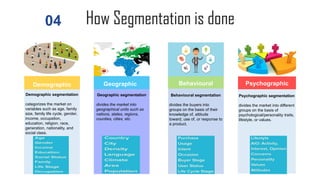
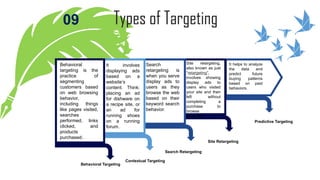
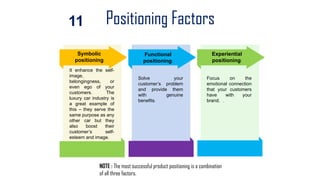
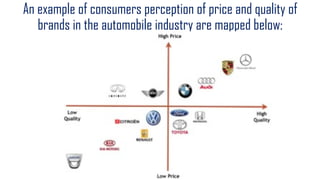
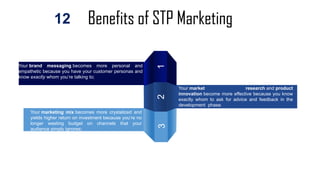
The document discusses the concepts of marketing, specifically focusing on segmentation, targeting, and positioning (STP). It elaborates on the importance of market segmentation in understanding customer needs and creating effective marketing strategies tailored to specific consumer groups. Additionally, it explains different types of segmentation and targeting strategies, highlighting examples and benefits of implementing STP in marketing practices.