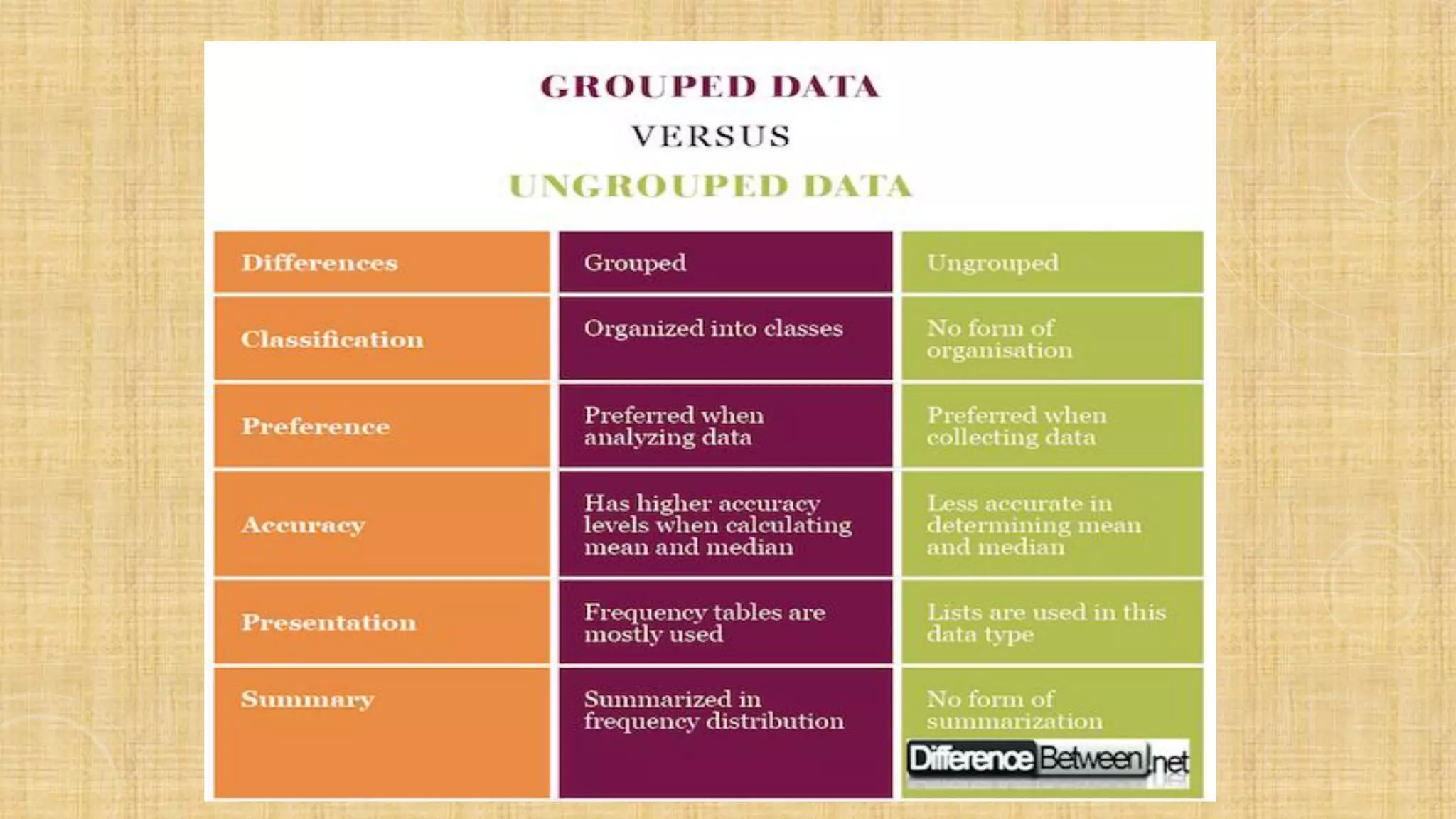
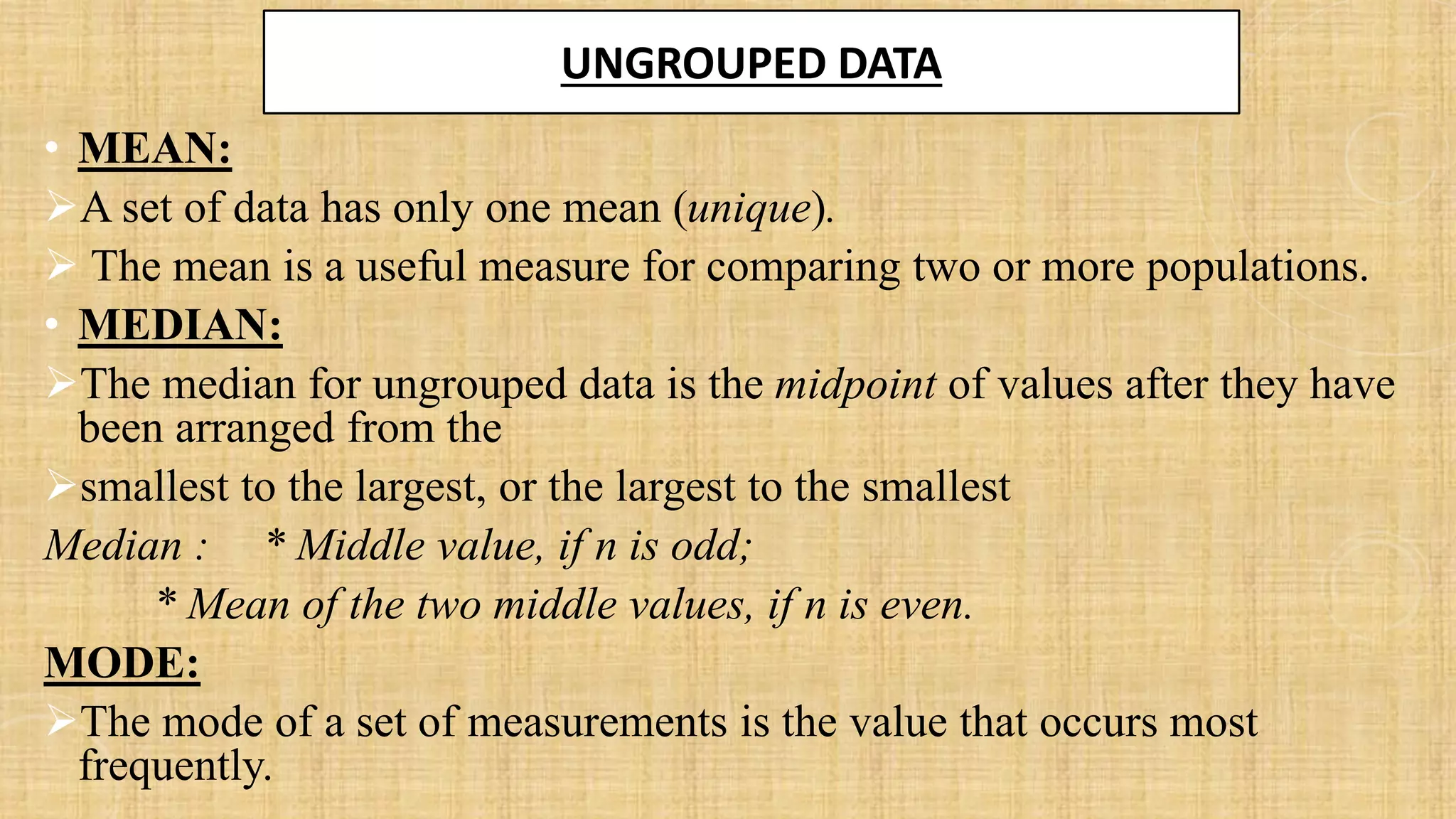
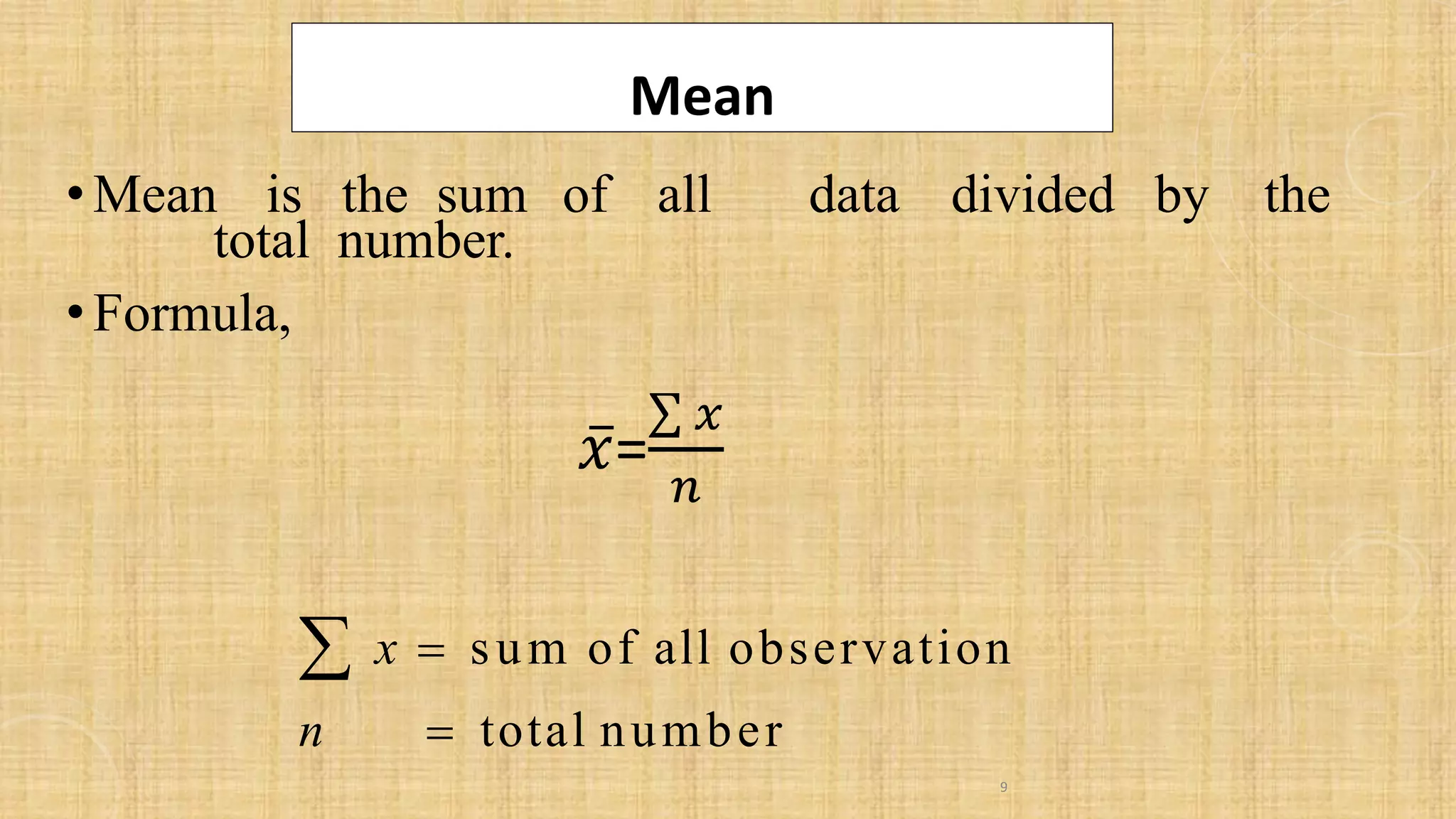
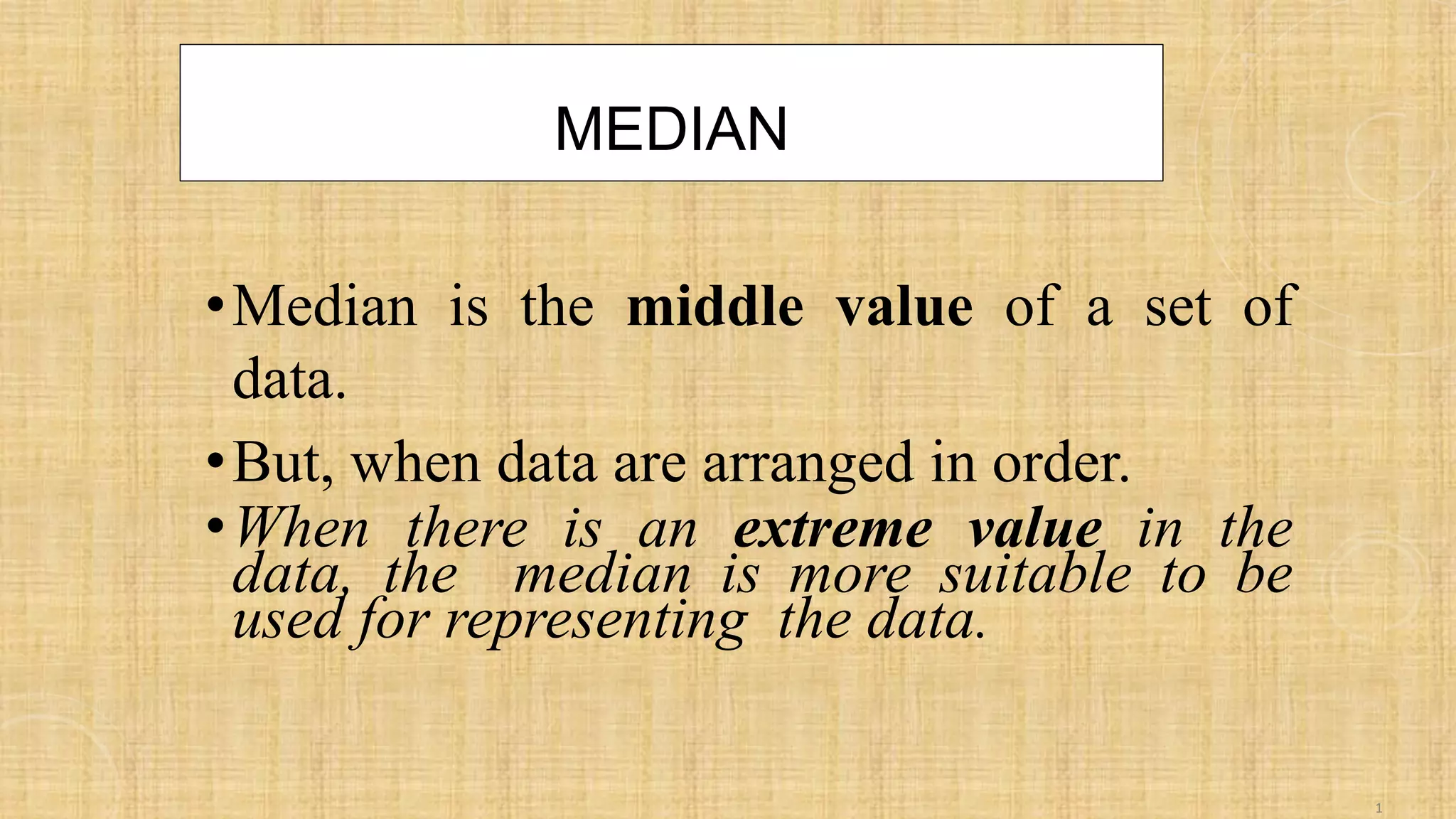
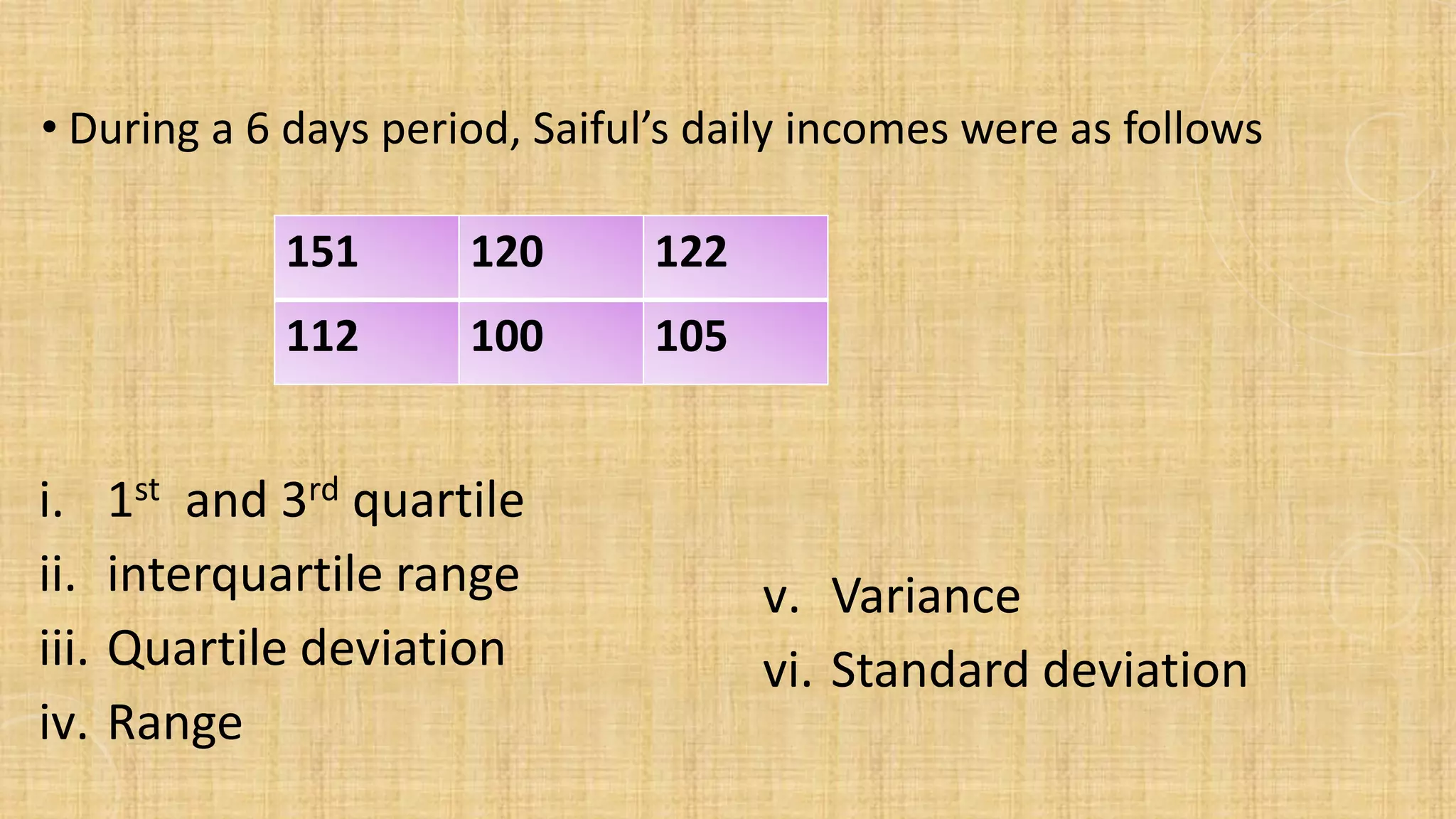
- This document discusses descriptive statistics for ungrouped data, including how to organize raw data into a frequency distribution and present it graphically. It also defines measures of central tendency like mean, median and mode, as well as measures of dispersion like range, variance and standard deviation. Several examples and exercises are provided to illustrate calculating these common statistical measures for ungrouped data sets.