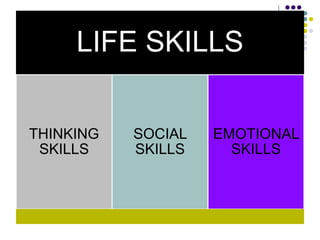
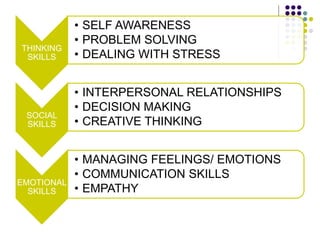
The document outlines the development of life skills using the metaphor of a thirsty crow, illustrating concepts such as self-awareness, critical thinking, problem solving, creative thinking, and effective communication. It emphasizes the importance of life skills in promoting physical, mental, and emotional well-being, especially among adolescents. Key life skills include interpersonal relationships, empathy, decision making, coping with stress, and communication, which are essential for navigating daily challenges and fostering positive behaviors.