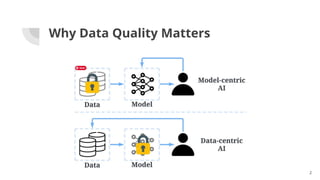
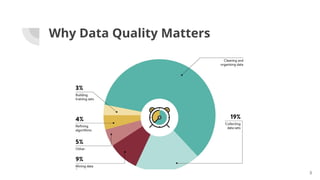
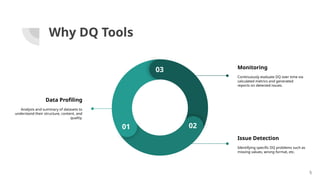
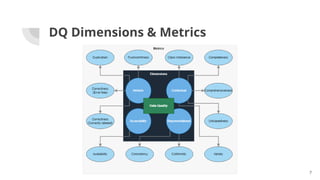
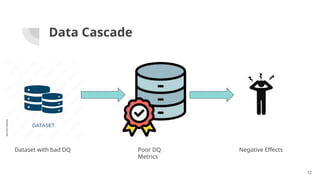
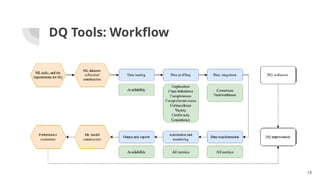
The document discusses the importance of data quality (DQ) in machine learning, detailing the dimensions and metrics used to assess it, including intrinsic, contextual, representational, and accessibility aspects. It highlights challenges in maintaining DQ metrics due to rapid ML developments and the lack of standardization, while also reviewing various DQ tools and their capabilities. The conclusion emphasizes the critical nature of DQ for successful ML projects and suggests improvements in AI integration, automation, and usability for existing tools.