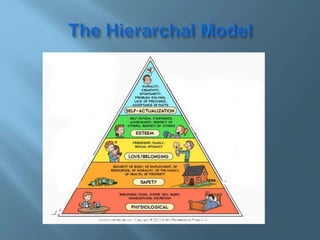
The document discusses the various causes and types of stress and conflict. It outlines physical and emotional symptoms of stress and provides strategies for managing stress through relaxation techniques, exercise, meditation, counseling and changing perceptions. The document also categorizes different types of conflicts such as interest conflicts, information conflicts, and conflicts resulting from changes in resources, authority, or access.