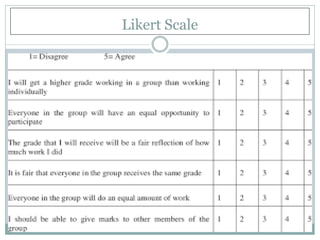
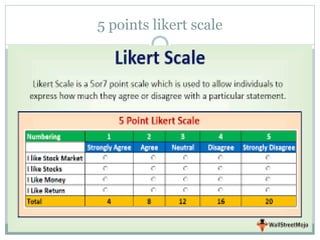
The Likert scale is a psychometric scale used in questionnaires to measure respondents' attitudes or reactions to statements. It was developed by psychologist Rensis Likert in the 1930s. A Likert scale typically has 5 or 7 points ranging from "strongly disagree" to "strongly agree." It is one of the most widely used scale formats in survey research for gauging attitudes, opinions, and perceptions. Some advantages include ease of use, quick collection of feedback, and ability to make market predictions. However, disadvantages include possibility of lying, misunderstanding questions, inability to determine emotions, and potential faking of results.