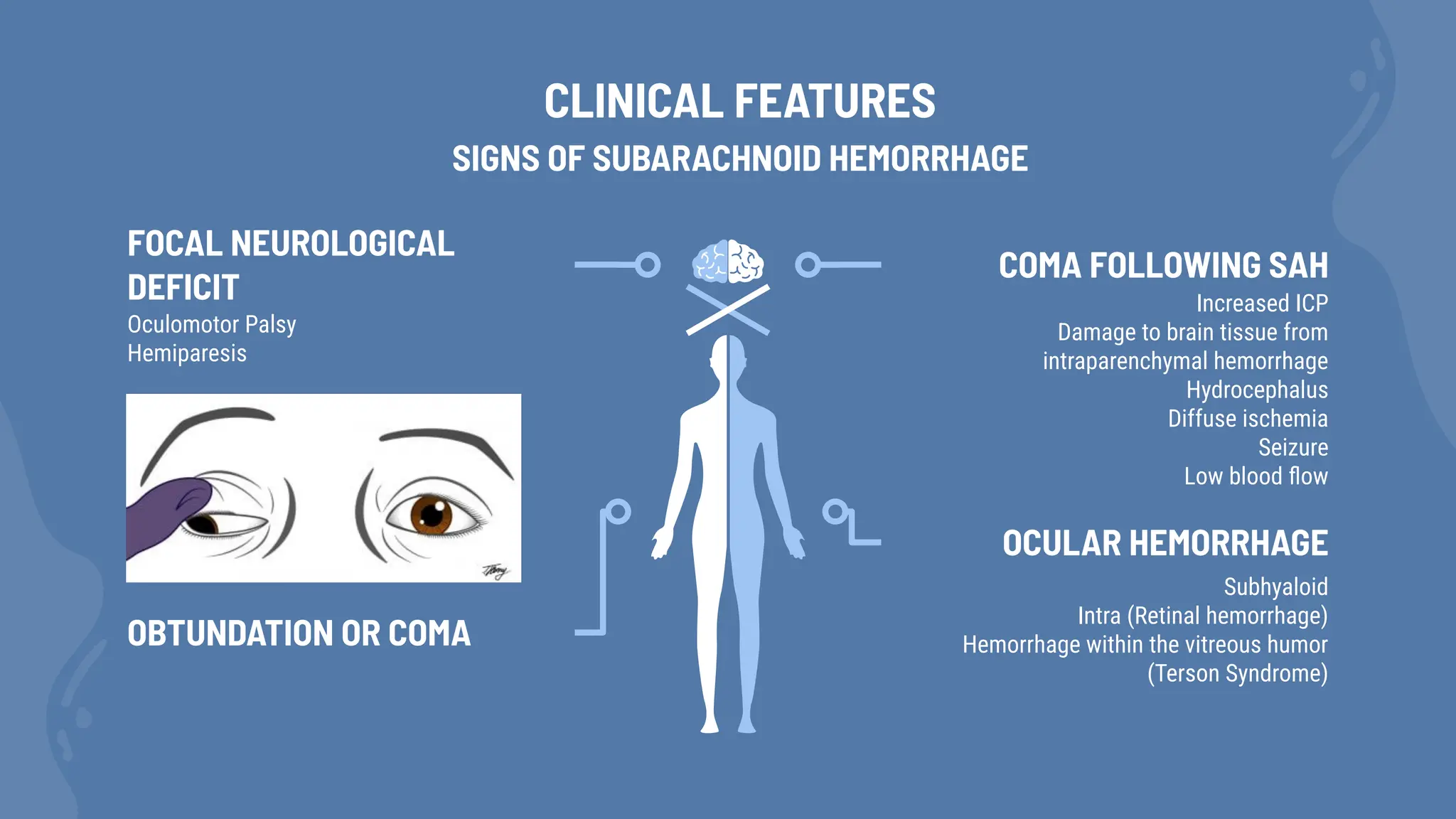
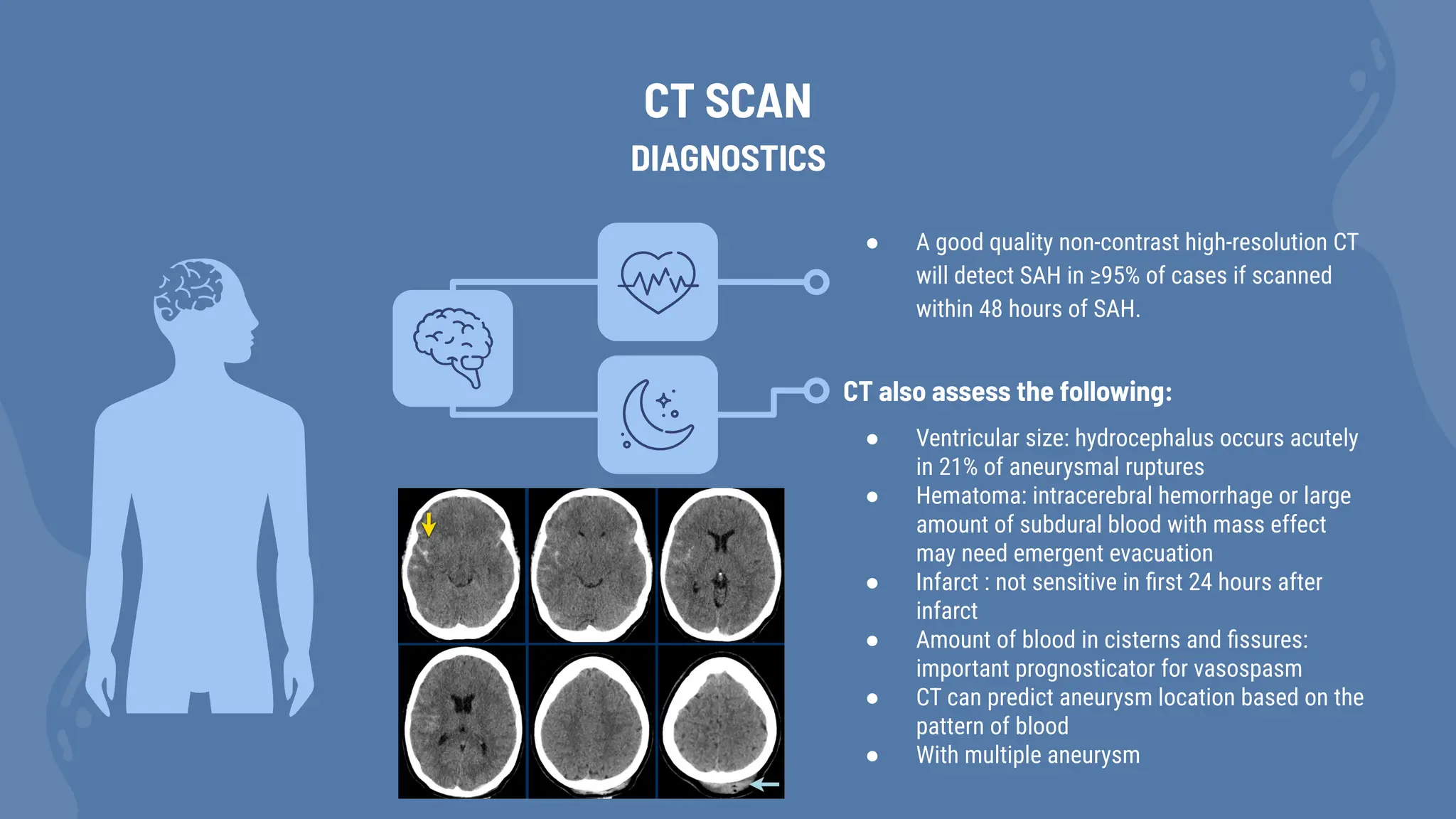
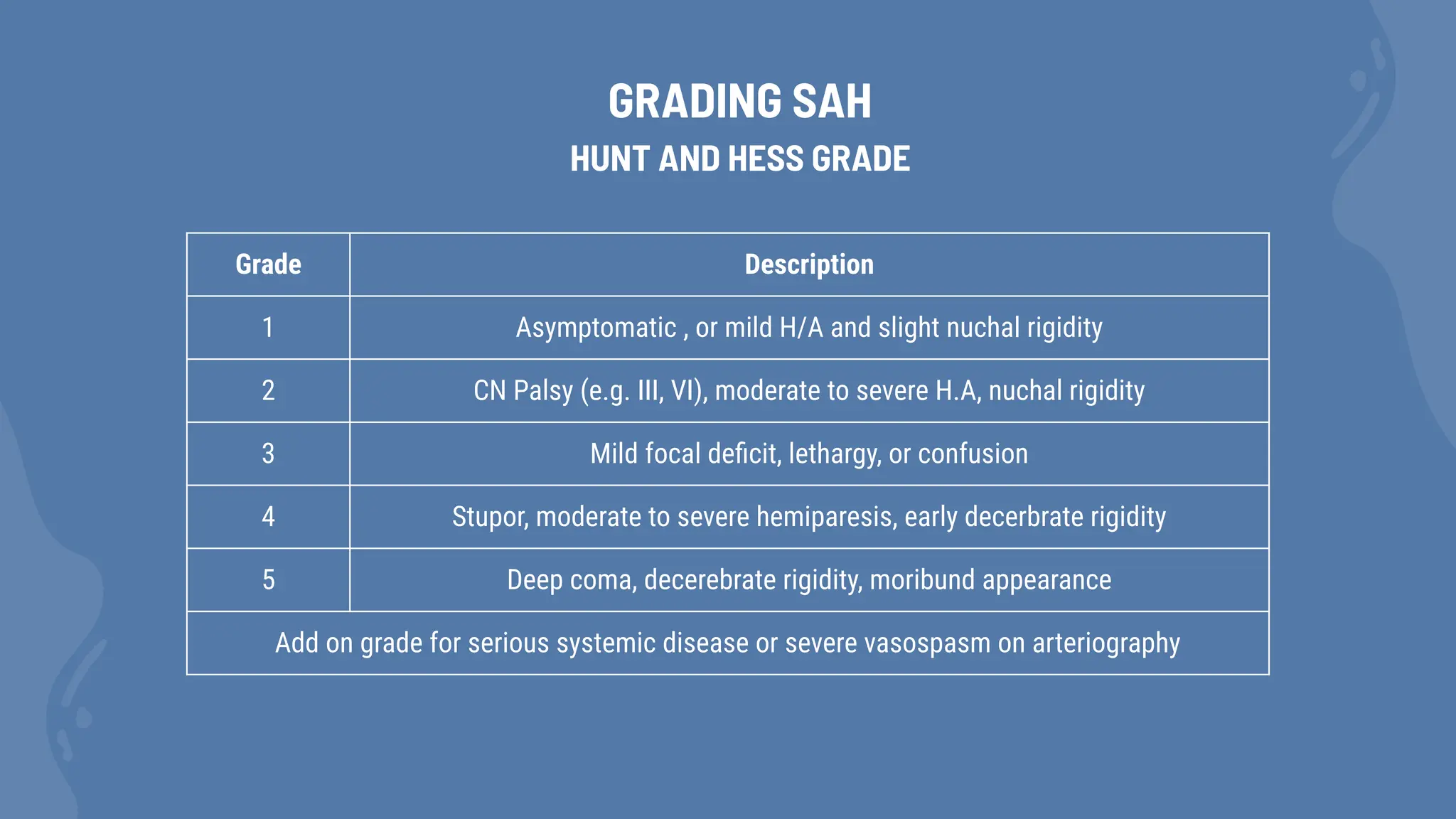
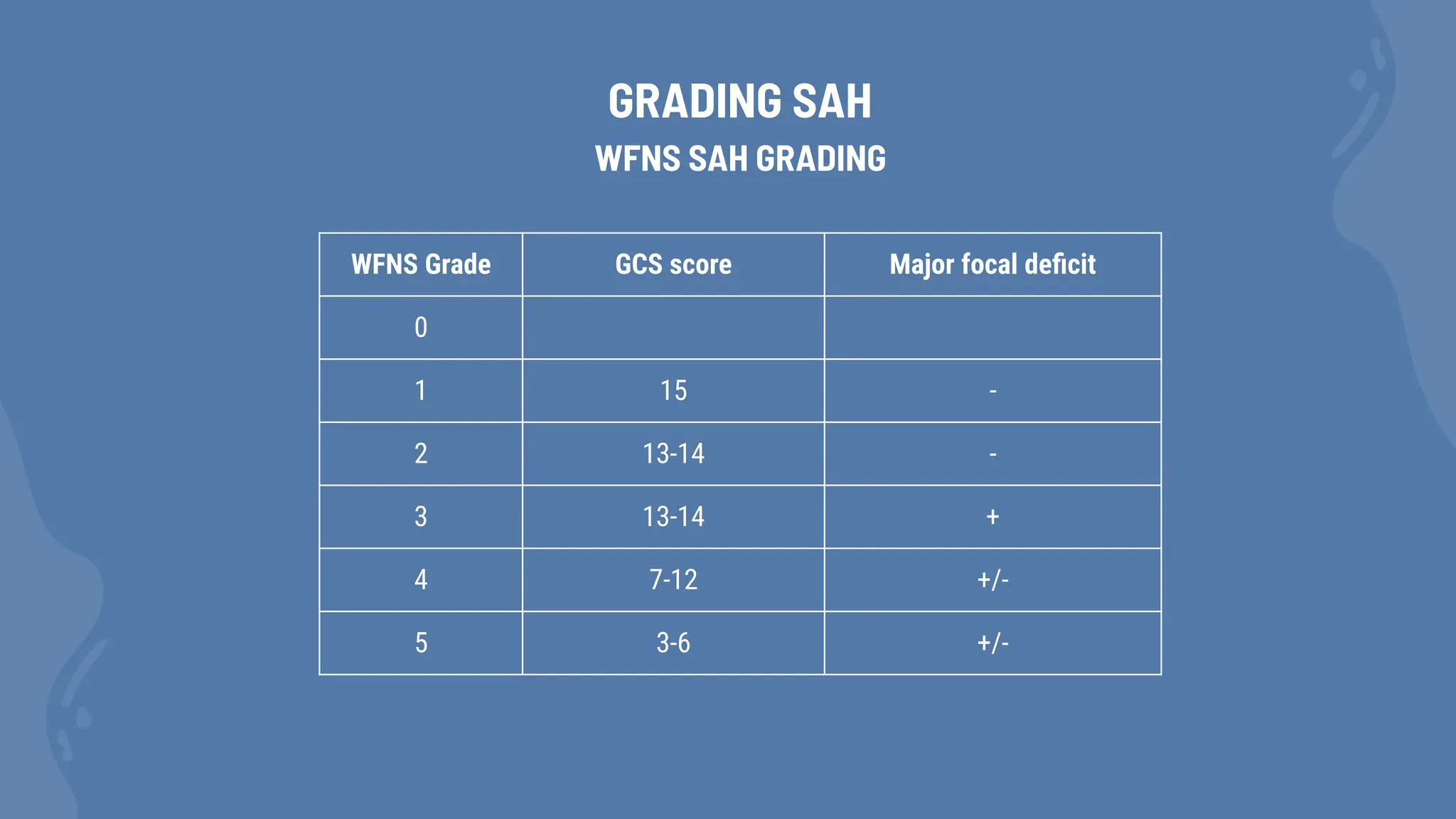
Subarachnoid hemorrhage (SAH) is characterized by blood in the subarachnoid space, commonly resulting from aneurysm rupture, with a peak incidence in individuals aged 55-60 years. It is often preceded by a sentinel headache and can lead to severe complications such as hydrocephalus and delayed cerebral ischemia. Diagnosis is primarily through CT scans, lumbar puncture, and angiography to identify potential aneurysms.