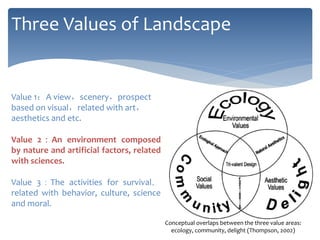
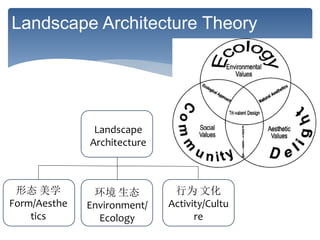
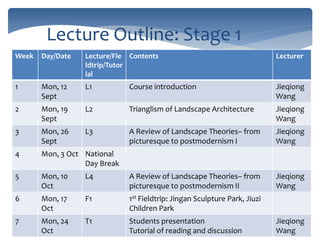
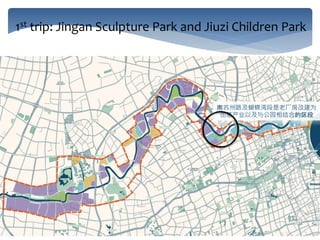
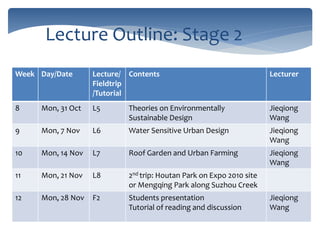
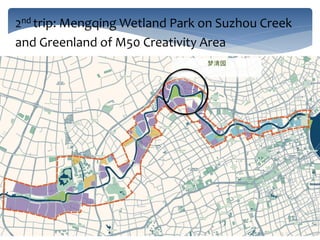
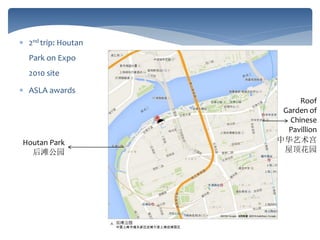
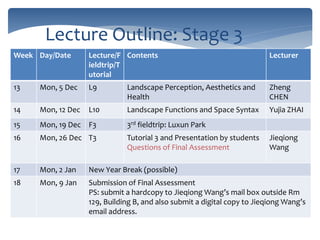
This document provides an introduction and syllabus for the course "Theories of Landscape Architecture" taught by Prof. Binyi LIU and several guest lecturers. The course will be held on Mondays from 13:30-15:00 in room D3 and cover three phases: the development of landscape theories, theories of environmental sustainable design, and theories of perceptions and activities. Assessment will consist of tutorial presentations and a final case study. Three field trips are planned to various parks in Shanghai to supplement the lectures and readings.


![Two Books
Thompson I H. Ecology, Community and
Delight: Sources of values in landscape
architecture[M]. Taylor & Francis, 2000.
Liu, B. Y. 2005. Modern Landscape Planning
and Design [M], Southeast University Press.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lecture1landscapearchitheory-230126191221-aa5c99a4/85/Lecture-1_landscape-archi-theory-pdf-3-320.jpg)