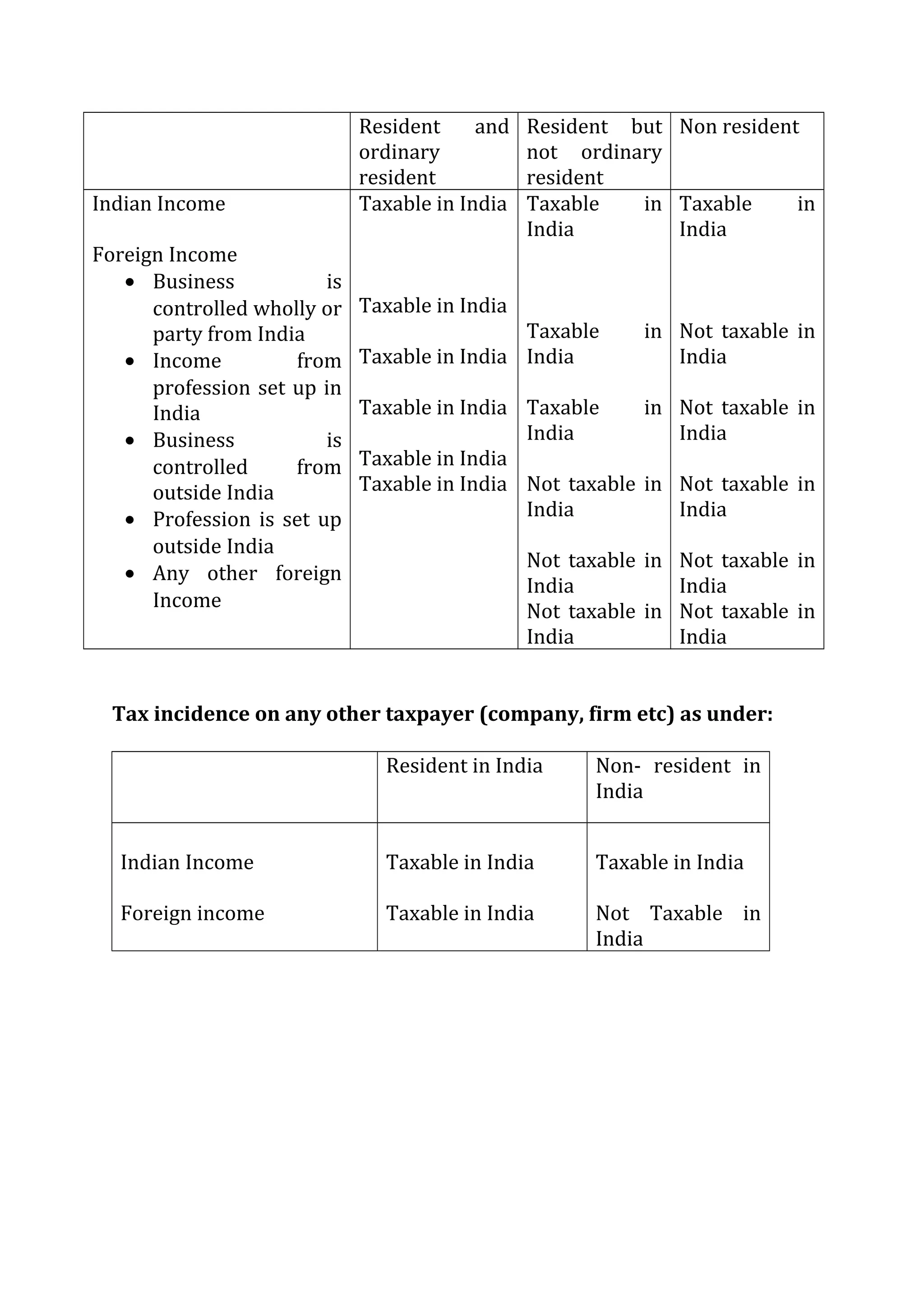
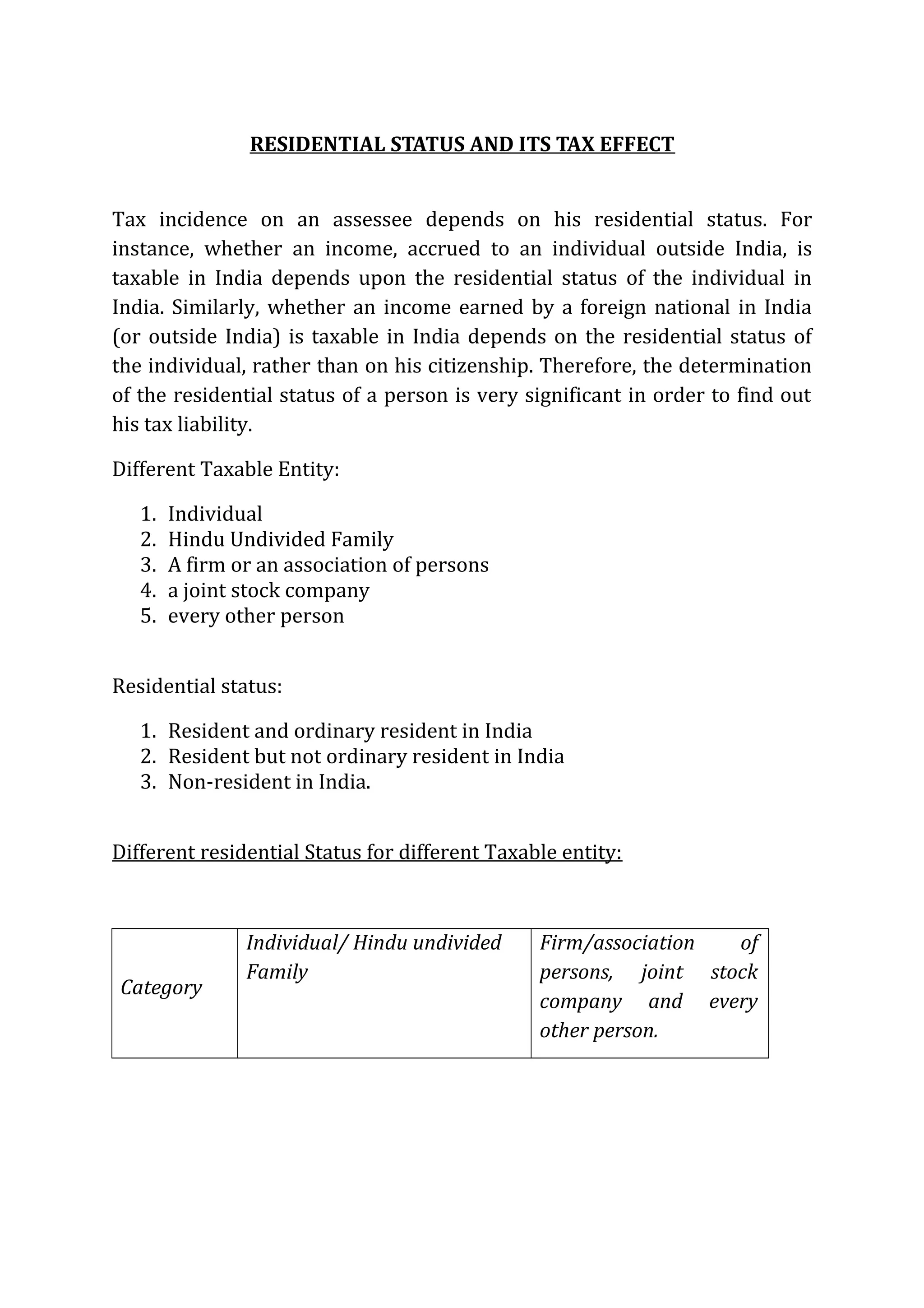
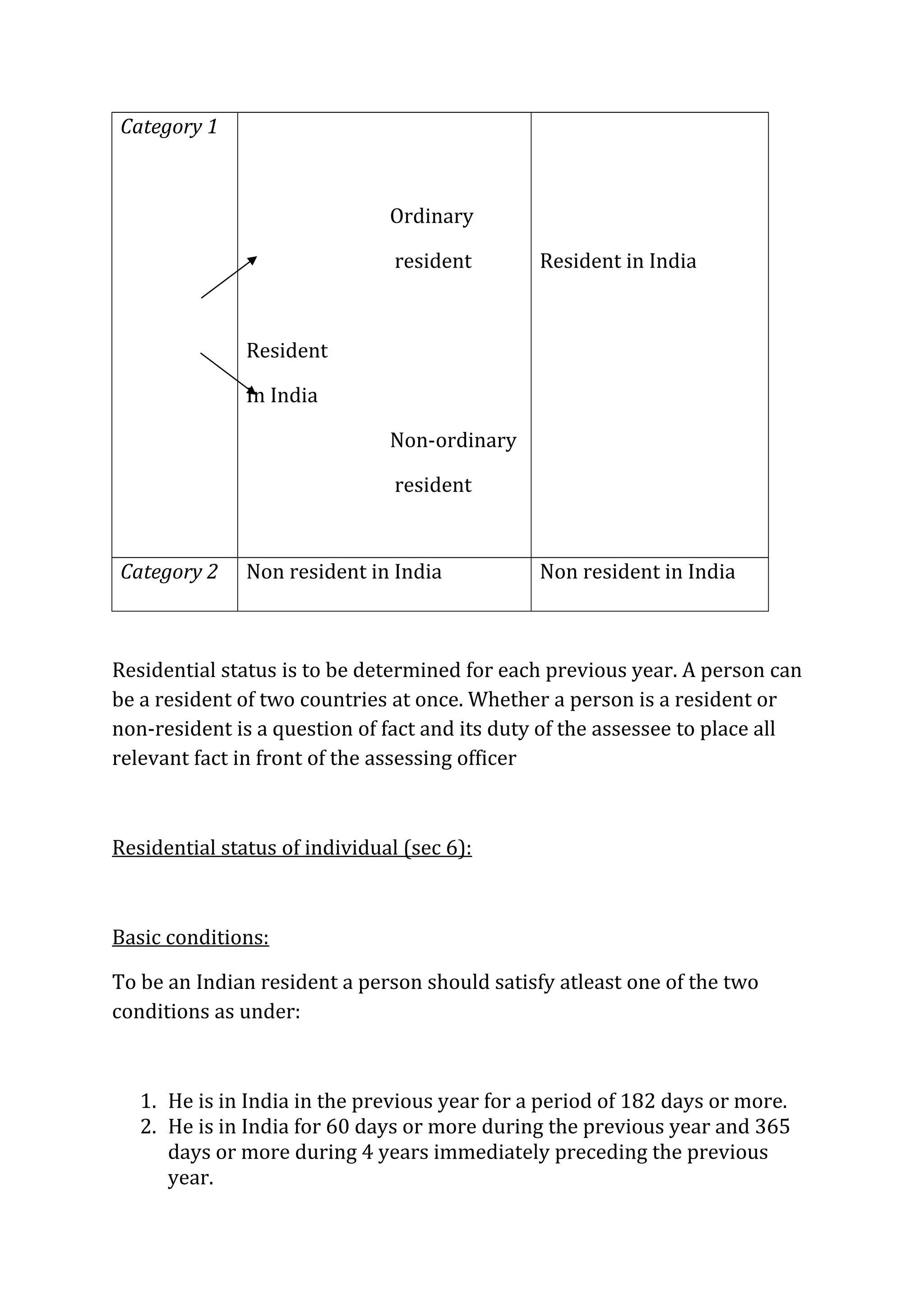
An individual's residential status determines their tax liability in India. There are three residential statuses: resident and ordinary resident, resident but not ordinary resident, and non-resident. An individual's residential status depends on the number of days they spent in India in the last year and last few years. Additionally, an individual must meet further criteria to be considered an ordinary resident. The residential status principles are also applied to HUFs, firms, companies, and other entities to determine their tax obligations. An individual or entity's residential status then dictates whether their global income is subject to tax in India.
![Exceptions:
In the following two cases a person will be a resident if he satisfies only the
first condition, the second condition is not applicable.
1. In case of an Indian citizen who leaves India for the purpose of
employment or as a member of the crew of an Indian ship.
2. In the case of an Indian citizen or a person of Indian origin who
comes on a visit to India in the previous year.
Additional Conditions:
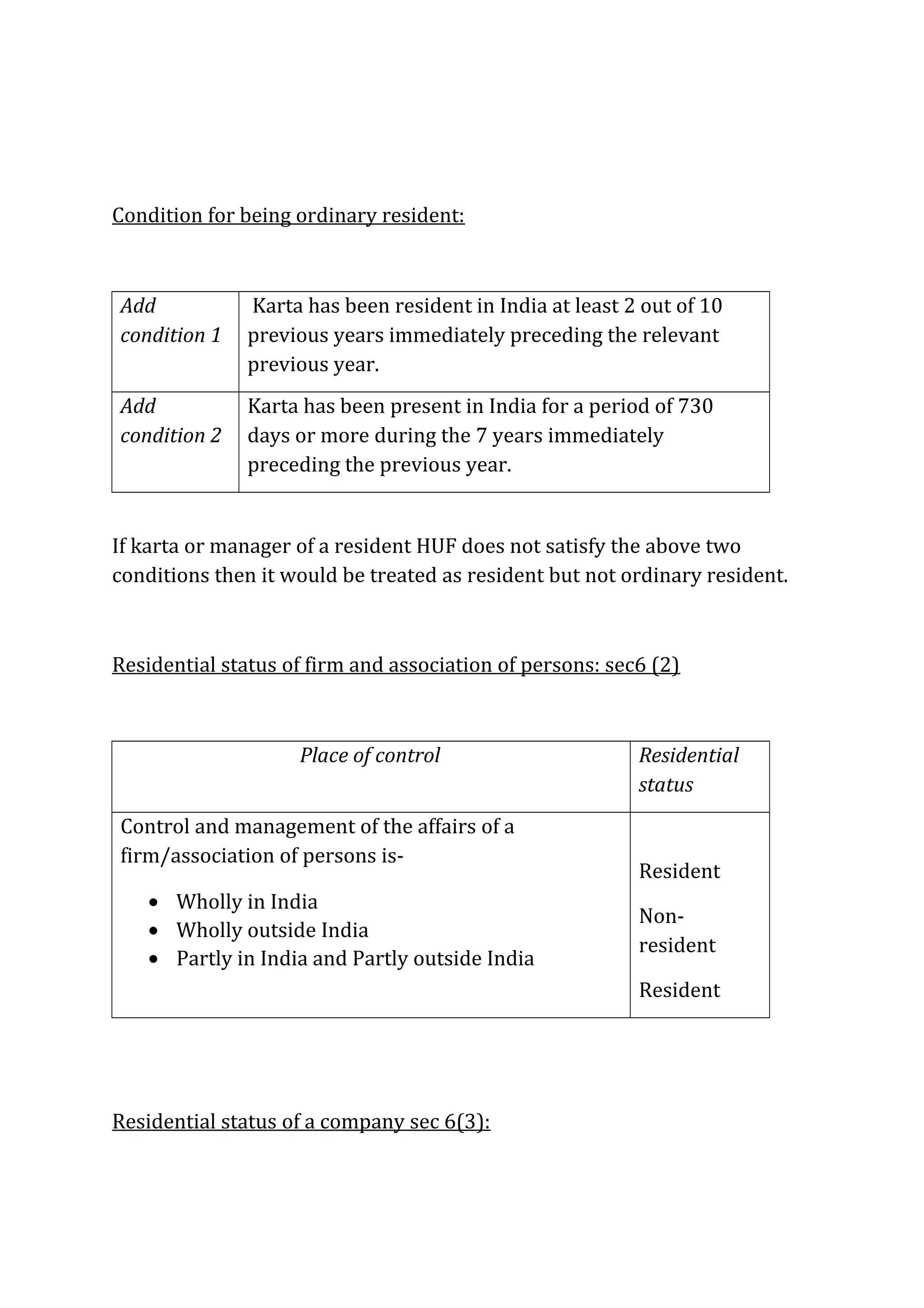
For a resident to be classified as an ordinary resident the following two
additional conditions should be fulfilled. In case any one of them is not
fulfilled then the person will be under the category of resident but not an
ordinary resident.
1. He should be resident in India for at least 2 years out of the preceding
10 years.
2. He should be in India for at least 730 days out of the immediately
preceding 7 years.
RESIDENT BUT NOT ORDINARILY RESIDENT
• As per section 6(1), an individual who satisfies at least one of the
basic conditions[Basic condition (a)He is in India in the previous year
for a period of 182days or more. Basic condition (b)He is in India for
a period of 60 days or more during the previous year and 365 days or
more during 4 years immediately preceding the previous year] but
does not satisfy the two additional conditions](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lecture2-residentstatus-141209104450-conversion-gate02/75/Lecture-2-resident-status-3-2048.jpg)
![1.An Indian citizen who leaves India during the previous year for the
purpose of taking employment outside India or an Indian citizen leaving
India during the previous year as a member of the crew of an Indian ship.
2.An Indian citizen or a person of Indian origin who comes on visit to India
during the previous year (a person is said to be of Indian origin if either
their any of his parents or any of his grand parents was born in
undivided India)], is treated as a resident but not ordinarily resident in
India.
Resident and Not Ordinarily Resident – u/s 6(6)
• Individual who satisfies at least one of the basic conditions u/s 6 (1)
but does not satisfy the additional conditions under u/s 6 (6)
Non Resident
• Individual who does not satisfy at least one of the basic conditions
u/s 6 (1).
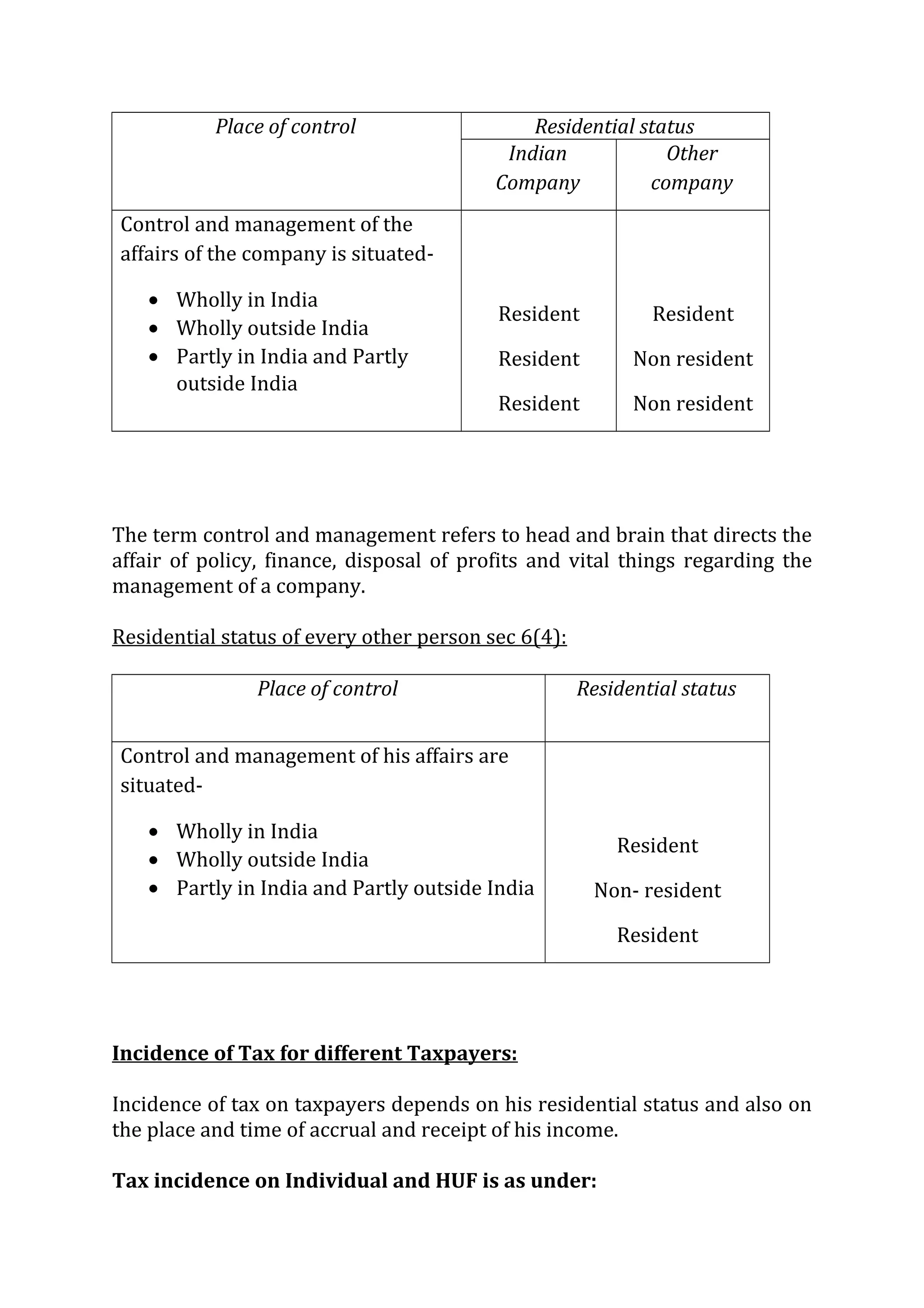
Residential Status of a Hindu undivided Family sec 6(2):
HUF is classified as a resident and non resident according to its control and
management status. Control and management means the de facto control
and management and not just the right to control and manage.
Place of control
Residential
status of HUF
Ordinary
resident or
not
Control and management is wholly
in India
Resident Next table
Control and management is wholly
outside India
Non-resident --
Control and management is partly
in India and partly outside India
Resident Next table](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lecture2-residentstatus-141209104450-conversion-gate02/75/Lecture-2-resident-status-4-2048.jpg)