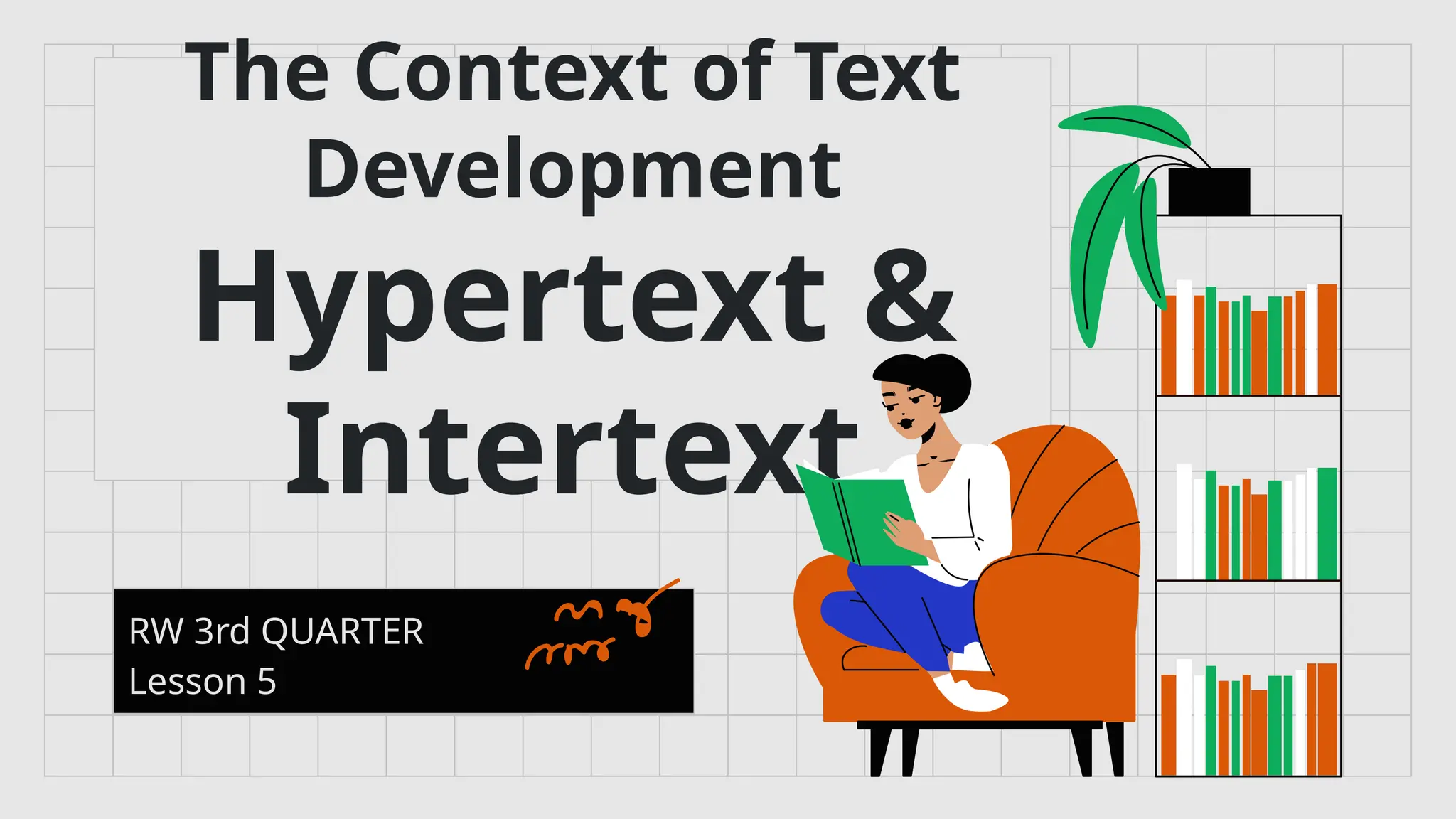
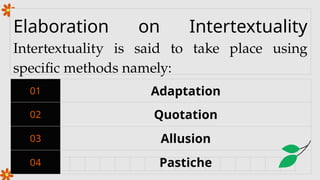
Context, hypertext, and intertextuality are important concepts in understanding how texts create meaning. Context refers to the background information—such as culture, history, situation, and audience—that helps readers interpret a text accurately. Hypertext involves non-linear texts, usually in digital form, that use links to connect one text to another, allowing readers to navigate information interactively. Intertextuality describes the relationship between texts, where one text references, echoes, or is influenced by another, helping readers see deeper meanings through connections across different works.