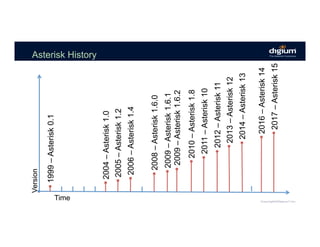
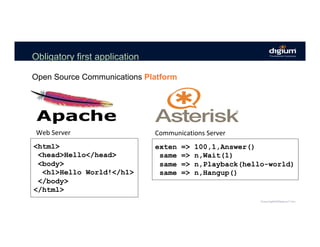
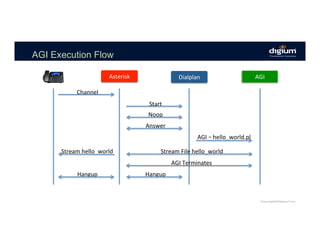
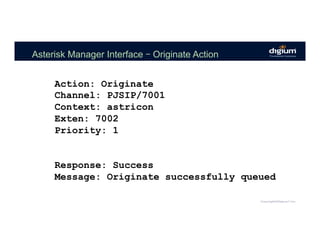
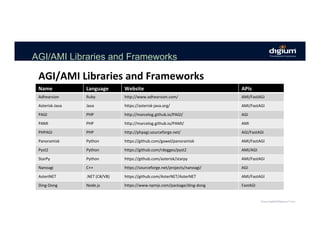
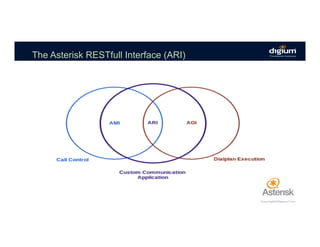
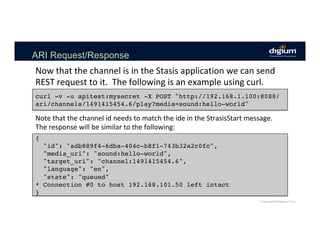
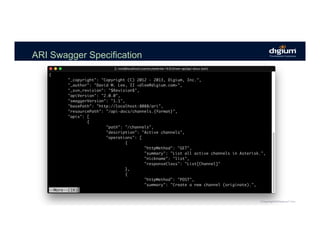
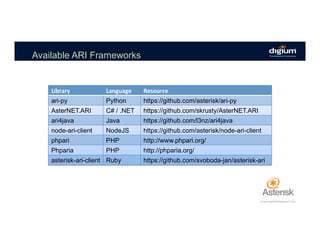
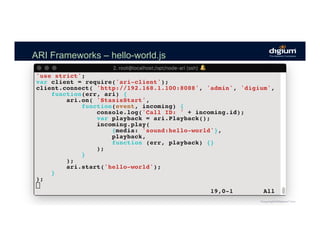
The document provides an overview of the Asterisk RESTful Interface (ARI) and demonstrates how to build communication applications using ARI. It discusses the history and purpose of ARI and compares it to other Asterisk APIs like AGI and AMI. The document then demonstrates connecting to ARI via a WebSocket connection to receive events and making REST requests to play audio on a channel. It provides examples of the resources and categories available in the ARI specification.















![The AGI Dialplan App
You will need to create an extension that calls the AGI
dialplan application.
[internal]
exten => 301,1,NoOp(Hello World)
same => n,Answer()
same => n,AGI(hello-world.pl)
same => n,Hangup()
The AGI application hands off call control to the program specified in
the argument. ( default location /var/lib/asterisk/agi-bin/ )](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/creatingcommunicationapplicationsusingtheasteriskrestfulinterface-171109220317/85/LF_APIStrat17_Creating-Communication-Applications-using-the-Asterisk-RESTFul-Interface-ARI-18-320.jpg)

![Asterisk Manager Interface
[root@localhost ~]# nc 127.0.0.1 5038
Asterisk Call Manager/3.2.0
Action: Login
Username: test
Secret: mysecret
Response: Success
Message: Authentication accepted](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/creatingcommunicationapplicationsusingtheasteriskrestfulinterface-171109220317/85/LF_APIStrat17_Creating-Communication-Applications-using-the-Asterisk-RESTFul-Interface-ARI-21-320.jpg)








![ARI Quick Start Guide
1. Enable the Asterisk HTTP service in http.conf:
[general]
enabled = yes
bindaddr = 0.0.0.0
2. Configure an ARI user in ari.conf:
[general]
enabled = yes
pretty = yes
[asterisk]
type = user
read_only = no
password = asterisk](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/creatingcommunicationapplicationsusingtheasteriskrestfulinterface-171109220317/85/LF_APIStrat17_Creating-Communication-Applications-using-the-Asterisk-RESTFul-Interface-ARI-33-320.jpg)
![The Stasis Dialplan App
You will need to create an extension that calls the Stasis
dialplan application.
[internal]
exten => 403,1,NoOp()
same => n,Answer()
same => n,Stasis(hello-world)
same => n,Hangup()
Stasis is the mechanism that Asterisk uses to hand control of a
channel over from the dialplan - which is the traditional way in which
channels are controlled - to ARI and the client.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/creatingcommunicationapplicationsusingtheasteriskrestfulinterface-171109220317/85/LF_APIStrat17_Creating-Communication-Applications-using-the-Asterisk-RESTFul-Interface-ARI-34-320.jpg)

![The ARI Websock Session
When you call the
extension of the Stasis
application you will see a
StasisStart message in
your wscat section. Note
the “id:” attribute. We
will use that to issue
commands to the call.
{
"type": "StasisStart",
"timestamp": "2017-04-05T11:04:14.869-0700",
"args": [],
"channel": {
"id": "1491415454.6",
"name": "PJSIP/302-00000003",
"state": "Up",
"caller": {
"name": "302",
"number": "302"
},
"connected": {
"name": "",
"number": ""
},x
"accountcode": "",
"dialplan": {
"context": "internal",
"exten": "401",
"priority": 3
},
"creationtime": "2017-04-05T11:04:14.714-0700",
"language": "en"
},
"application": "hello-world"
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/creatingcommunicationapplicationsusingtheasteriskrestfulinterface-171109220317/85/LF_APIStrat17_Creating-Communication-Applications-using-the-Asterisk-RESTFul-Interface-ARI-36-320.jpg)









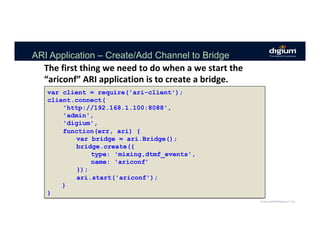
![ARI Application – Cleanup Bridges
Note: Bridges don’t die when ARI script dies.
function cleanupBridges() {
ari.bridges.list(
function(err, bridges) {
var ariconfBridges = bridges.filter(
function(candidate) {
return candidate['name'] === 'ariconf';
}
);
ariconfBridges.forEach(
function(bridge) {
bridge.destroy(function(err) {});
});
}
);
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/creatingcommunicationapplicationsusingtheasteriskrestfulinterface-171109220317/85/LF_APIStrat17_Creating-Communication-Applications-using-the-Asterisk-RESTFul-Interface-ARI-52-320.jpg)

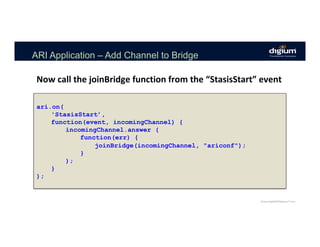
![ARI Application – Add Channel to Bridge
function joinBridge(channel) {
ari.bridges.list(
function(err, bridges) {
var bridge = bridges.filter(
function(candidate) {
return candidate['name'] === ‘ariconf’;
}
)[0];
if (!bridge) {
console.log("bridge not found!");
} else {
bridge.addChannel({channel: channel.id});
}
);
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/creatingcommunicationapplicationsusingtheasteriskrestfulinterface-171109220317/85/LF_APIStrat17_Creating-Communication-Applications-using-the-Asterisk-RESTFul-Interface-ARI-54-320.jpg)

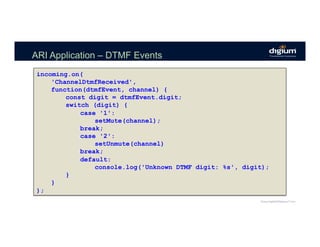


![ARI Application – Monkeys Dialplan
The dialplan for the tt-monkeys playback
[monkeys]
exten => monkeys,1,Noop(playback tt-monkeys)
same => n,Playback(tt-monkeys)
same => n,Hangup()](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/creatingcommunicationapplicationsusingtheasteriskrestfulinterface-171109220317/85/LF_APIStrat17_Creating-Communication-Applications-using-the-Asterisk-RESTFul-Interface-ARI-60-320.jpg)