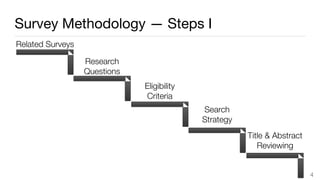
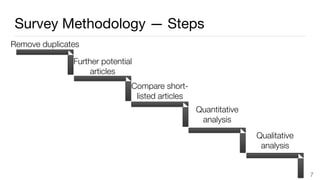
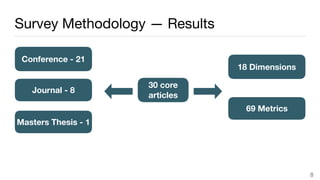
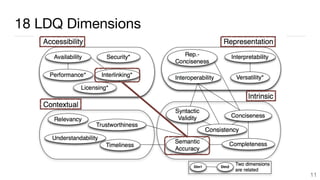
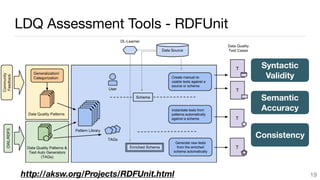
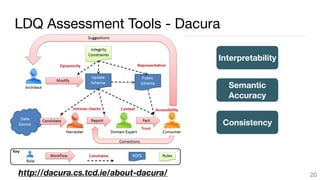
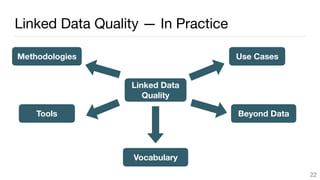
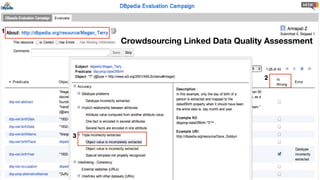
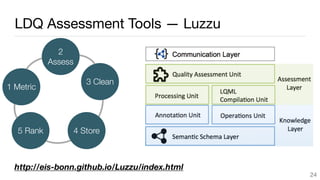
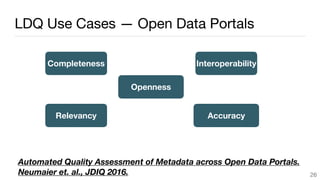
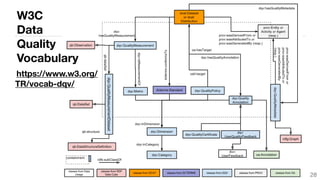
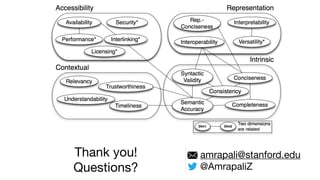
This document summarizes a survey of approaches for assessing the quality of linked data. It outlines the survey methodology, identifies 18 common dimensions of linked data quality (such as availability, interpretability, and timeliness) and 69 associated metrics. It also describes several existing tools for linked data quality assessment, such as RDFUnit, Dacura, Luzzu, and LODLaundromat. Finally, it discusses real-world use cases of linked data quality assessment in domains like open data portals and mapping quality, and outlines challenges in the area.