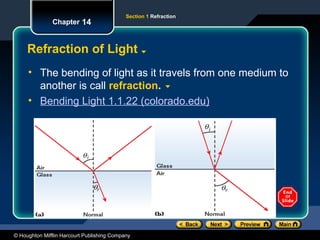
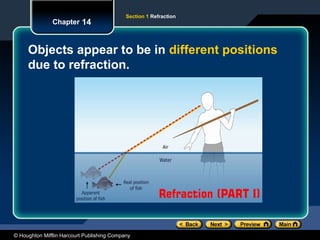
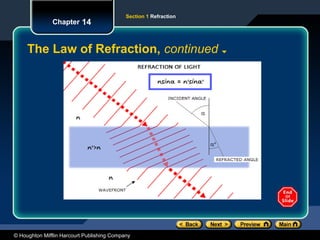
The document discusses the concept of refraction, which is the bending of light as it moves between different media. It outlines the law of refraction, including Snell's law, and explains how the index of refraction determines the angle at which light bends. Sample problems are provided to illustrate the calculation of refraction angles and indices.