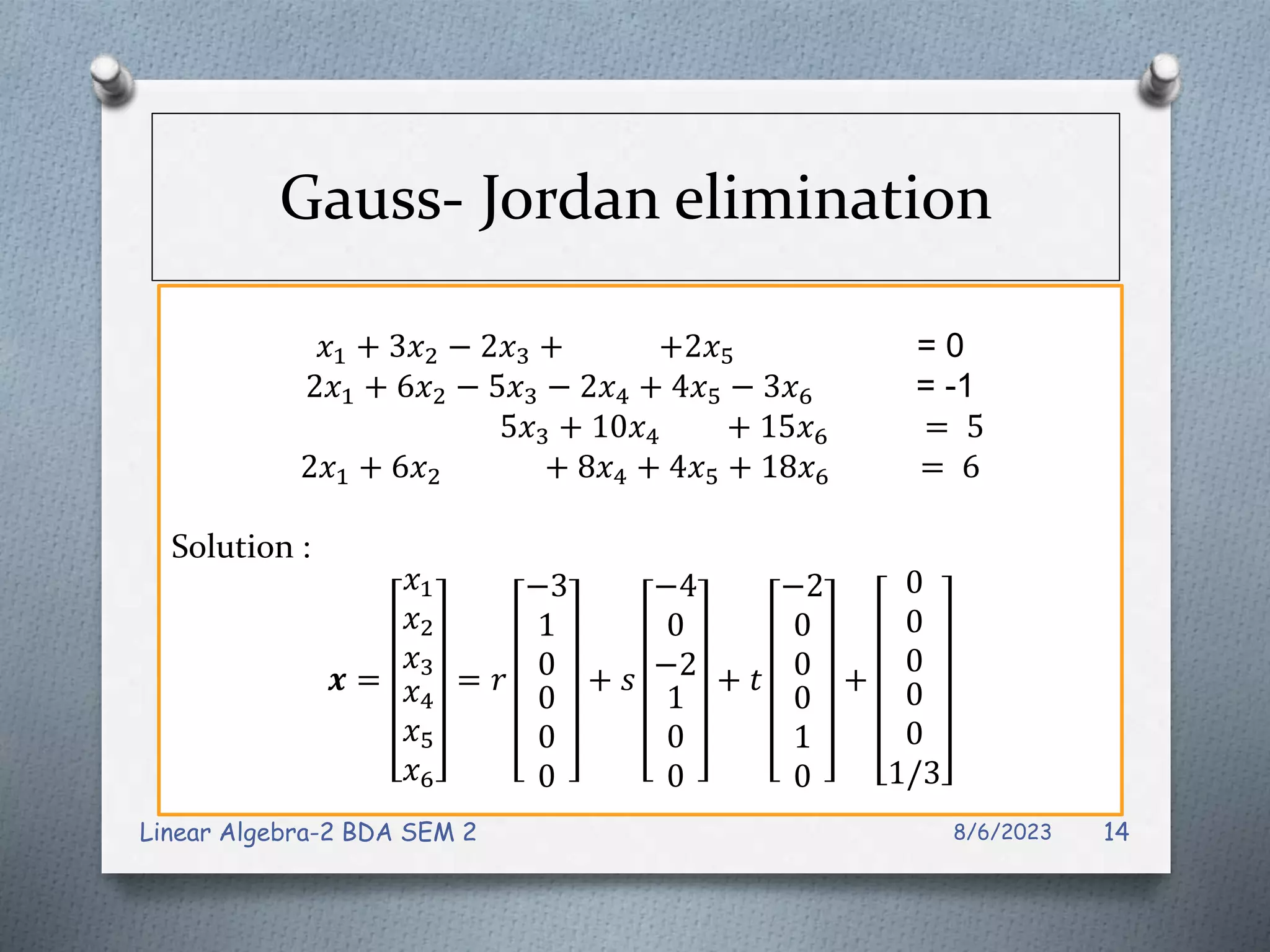
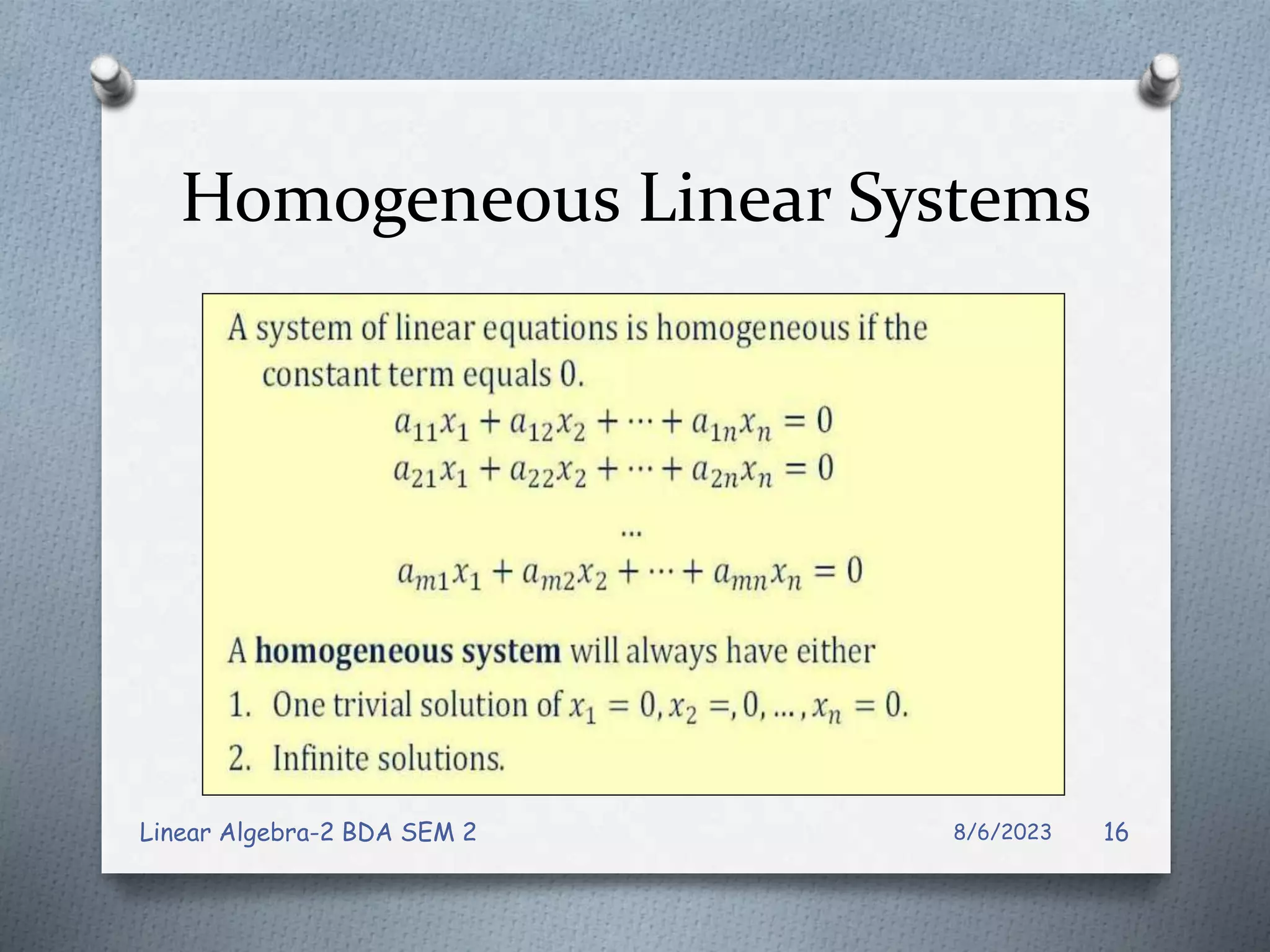
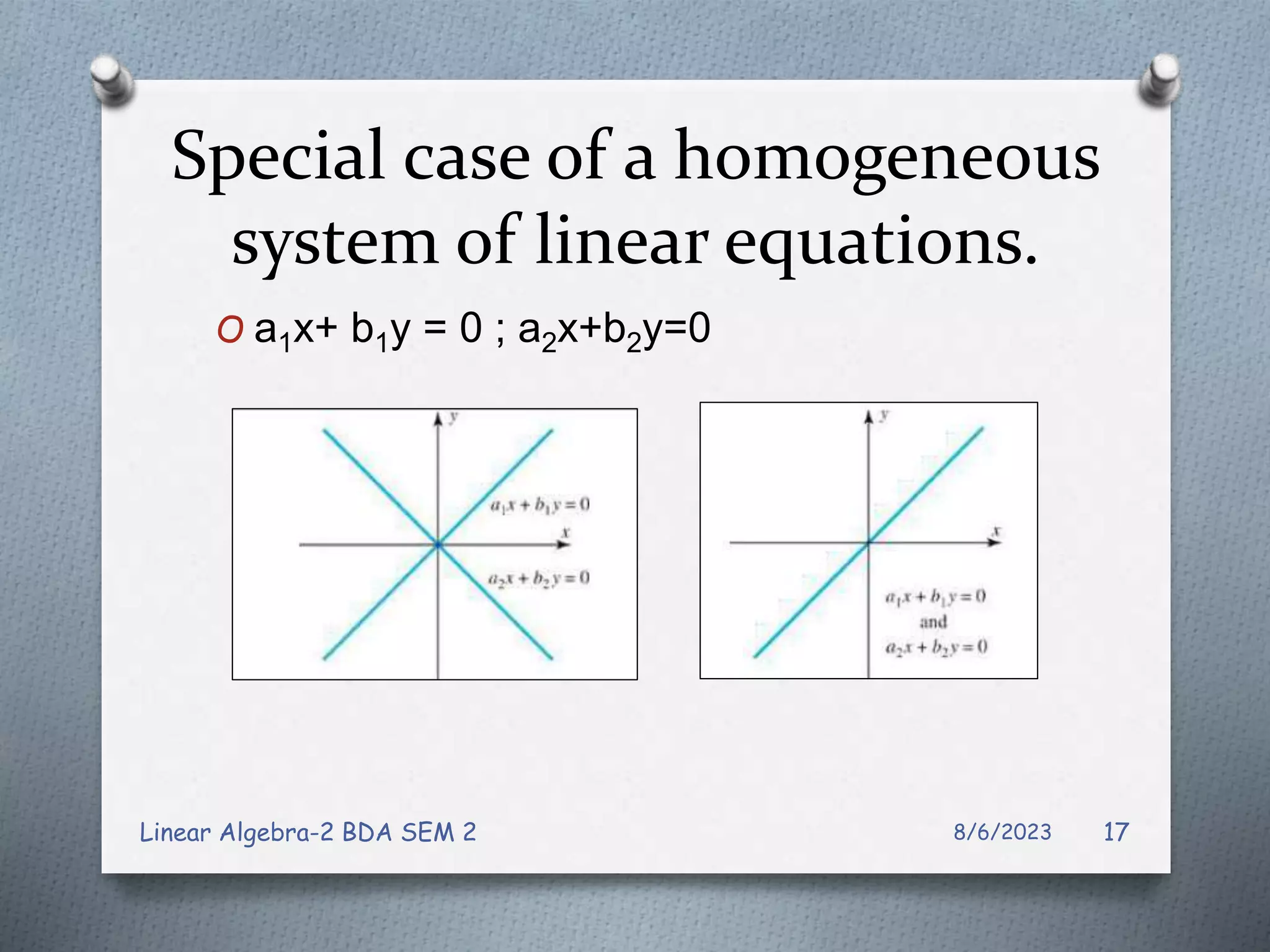
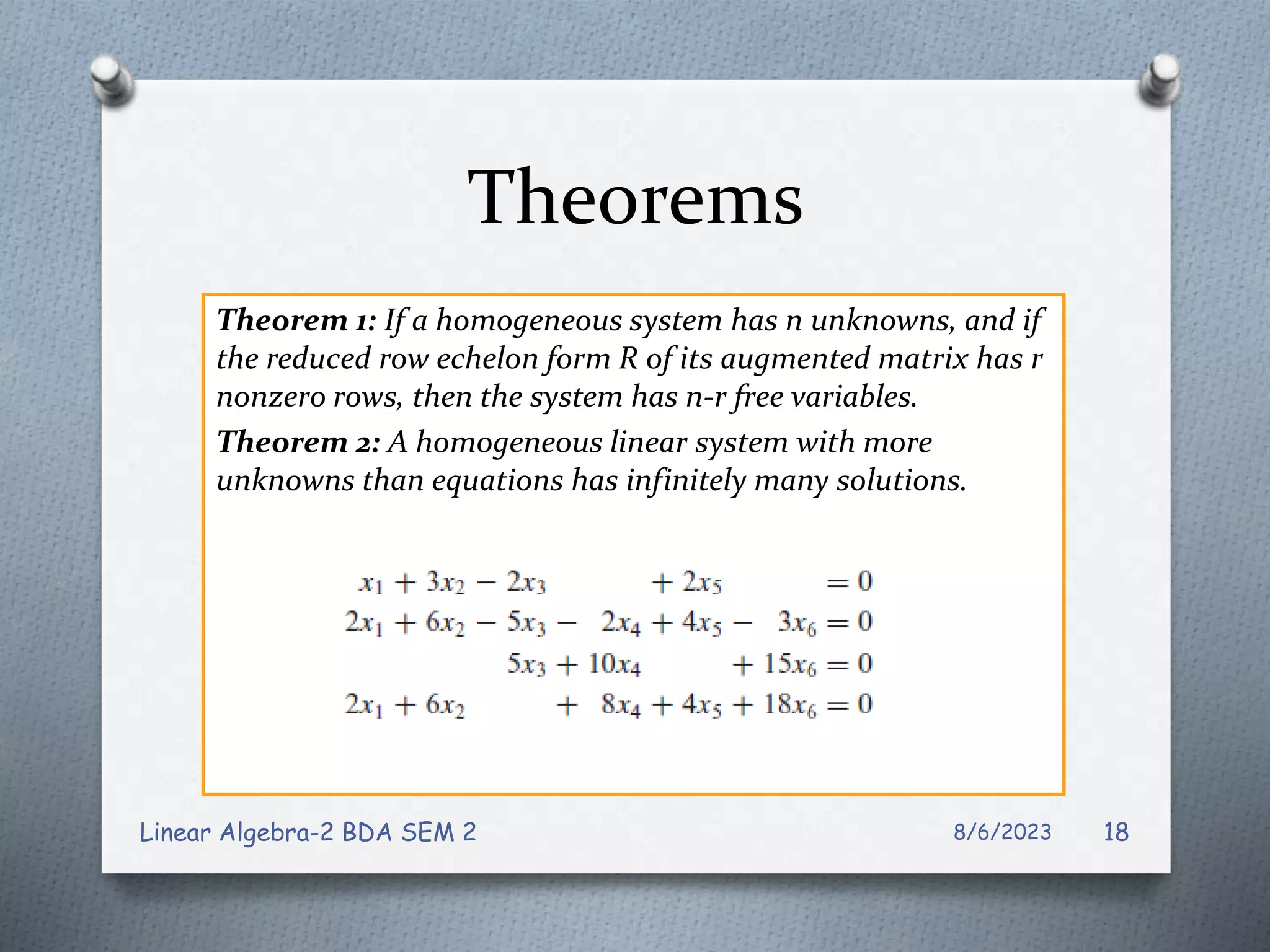
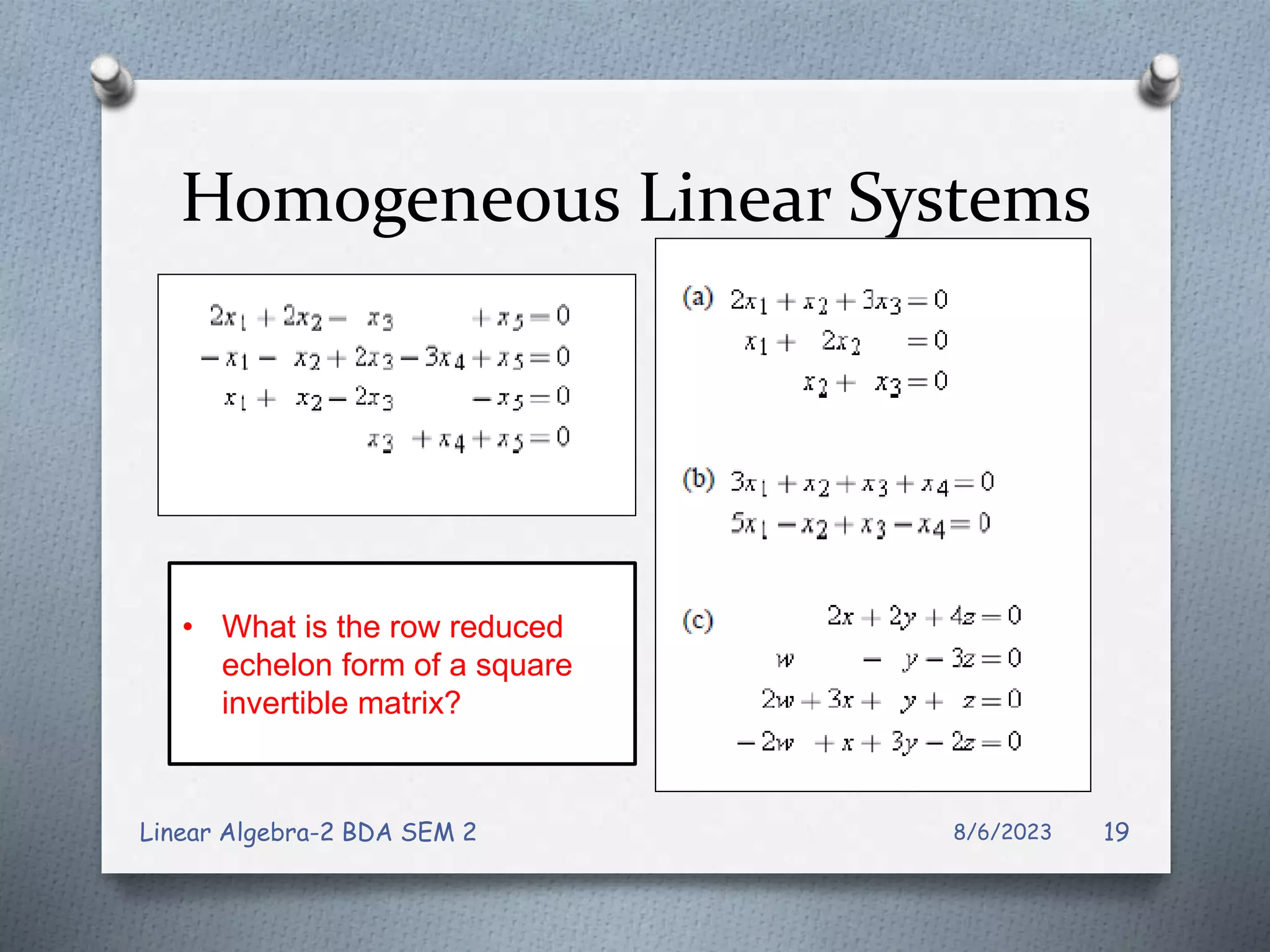
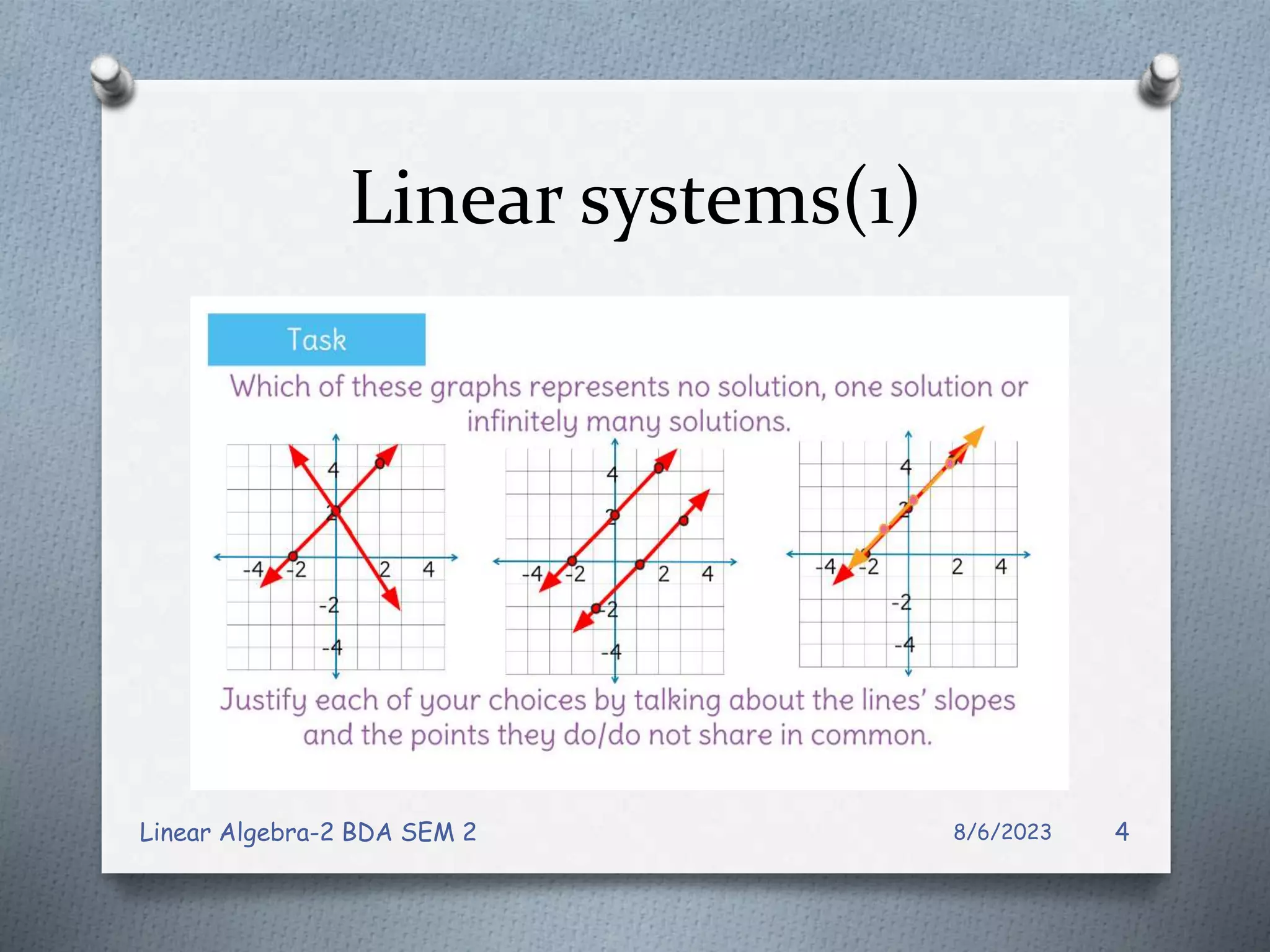
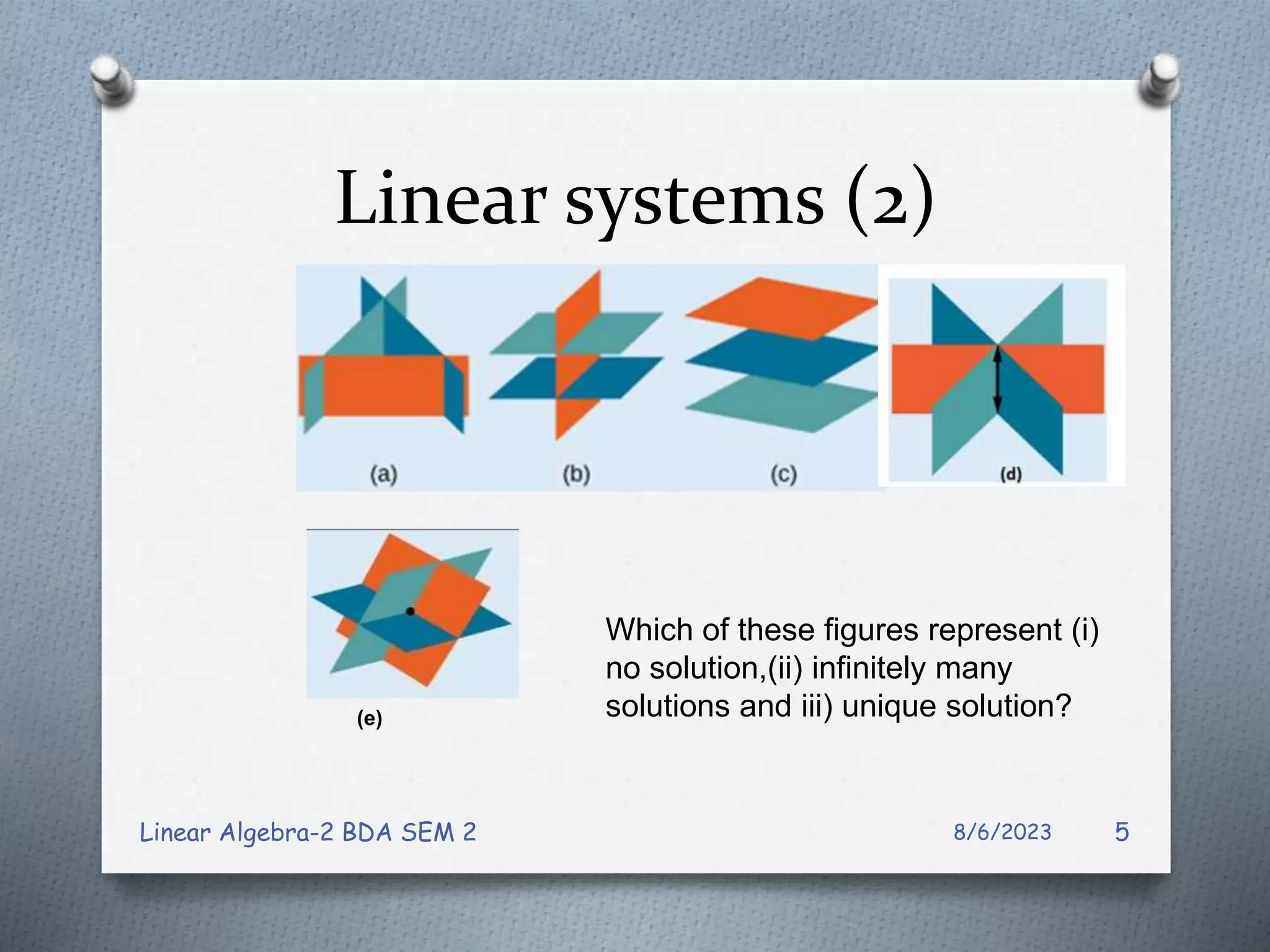
This document contains notes from a Linear Algebra class covering systems of linear equations and matrices. Key topics discussed include linear systems, the matrix representation of linear systems using augmented matrices, Gaussian elimination to solve systems, elementary row operations, echelon forms, homogeneous systems, and issues with numerical stability in solving systems. Examples are provided to illustrate Gaussian elimination, Gauss-Jordan elimination, and determining the solution set of homogeneous systems from the reduced row echelon form.



![Augmented matrix
8/6/2023
Linear Algebra-2 BDA SEM 2 7
2x1+3x2=4
7x1+6x2=9
A=
2 3
7 6
b=
4
9
Augmented matrix
[A b]
𝐴 𝑏 =
2 3 4
7 6 9
Write the augmented
matrix :
x - y + z =9
y – x = 8
2x + z = 10](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/linearalgebra1-230806132454-afe62ac4/75/Linear-Algebra-1-pptx-6-2048.jpg)

![Gaussian elimination
Step 4:Forward elimination:
[A b] =
3 1 9
1 1 8
→
3 1 9
0
2
3
5 R2-(1/3)R1
3𝑥 + 𝑦 = 9 → (𝑒𝑞. 1) Ax=b Ux=c
0𝑥 +
2
3
𝑦 = 5 → (𝑒𝑞. 2)
Step 5: Backward substitution:
Solving the equation(2) we get, 𝑦 = 7.5.Substituting in (1), we get
3𝑥 + 7.5 = 9
3𝑥 = 9 − 7.5
𝑥 = 0.5
Hence,(0.5,7.5) is the solution of the system of linear equations in
x and y.
8/6/2023
Linear Algebra-2 BDA SEM 2 9](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/linearalgebra1-230806132454-afe62ac4/75/Linear-Algebra-1-pptx-8-2048.jpg)



![Elementary row operations
𝑥 + 𝑦 + 2𝑧 = 9 𝐴 𝑏 =
1 1 2
2 4 −3
3 6 −5
9
1
0
=
1 1 2
0 2 −7
0 3 −11
9
−17
−27
=
1 1 2
0 2 −7
0 0 −1/2
9
−17
−3/2
2𝑥 + 4𝑦 − 3𝑧 = 1
3𝑥 + 6𝑦 − 5𝑧 = 0 R3=R3-(3/2)R2 [U c]
Row echelon form:
1 1 2
0 1
−7
2
0 0
−1
6
9
−17
2
−1
2
-----------Gaussian elimination -1/2 z= -3/2 ; z=3
2y-7z=-17; 2y-21=-17 ;2y=4, y=2
Reduced row echelon form R:
1 0 0
0 1 0
0 0 1
1
2
3
-----Gauss-Jordan elimination
𝒙 = 𝟏; 𝒚 = 𝟐; 𝒛 = 𝟑
Gaussian elimination: In this procedure, there is a forward phase in which zeros are introduced below the leading
1’s.
Gauss-Jordan elimination: This algorithm has two phases; a forward phase in which zeros are introduced below
the leading 1’s and a backward phase in which zeros are introduced above the leading 1’s.
8/6/2023
Linear Algebra-2 BDA SEM 2 13](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/linearalgebra1-230806132454-afe62ac4/75/Linear-Algebra-1-pptx-12-2048.jpg)