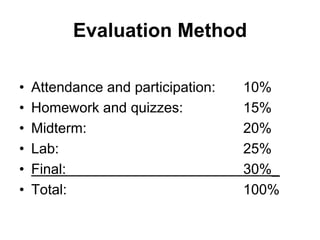
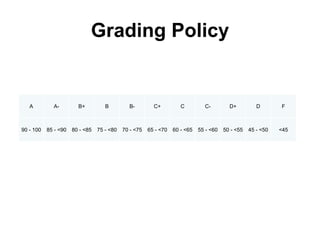
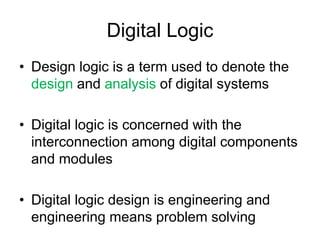
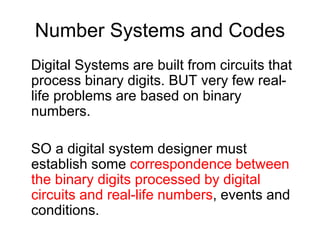
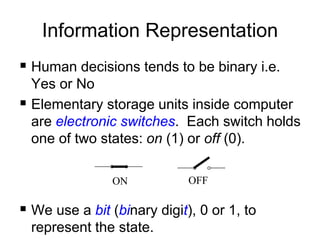
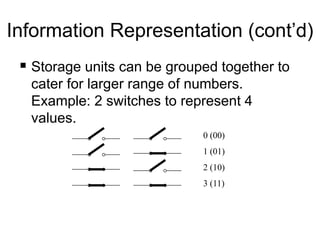
This document provides an overview and syllabus for the CSE 204 Digital Logic Design course. The class will meet once a week for theory and once a week for lab. Evaluation will be based on attendance, homework, quizzes, midterm, lab, and final exam. The textbook is Logic and Computer Design Fundamentals by Mano and Kime. Digital logic design involves representing real-world analog inputs digitally using bits and binary and then processing the digital data. Key topics that will be covered include number systems, information representation using bits, digital vs analog, limitations and advantages of digital systems, and digital logic.