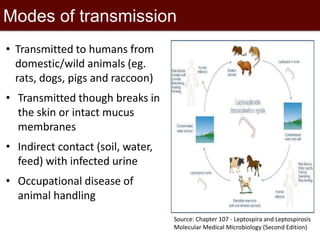
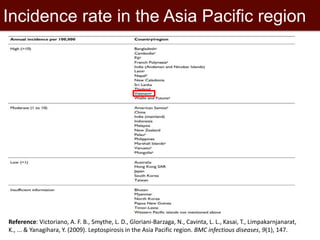
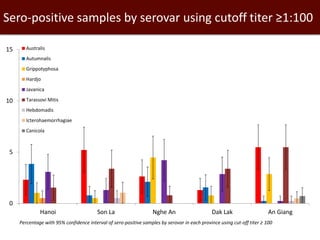
This document summarizes two epidemiological studies on leptospirosis in pigs in Vietnam. The first study found a seroprevalence of 8.17% among 1,959 pig samples from 5 provinces tested using microscopic agglutination testing. The most common serovars were Tarassovi and Javanica. The second study of 2,000 pig samples from 10 provinces found a seroprevalence of 21.05% with Bratislava and Pyrogenes being the most common serovars. Future research directions include investigating associations with environmental factors and seasonal patterns in animals and humans.