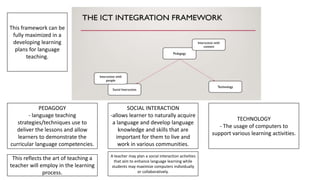
The document discusses various pedagogical frameworks and approaches for language teaching, including the Laurillard's Conversational Framework (LCF). The LCF requires appropriate use of technology and relates language teaching events to learning events. It can be used to develop learning plans. The document also discusses pedagogy, social interaction, technology, inquiry-based learning, problem-based learning, and project-based learning as approaches for developing language skills.