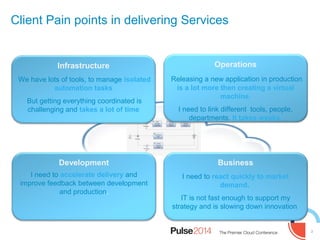
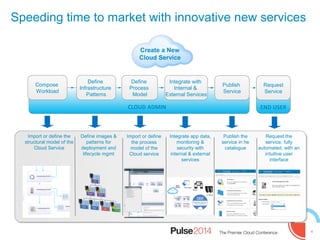
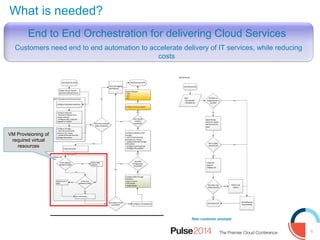
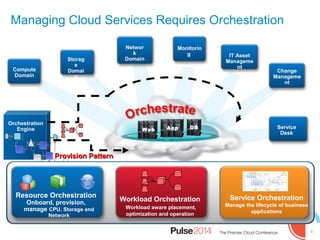
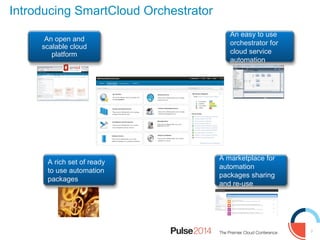
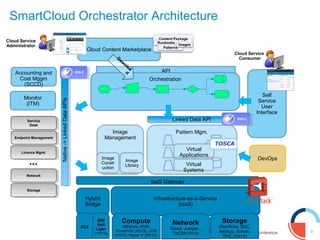
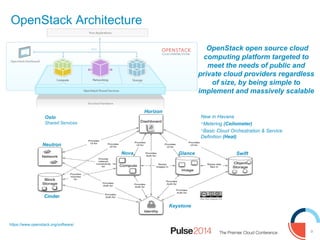
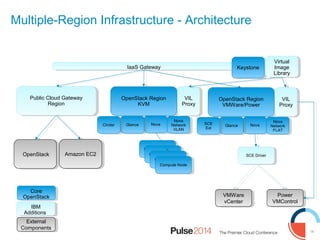
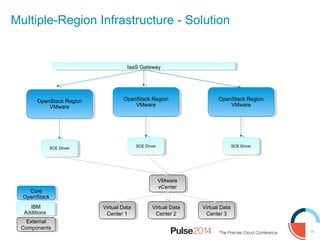
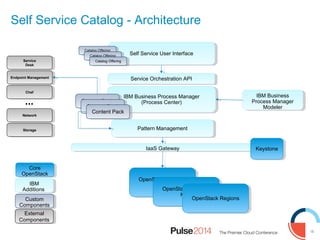
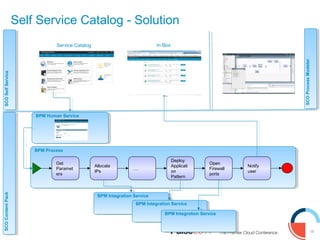
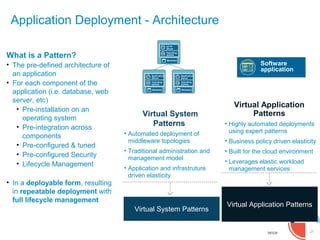
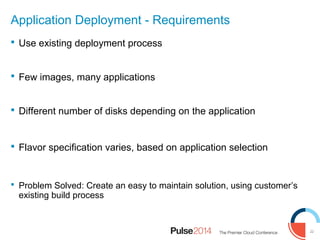
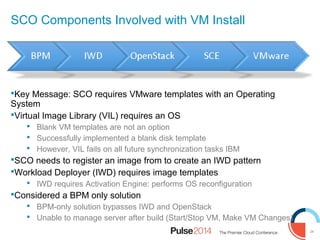
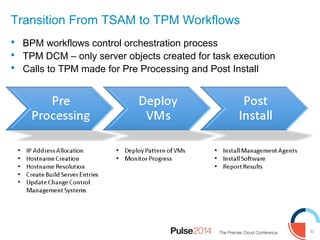
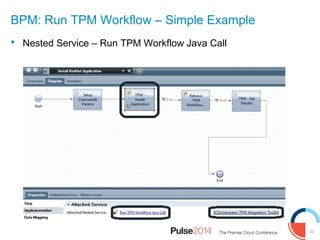
IBM presented lessons learned from deploying SmartCloud Orchestrator at a large telecommunications provider to automate cloud service delivery. Key challenges included managing a multi-region infrastructure, publishing self-service catalogs, and automating application deployments. The solution involved using OpenStack regions with IBM additions to provide a unified interface and orchestrate deployments across regions. Processes were modeled to provision resources and deploy application stacks through reusable patterns.