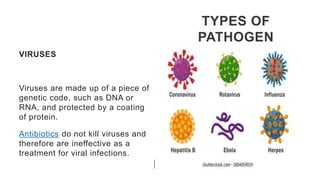
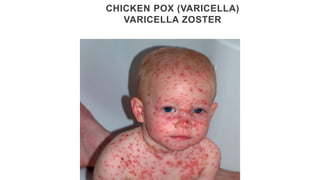
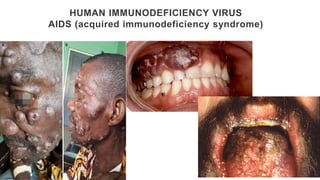
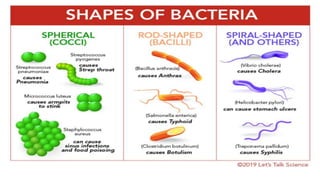
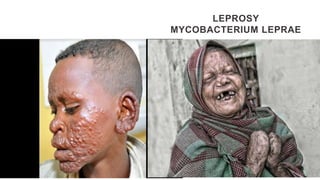
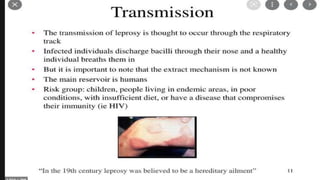
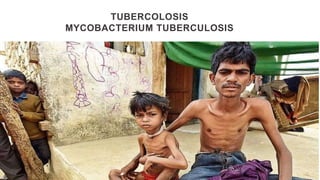
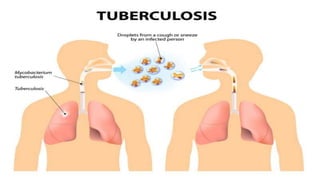
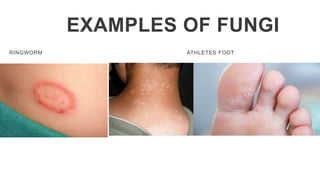
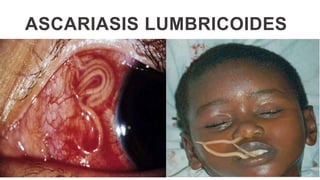
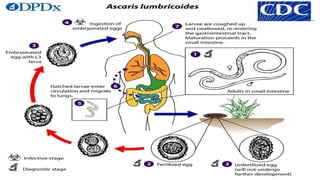
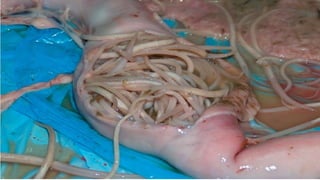
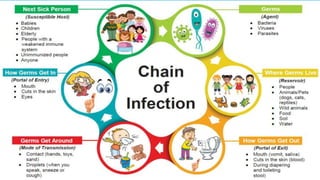
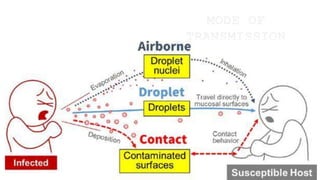
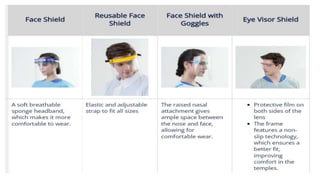
This document provides an overview of infection control concepts including the chain of infection, modes of transmission, and methods for breaking the chain of infection. It discusses key topics like pathogens, types of pathogens including viruses, bacteria, fungi and parasites. It also covers the chain of infection process including modes of transmission like contact, droplet, and airborne transmission. Methods for preventing the spread of infections are outlined such as frequent hand hygiene, vaccination, covering coughs and sneezes, staying home when sick, proper use of PPE, isolation, and environmental cleaning and disinfection. The document concludes with reminders about an upcoming exam and performance task.