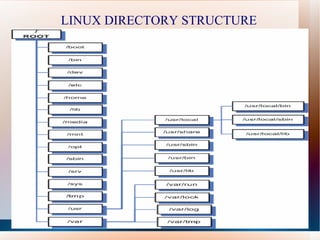
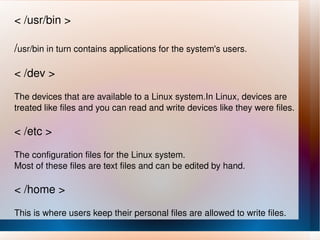
Linux was created by Linus Torvalds in 1991 and is an open-source operating system that is freely available. It has features like virtual memory, networking capabilities, security protections, and a graphical user interface. Reasons to use Linux include that it is free, runs on various hardware, is stable, and has available source code. Common Linux commands are used to view system information, manage files and directories, and perform other tasks. The root directory contains subdirectories for essential system components, user files, programs, and more.