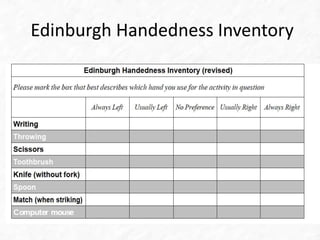
This document provides an overview of left-handedness, including its definition, theories around its development and inheritance, myths and facts, and issues faced by left-handed individuals. It discusses definitions of handedness and theories such as environmental, developmental, evolutionary, and genetic factors. It also addresses myths such as left-handed individuals having shorter lifespans or lower incomes, as well as issues like tools and social situations being designed for right-handedness. Famous left-handed historical and current figures are also listed.