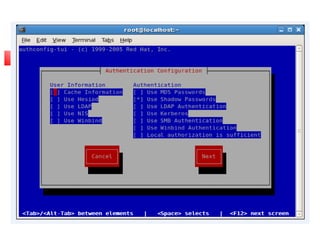
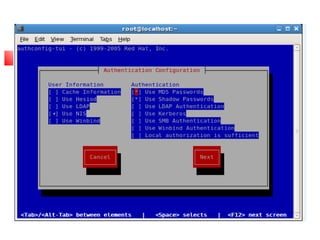
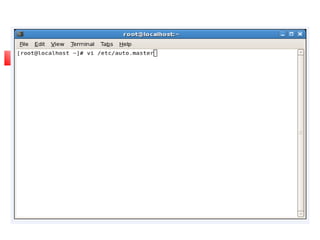
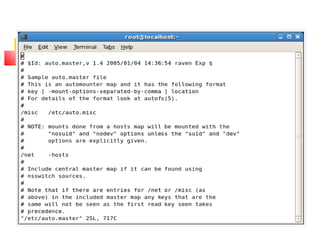
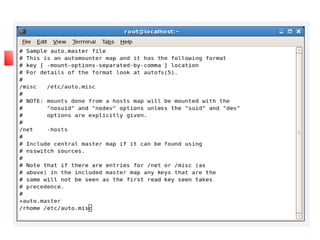
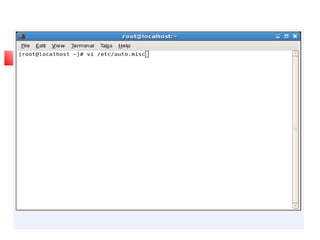
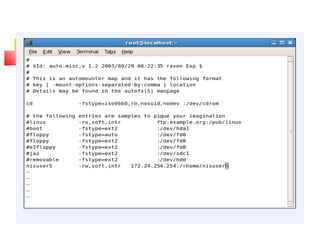
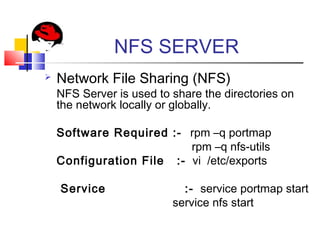
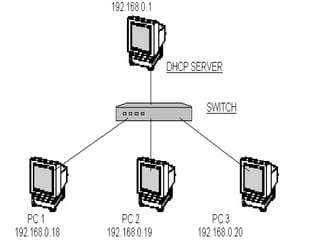
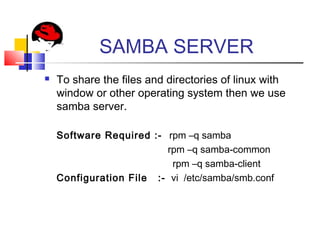
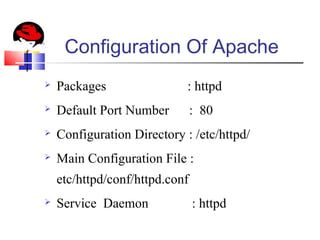
This document provides an overview of a seminar presented on Red Hat Linux and NIS servers. It discusses key topics like the history and features of Linux, an overview of the Linux kernel and file system, Linux shells, users and permissions, RAID and LVM concepts, and configurations for common Linux server types including NIS, NFS, DNS, DHCP, FTP, SSH, Telnet, SMTP, Samba, and Apache web servers. Screenshots are also included to demonstrate aspects of the configurations.