


![Macros: getting rid of parentheses (t-expressions)
#lang sweet-exp typed/racket
define: factorial([n : Integer]) : Integer
if {n <= 1}
1
{n * factorial{n - 1}}
factorial 5 ;- : Integer 120
#lang sweet-exp racket
define factorial(n)
if {n <= 1}
1
{n * factorial{n - 1}}
factorial 5 ;120](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lisp-180524125023/85/LISP-19-320.jpg)