This document summarizes several English grammar concepts:
1) How+adjective questions are used to ask about measurements and provide answers with adjectives like "high", "long", "wide", or "deep".
2) The differences between the to-infinitive and infinitive without to. Infinitives are used after certain verbs and modal verbs.
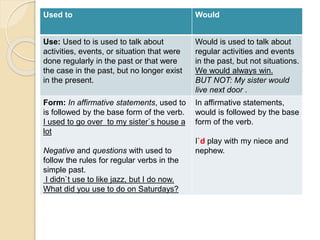
3) Conditionals come in three types - Type 0 for always true statements, Type 1 for probable present/future situations. Used to is used for past habits while would is used for past regular actions.