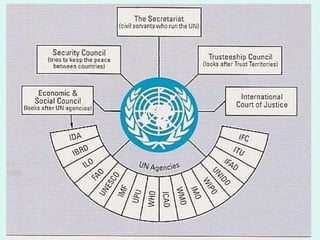
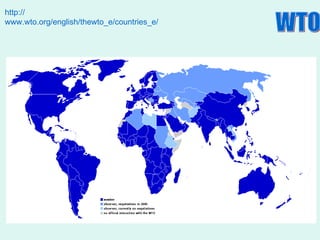
IGOs like the UN, NATO, IMF and World Bank allow powerful nations like the USA and EU to promote their interests on a global scale. While IGOs aim to foster cooperation, critics argue they are dominated by superpowers and promote their agendas. IGOs make key decisions influencing the global economy, conflicts, and environment, giving outsized influence to major donors. However, IGOs also help smaller nations and provided aid that rebuilt countries after WWII. Whether IGOs increase or decrease American power is debated, but they allow the USA to spread its ideology and priorities worldwide.