The document provides an introduction to linked lists, including:
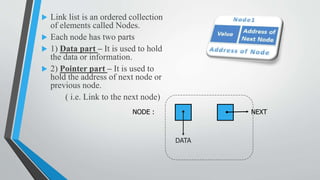
- Linked lists are dynamic data structures composed of nodes that contain data and a pointer to the next node. This allows for flexible sizes and easier insertion/deletion compared to arrays.
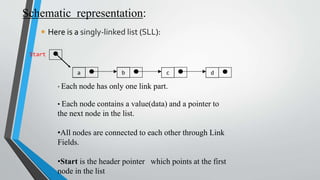
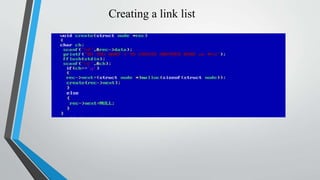
- A singly linked list is outlined, where each node contains the data and a pointer to the next node, but not the previous. Basic operations like creation, display, and insertion/deletion at various positions in the list are described.
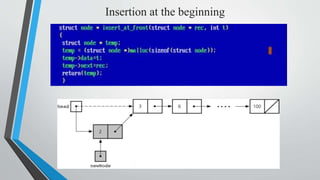
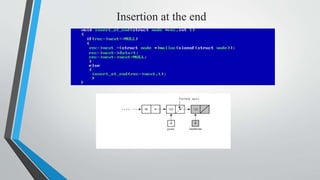
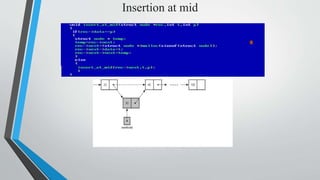
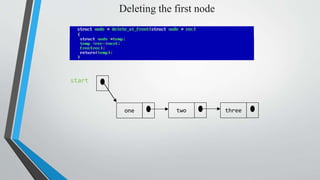
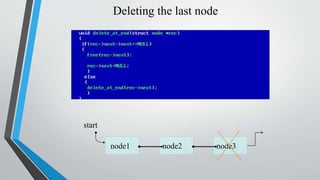
- Examples of inserting and deleting nodes from the beginning, middle, and end of a singly linked list are illustrated through diagrams.