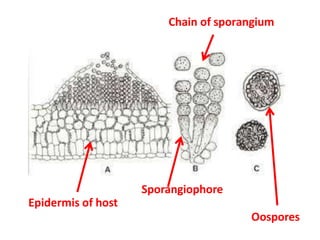
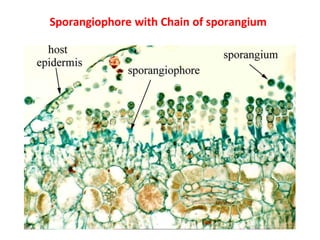
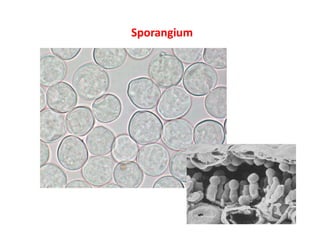
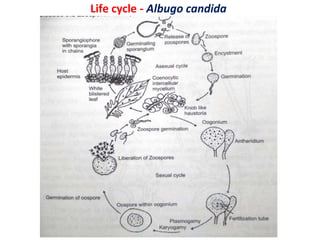
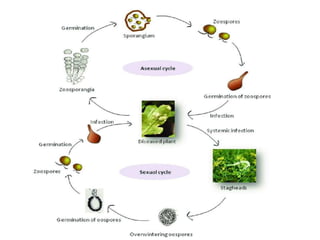
The document describes the fungus Albugo candida, which causes white blister disease in crucifers and amaranthus. It has a mycelial thallus that is intercellular and produces club-shaped sporangiophores bearing chains of sporangia. The sporangia rupture the leaf epidermis and appear as powdery white masses. Sexual reproduction involves the formation of antheridia and oogonia, followed by fertilization and the production of thick-walled oospores which can survive unfavorable conditions. The oospores later germinate to release zoospores that can infect new host plants.