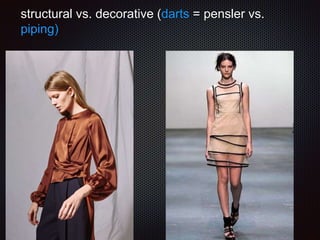
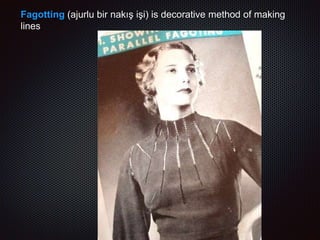
This document discusses elements of fashion design, specifically focusing on line as both a structural and decorative design method. It begins by defining dress and how meaning is created through visual and sensory codes. It then discusses key aspects of the design process like problem identification, research, ideation, and presentation. The document also covers different categories of line including straight, curved, vertical, horizontal, diagonal, curvilinear, and kinetic. It provides examples of how different types of lines can be used structurally in elements like pleats, gathers, and folds. The document concludes by discussing how line direction can influence mood and how designers have historically incorporated different line techniques.