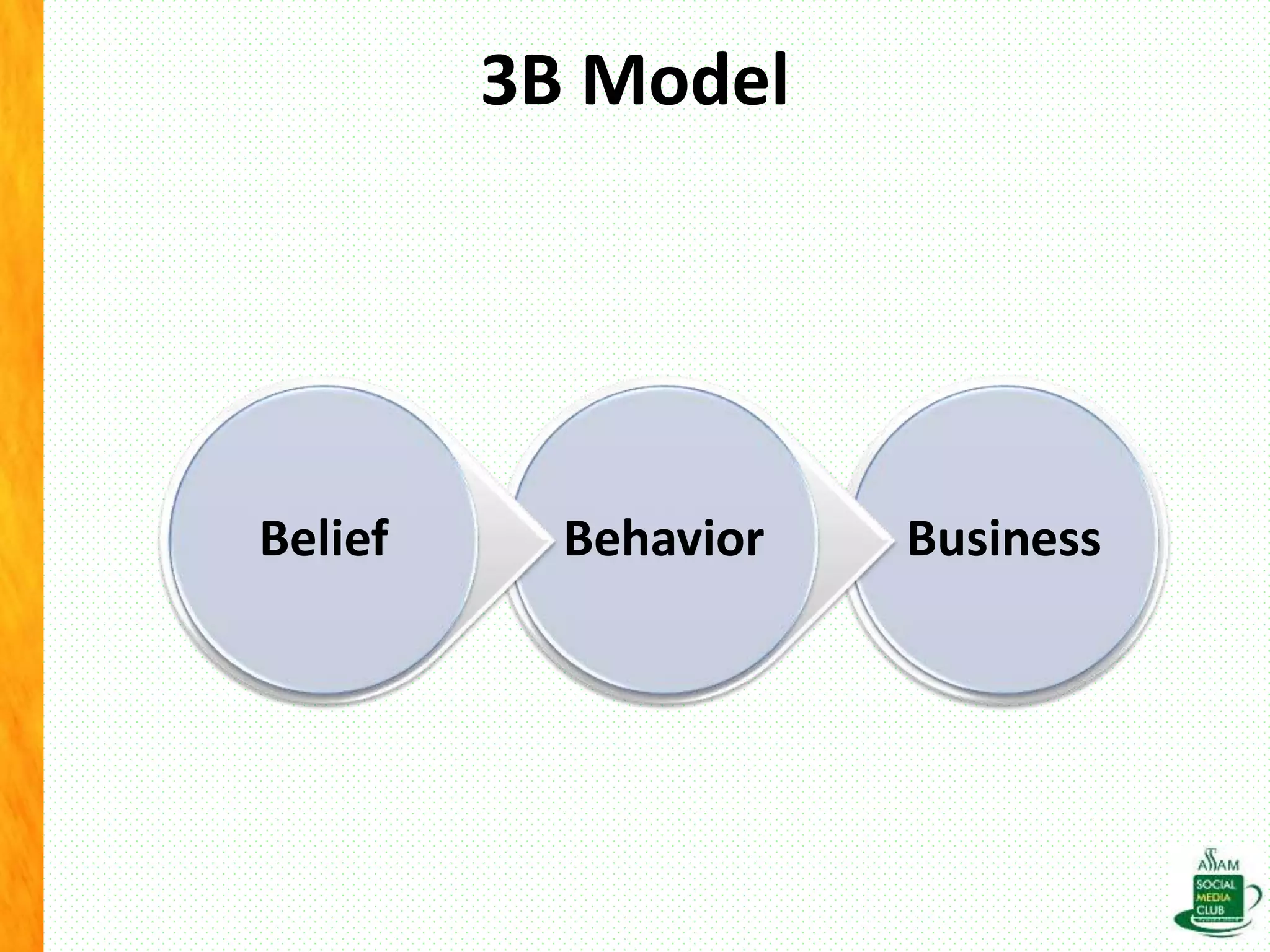
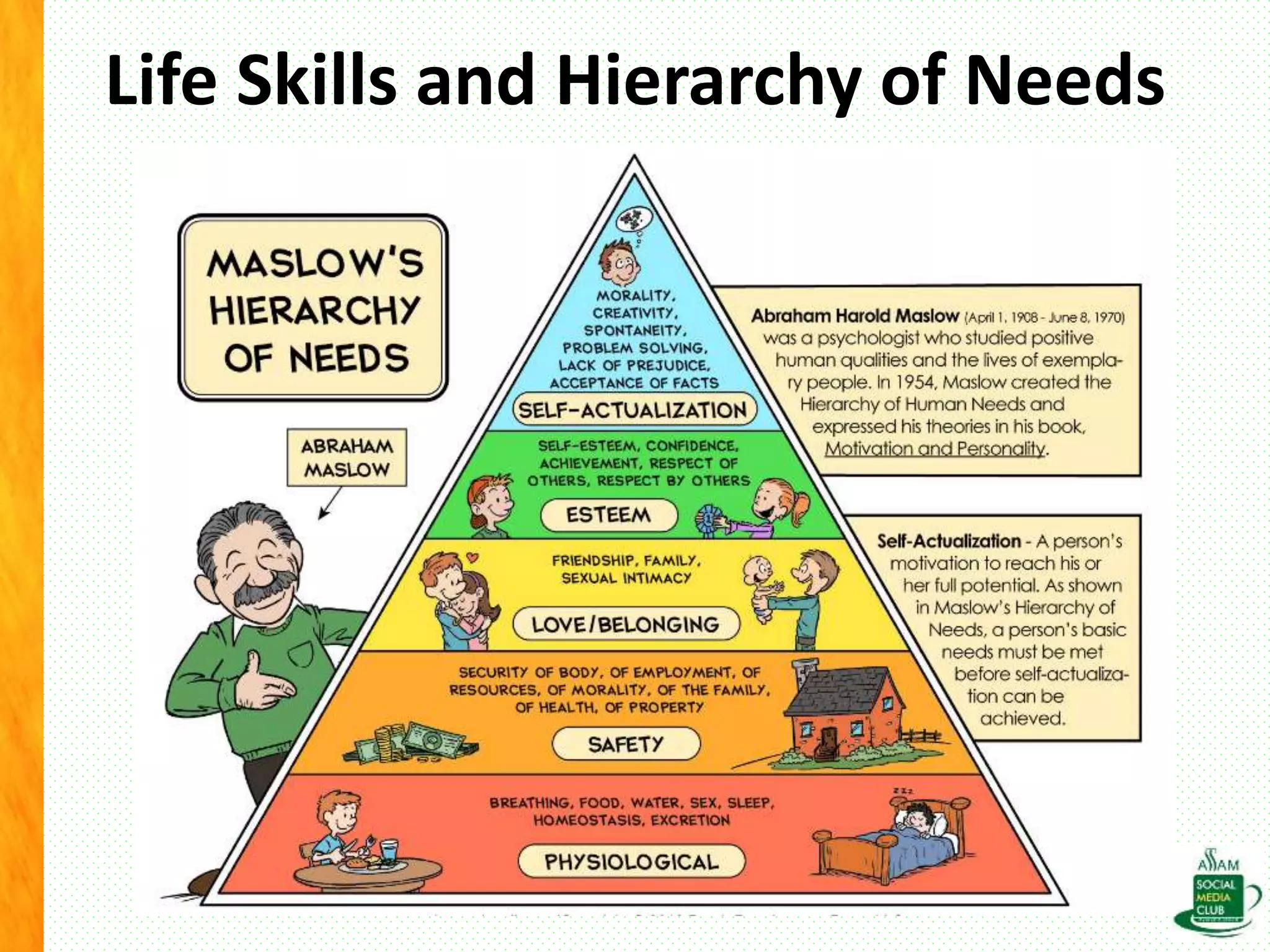
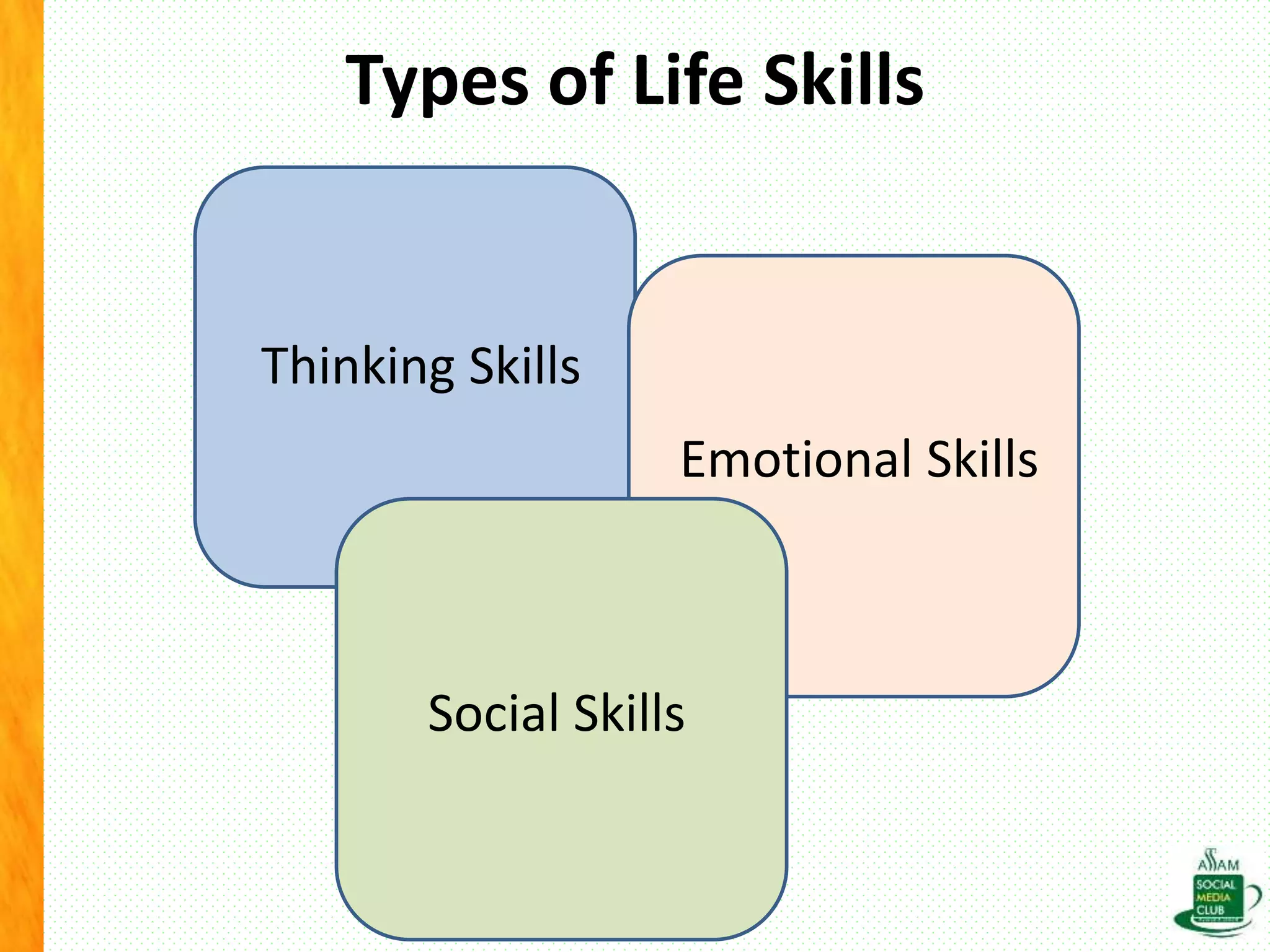
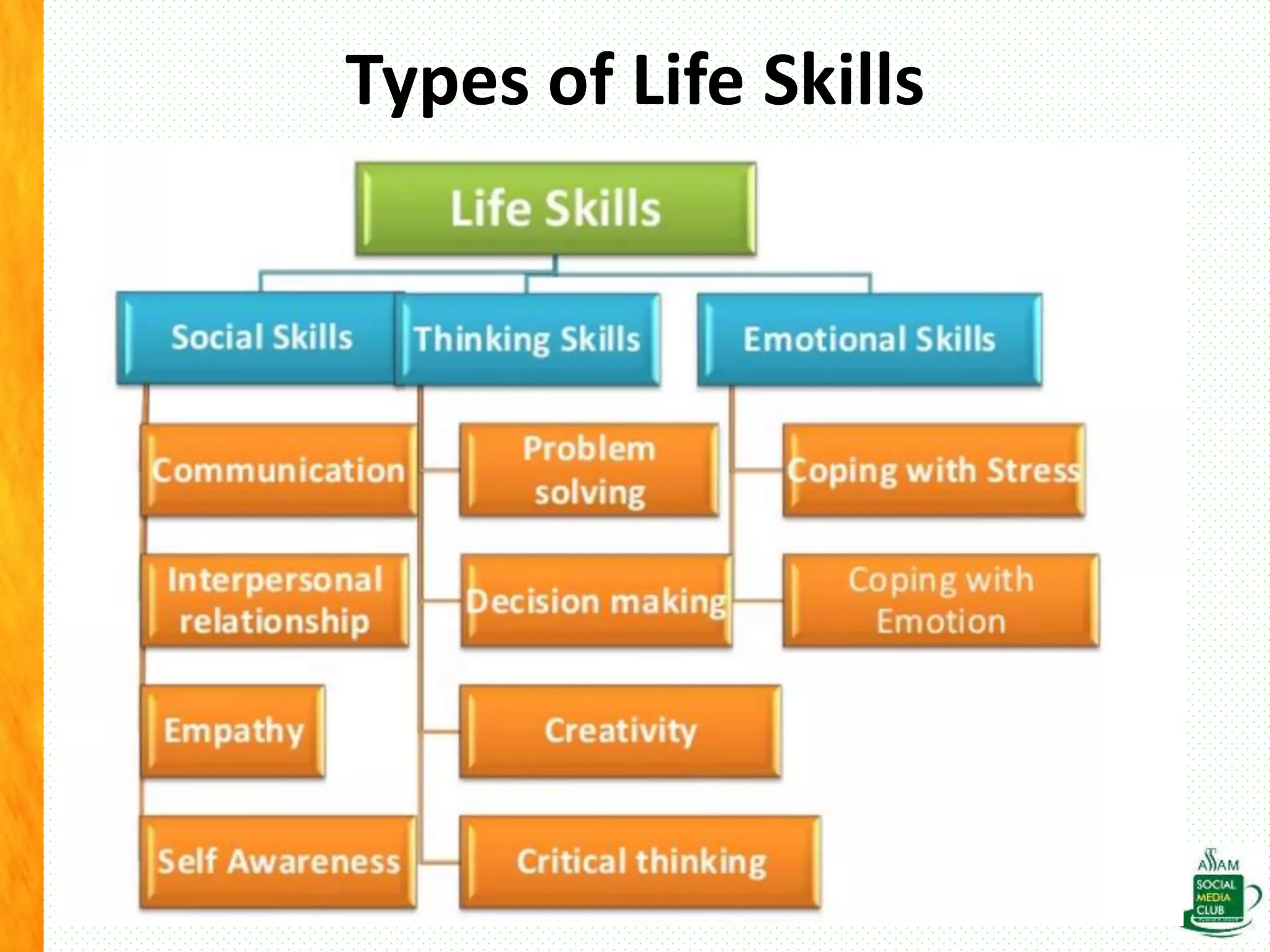
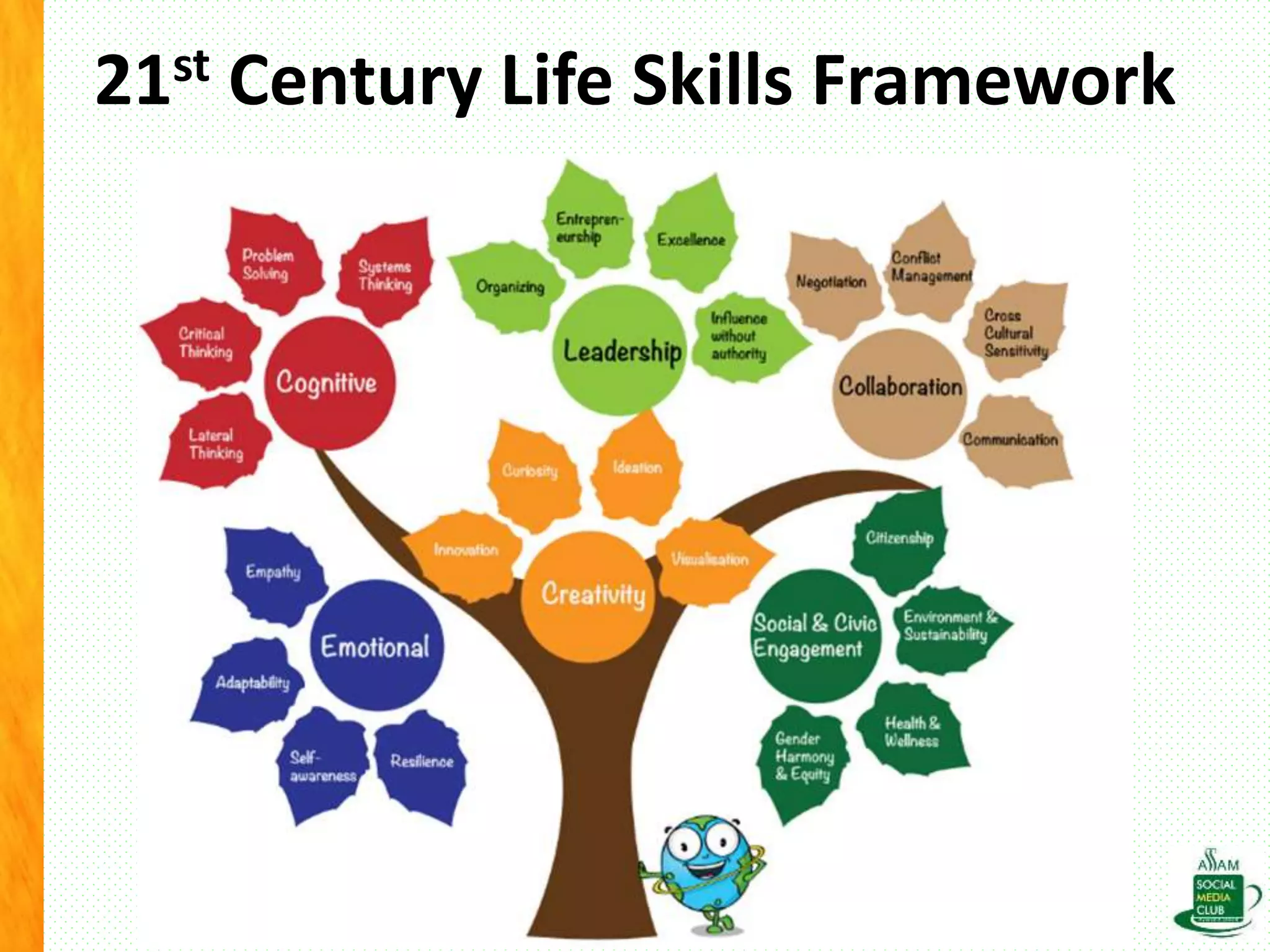
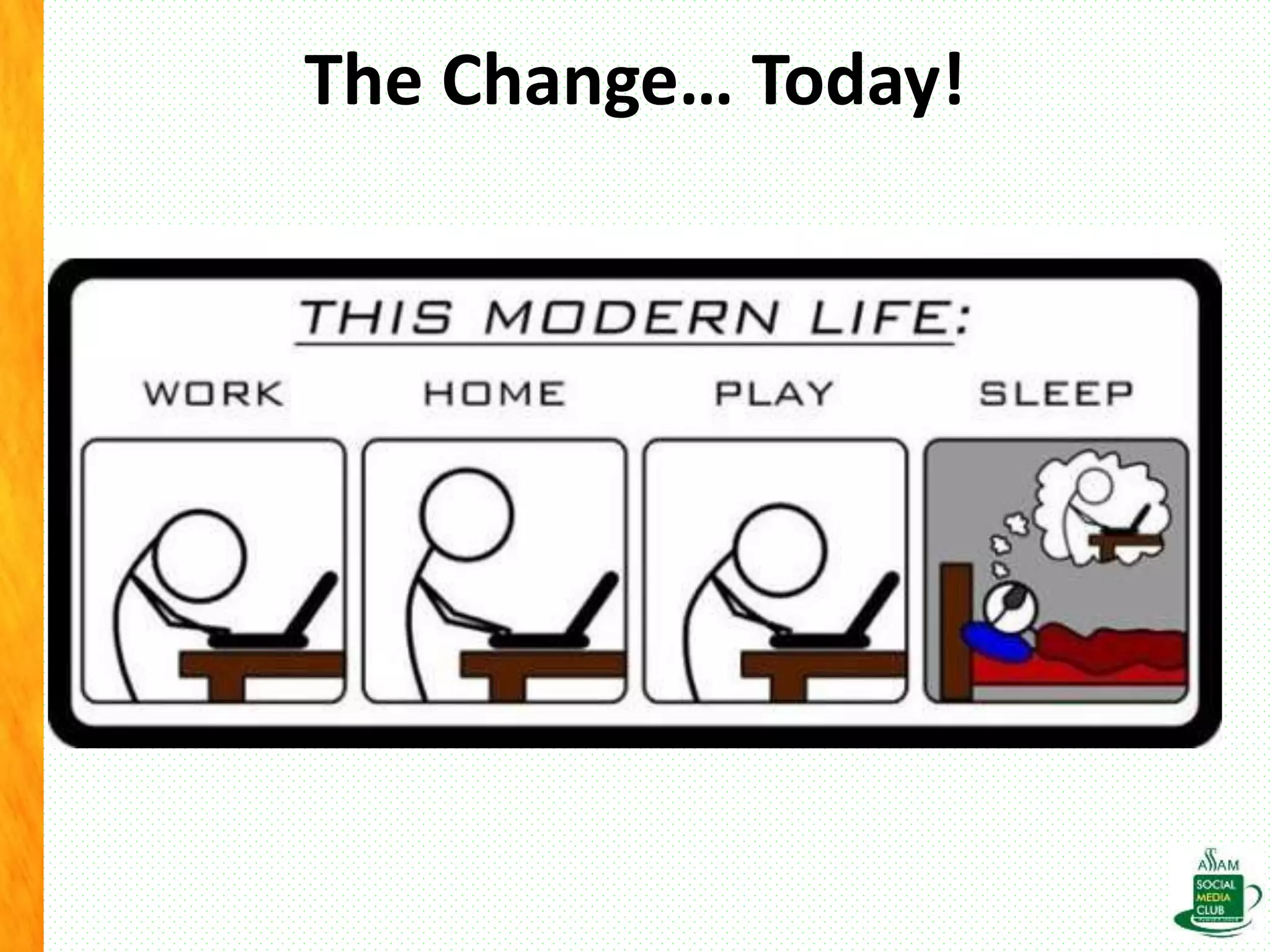
The document discusses the importance of life skills for National Service Scheme (NSS) cadets, emphasizing behavior change, emotional intelligence, and effective communication as essential components for personal and social development. It highlights the various types of life skills, including decision-making, problem-solving, and coping with stress, which contribute to an individual's ability to lead a productive life. Additionally, it addresses the impact of digital media on life skills and stresses the need for responsibility in a digitalized world.