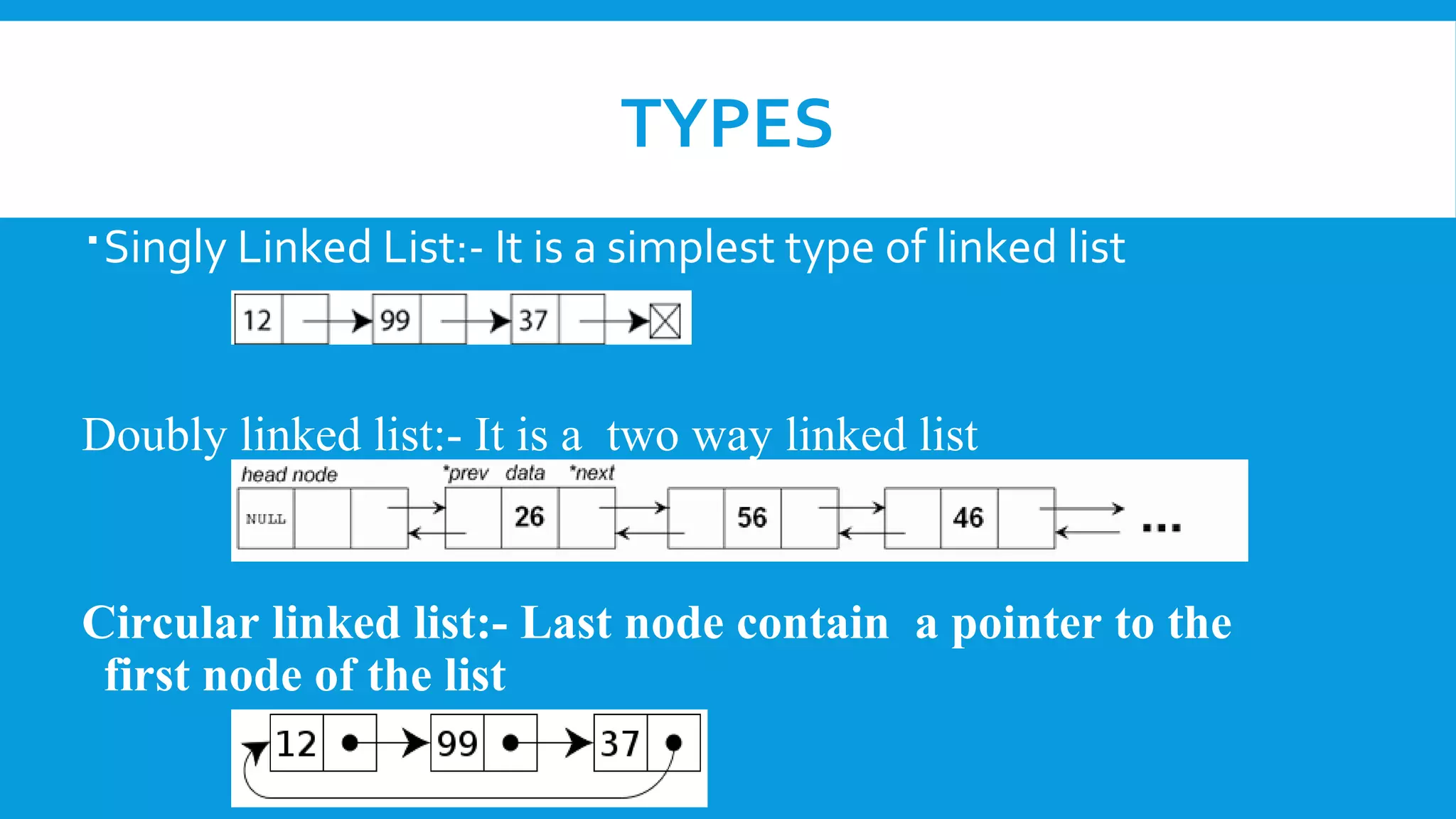
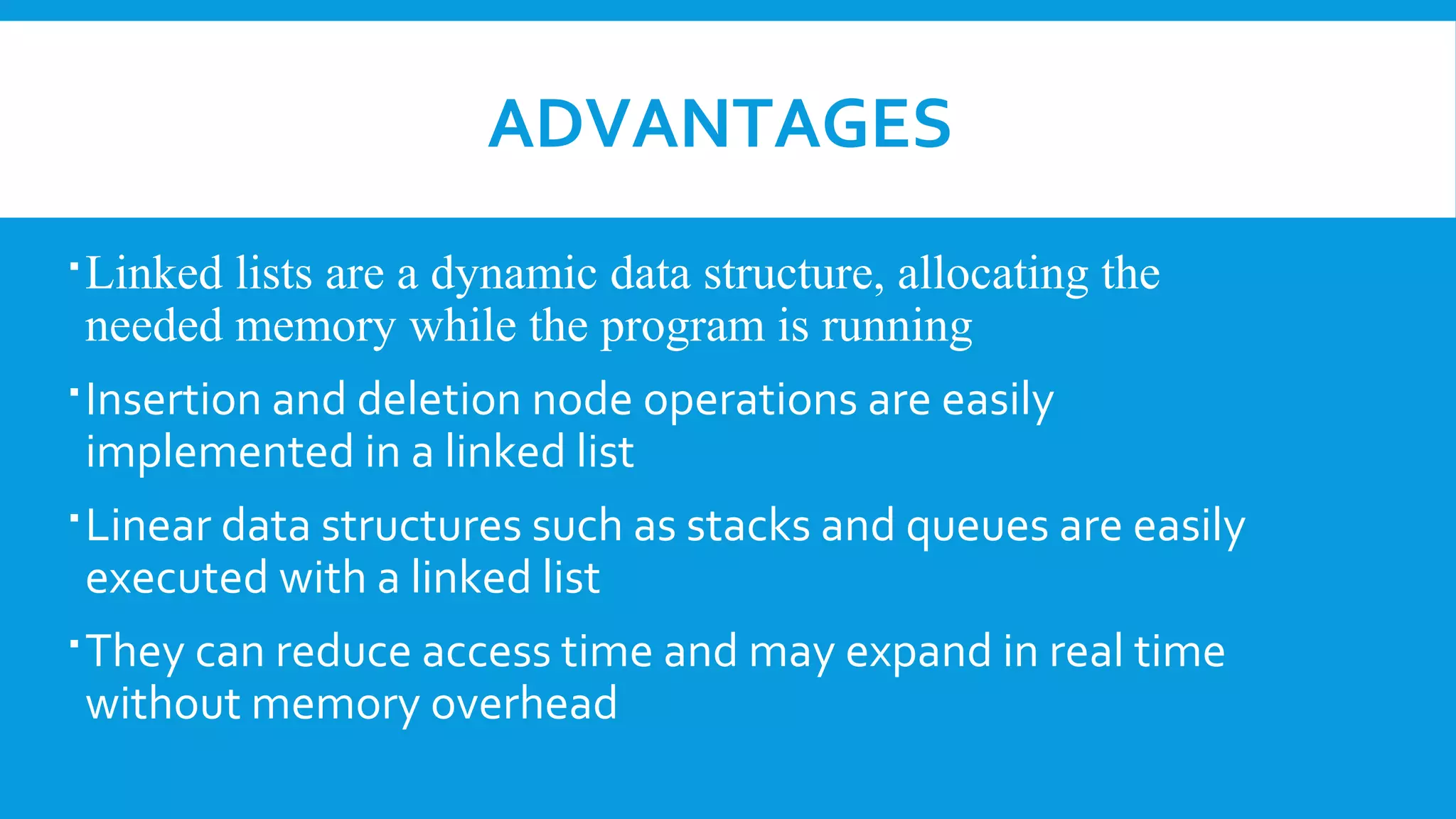
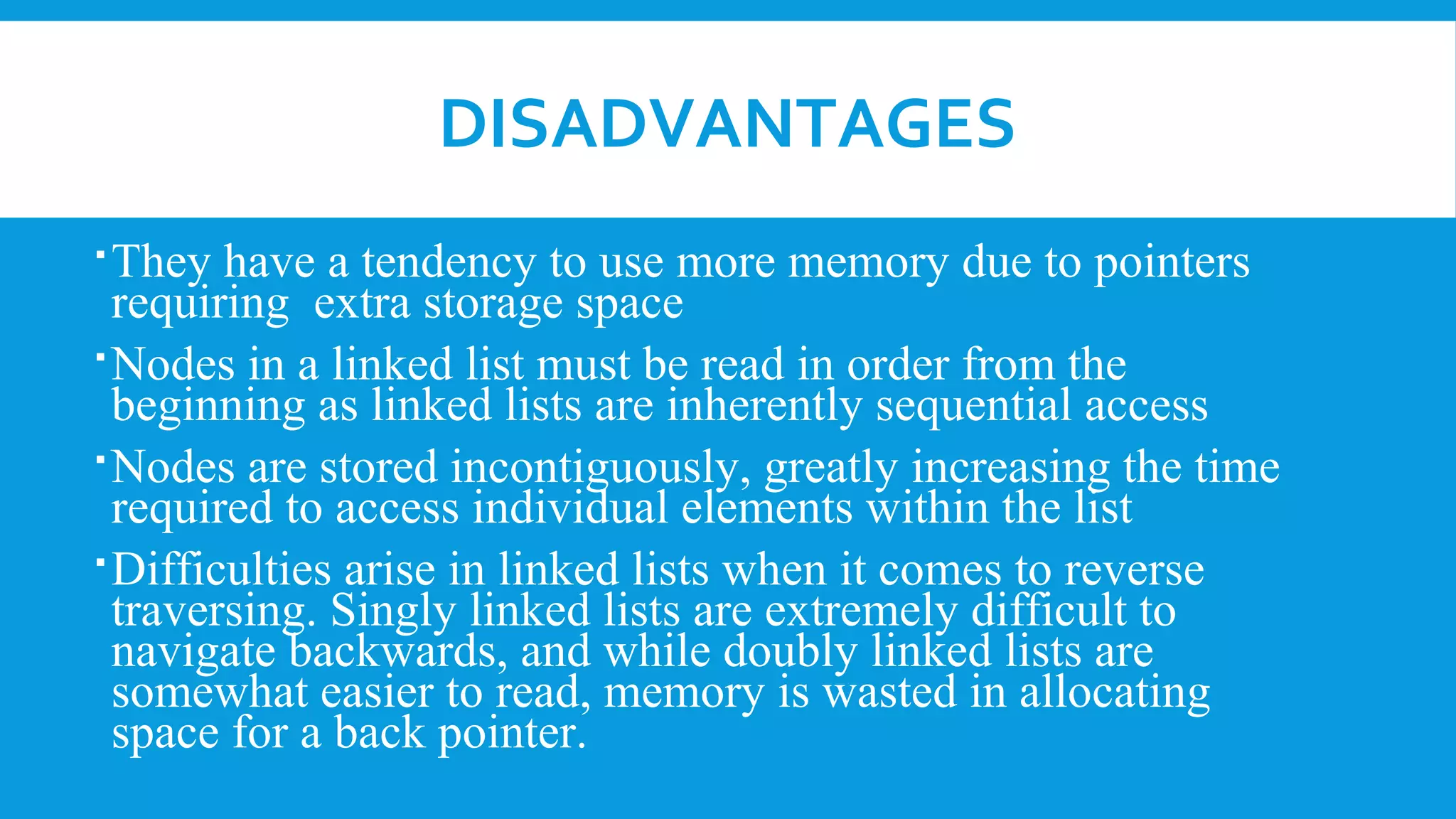
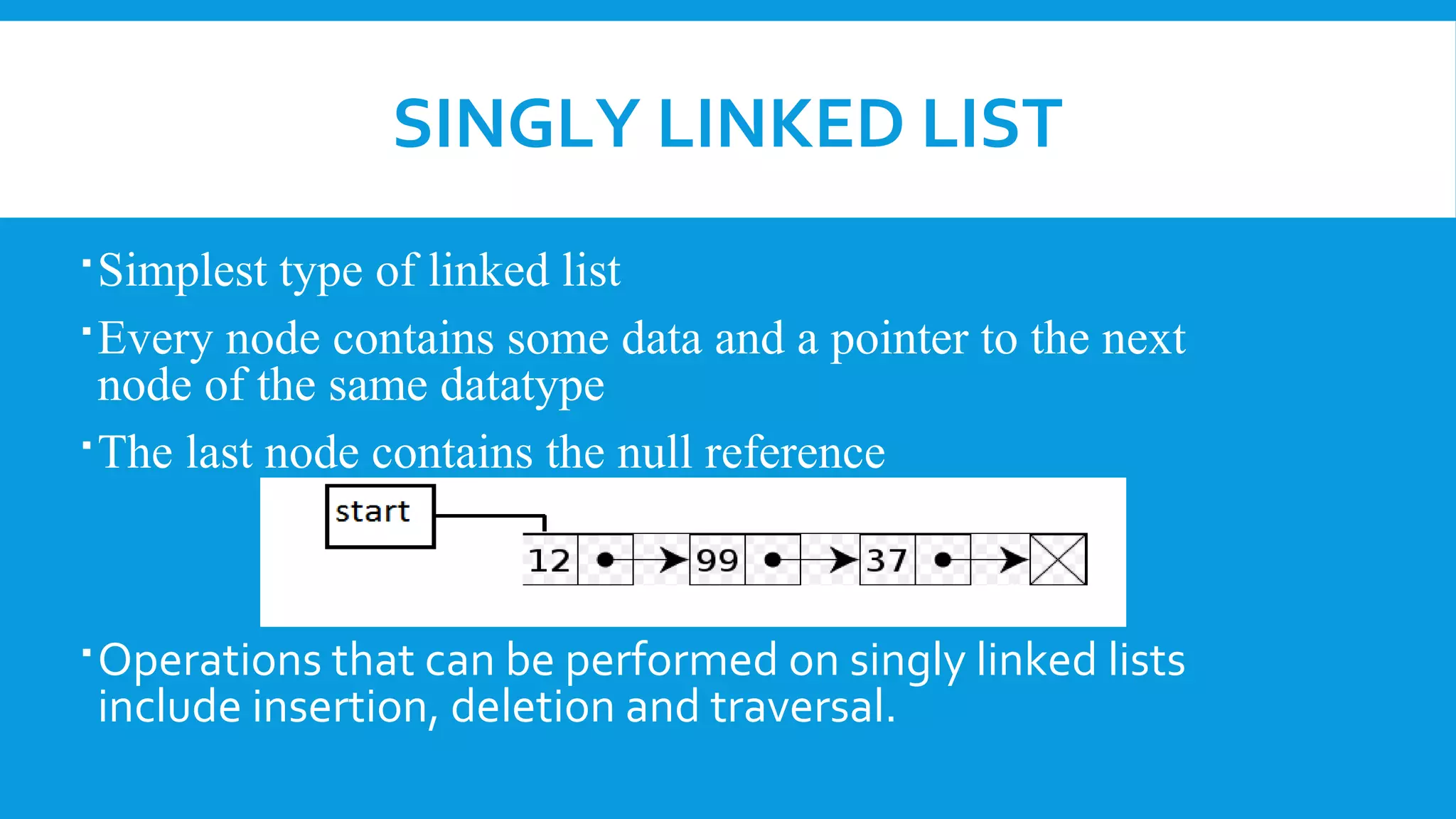
A linked list is a linear collection of nodes containing data and pointers to the next node, developed in the 1950s for information processing. There are three types: singly linked lists (one-direction), doubly linked lists (bi-direction), and circular linked lists (where the last node points back to the first). While linked lists allow dynamic memory allocation and easy insertion/deletion, they can use more memory and require sequential access, making reverse traversal difficult.



![ALGORITHM OF SINGLY LINKED LIST
If avail:=null then write :-” overflow and exit”.
Else new:=avail.
Avail:=link[avail].
Set info[new]:=data.
Set link[new]:=start.
Start :=new.
Exit.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/linkedlist-170708003214/75/Linked-list-8-2048.jpg)
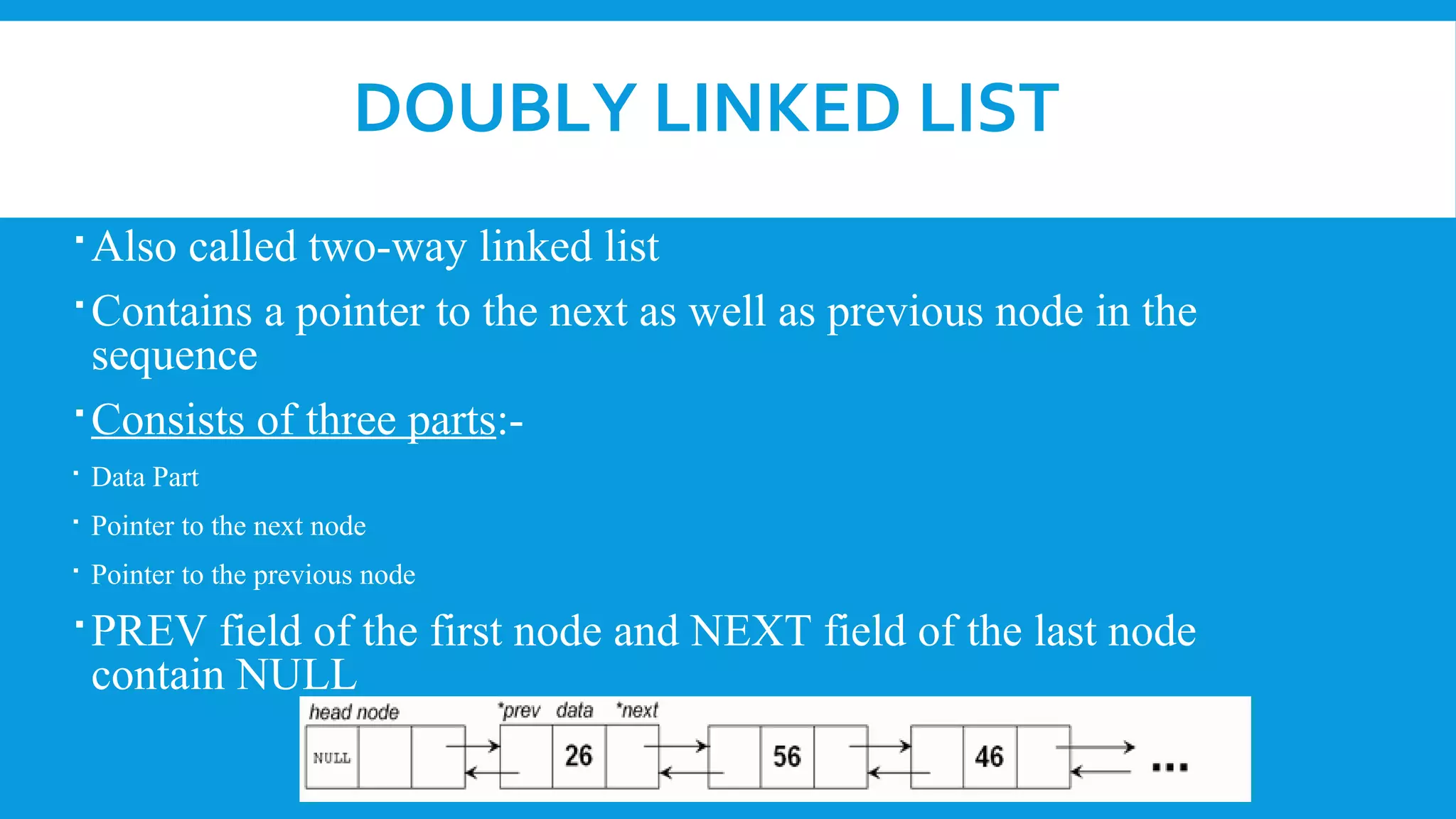
![ALGORITHM OF DOUBLY LINKED LIST
If avail:=NULL then write:”overflow and exit”
Else new:=avail.
Avail:=link[avail].
Set prev[new]:=NULL.
Set info[new]:=data
Set link[new]:=start.
Set prev[start]:=new.
Start :=new
Exit](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/linkedlist-170708003214/75/Linked-list-10-2048.jpg)

![ALGORITHM CIRCULAR LINKED LIST
If avail =NULL then write :”overflow and exit”
Else new:=avail
Avail :=Link[avail].
Set info[new]:=value.
Set ptr:=start.
Repeat step 6 while link[ptr]=!=start.
Ptr:=link[ptr].
(end of loop).](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/linkedlist-170708003214/75/Linked-list-12-2048.jpg)
![Link[new]:=start.
Link[ptr]:=new.
Start:=new
Exit](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/linkedlist-170708003214/75/Linked-list-13-2048.jpg)
