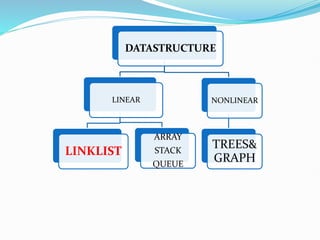
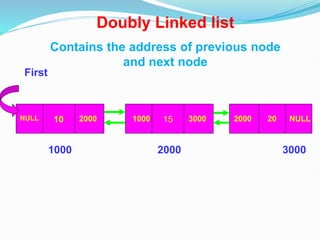
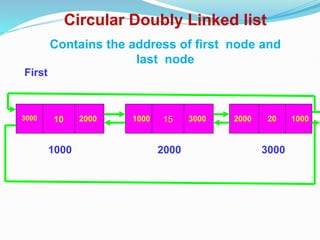
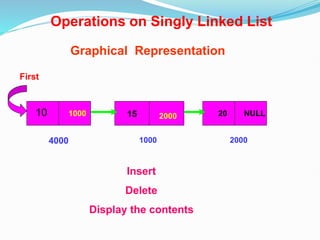
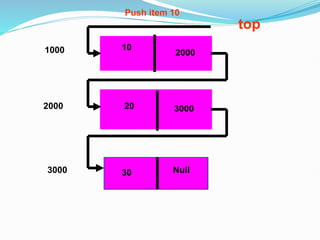
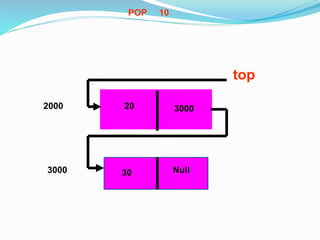
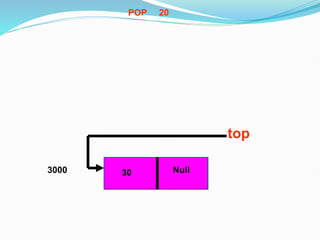
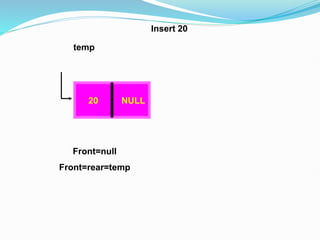
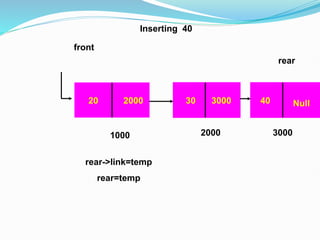
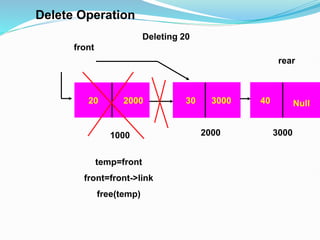
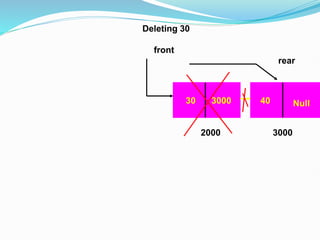
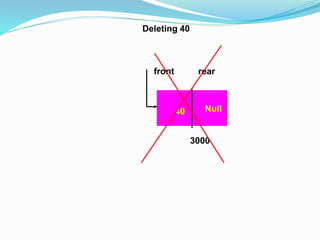
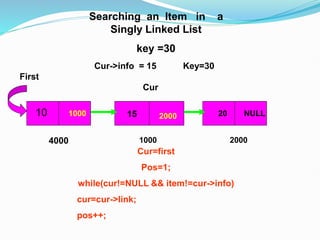
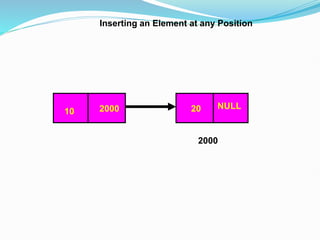
Data structures organize data in a way that allows for efficient storage, retrieval, searching, and manipulation. Linked lists are a non-linear data structure that store data in nodes that point to the next node in the list. They allow for simple and fast insertion and deletion of nodes at different positions. A linked list contains nodes with a data field and a pointer/address field. There are different types of linked lists including singly linked, doubly linked, circular linked lists.









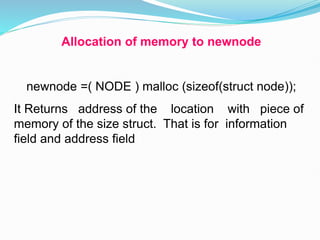
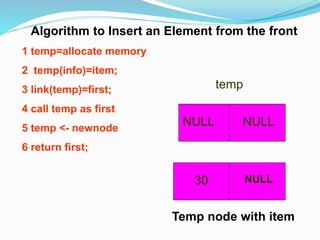
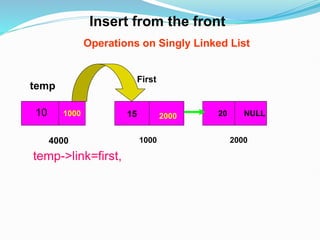










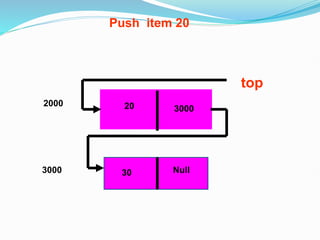


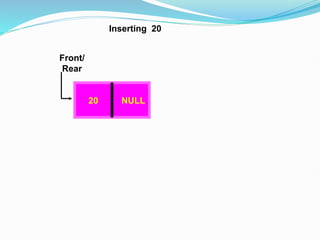
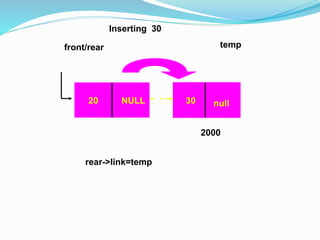
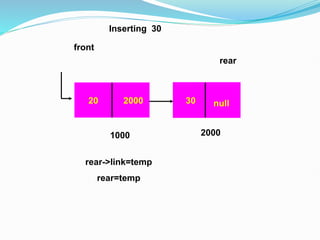
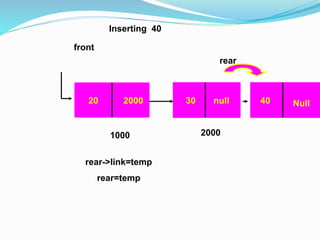





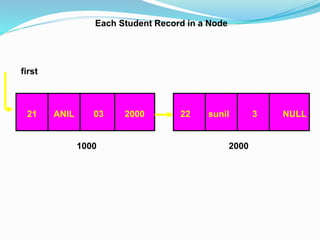
![Representation of the Record using Linked List
struct student
{
int id;
char name[20];
int sem;
struct student link;
};
typedef struct student *NODE;](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/dokumen-231210090341-39c86097/85/dokumen-tips_linked-list-ppt-5584a44be6115-pptx-50-320.jpg)
